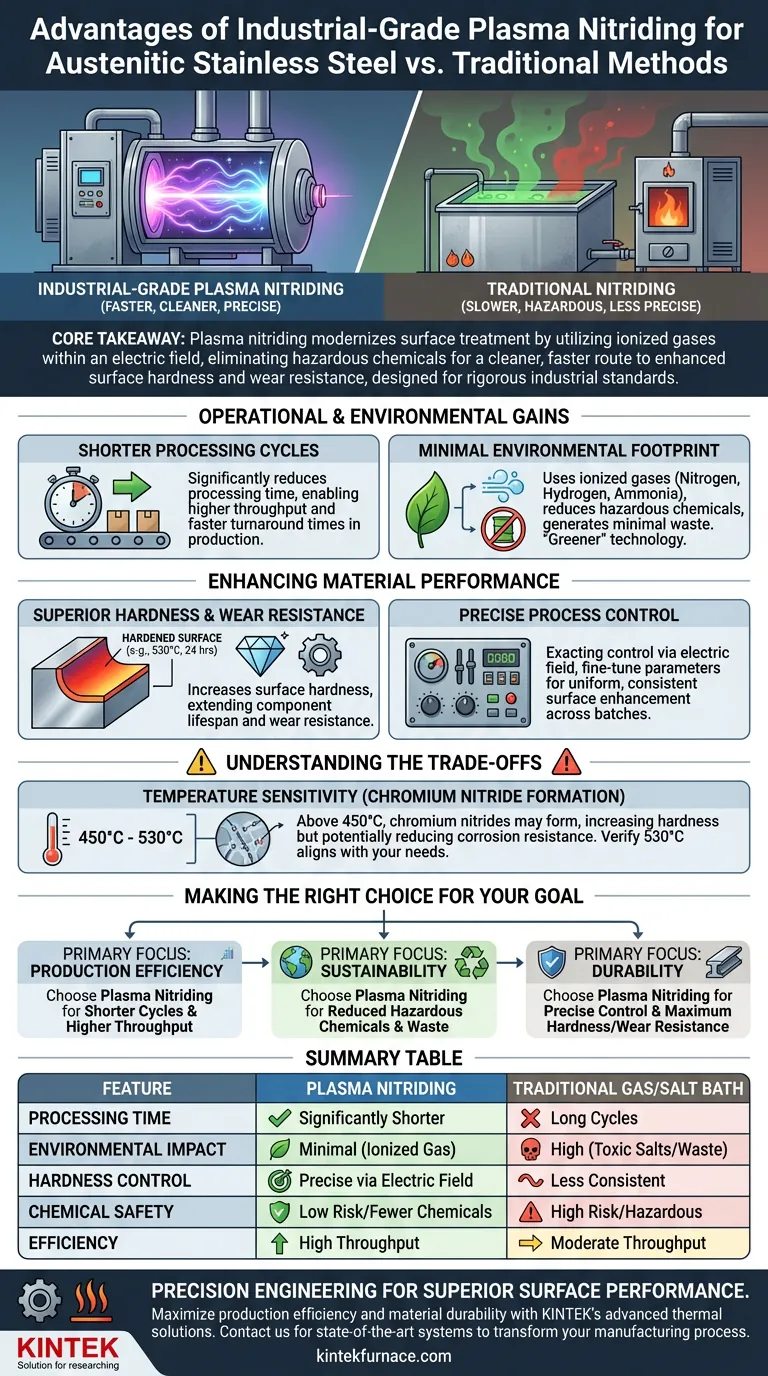
Industrial-grade plasma nitriding furnaces offer a superior alternative to traditional methods by significantly reducing processing time and environmental impact. By utilizing ionized gases within an electric field, these systems eliminate the need for many hazardous chemicals while delivering precise surface modifications.
Core Takeaway: Plasma nitriding modernizes surface treatment by replacing toxic salts and long cycles with a high-efficiency, ionized gas process. It provides a cleaner, faster route to enhanced surface hardness and wear resistance, specifically designed for rigorous industrial standards.

Operational and Environmental Gains
Shorter Processing Cycles
One of the most immediate benefits of industrial plasma nitriding is efficiency. Compared to traditional gas or salt bath methods, plasma nitriding significantly reduces processing time.
This allows for higher throughput and faster turnaround times in production environments.
Minimal Environmental Footprint
Traditional nitriding often involves toxic salts or excessive gas consumption. Plasma nitriding systems operate using ionized gases such as nitrogen, hydrogen, or ammonia.
This process requires fewer hazardous chemicals and generates minimal waste. It represents a much "greener" technology for facilities aiming to reduce their environmental impact.
Enhancing Material Performance
Superior Hardness and Wear Resistance
The primary goal of this surface modification is to improve the mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steel.
By subjecting the material to specific parameters—such as 530 degrees Celsius for 24 hours—the furnace effectively increases the surface hardness. This directly translates to improved wear resistance, extending the lifespan of the component.
Precise Process Control
Plasma nitriding allows for exacting control over the treatment environment via an electric field.
Operators can fine-tune parameters to achieve consistent results. This precision ensures that the enhancement of surface properties is uniform across the treated batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Sensitivity
While the primary reference highlights a process temperature of 530 degrees Celsius to maximize hardness, this specific temperature requires careful consideration for austenitic stainless steel.
At temperatures above 450°C, chromium within stainless steel can form nitrides, which increases hardness but may reduce corrosion resistance. You must verify that the 530°C parameter aligns with your specific corrosion resistance requirements, or if a lower-temperature variation is needed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this method fits your specific manufacturing needs, consider your priorities:
- If your primary focus is Production Efficiency: The shorter processing cycles of plasma nitriding will help you increase throughput without sacrificing quality.
- If your primary focus is Sustainability: The reduction in hazardous chemicals and waste makes this the superior choice for environmentally conscious operations.
- If your primary focus is Durability: The ability to precisely control parameters ensures you achieve the maximum necessary hardness and wear resistance for your specific application.
By leveraging the precision and efficiency of plasma nitriding, you can achieve a harder, more durable surface while adhering to modern environmental standards.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Plasma Nitriding | Traditional Gas/Salt Bath |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | Significantly Shorter | Long Cycles |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal (Ionized Gas) | High (Toxic Salts/Waste) |
| Hardness Control | Precise via Electric Field | Less Consistent |
| Chemical Safety | Low Risk/Fewer Chemicals | High Risk/Hazardous |
| Efficiency | High Throughput | Moderate Throughput |
Precision Engineering for Superior Surface Performance
Maximize your production efficiency and material durability with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers state-of-the-art Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as specialized high-temperature lab furnaces.
Whether you need to enhance wear resistance in austenitic stainless steel or require a fully customizable system for unique industrial needs, our experts are here to help. Contact us today to discover how our high-precision furnaces can transform your manufacturing process.
Visual Guide
References
- Viera Zatkalíková, Lenka Markovičová. Electrochemical Behavior of Plasma-Nitrided Austenitic Stainless Steel in Chloride Solutions. DOI: 10.3390/ma17174189
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature a low vacuum atmosphere furnace can achieve? Unlock Precision Heat Treatment Solutions
- What type of production are continuous furnaces favored for? High-Volume, Standardized Parts Processing
- What is the difference between a vacuum furnace and an atmospheric furnace? Choosing the Right Thermal Process
- What is a box-type atmosphere furnace? Master Controlled Heat for Material Processing
- Why are continuous controlled atmosphere furnaces critical for MIM steel parts? Achieve High-Density Sintering
- How are atmosphere furnaces classified? Choose the Right Type for Your Heat Treatment Needs
- What features are important when selecting an inert atmosphere furnace or oven? Ensure Purity and Efficiency for Your Lab
- For what purpose is a chemically reactive atmosphere used in a furnace? To Transform Material Surfaces



















