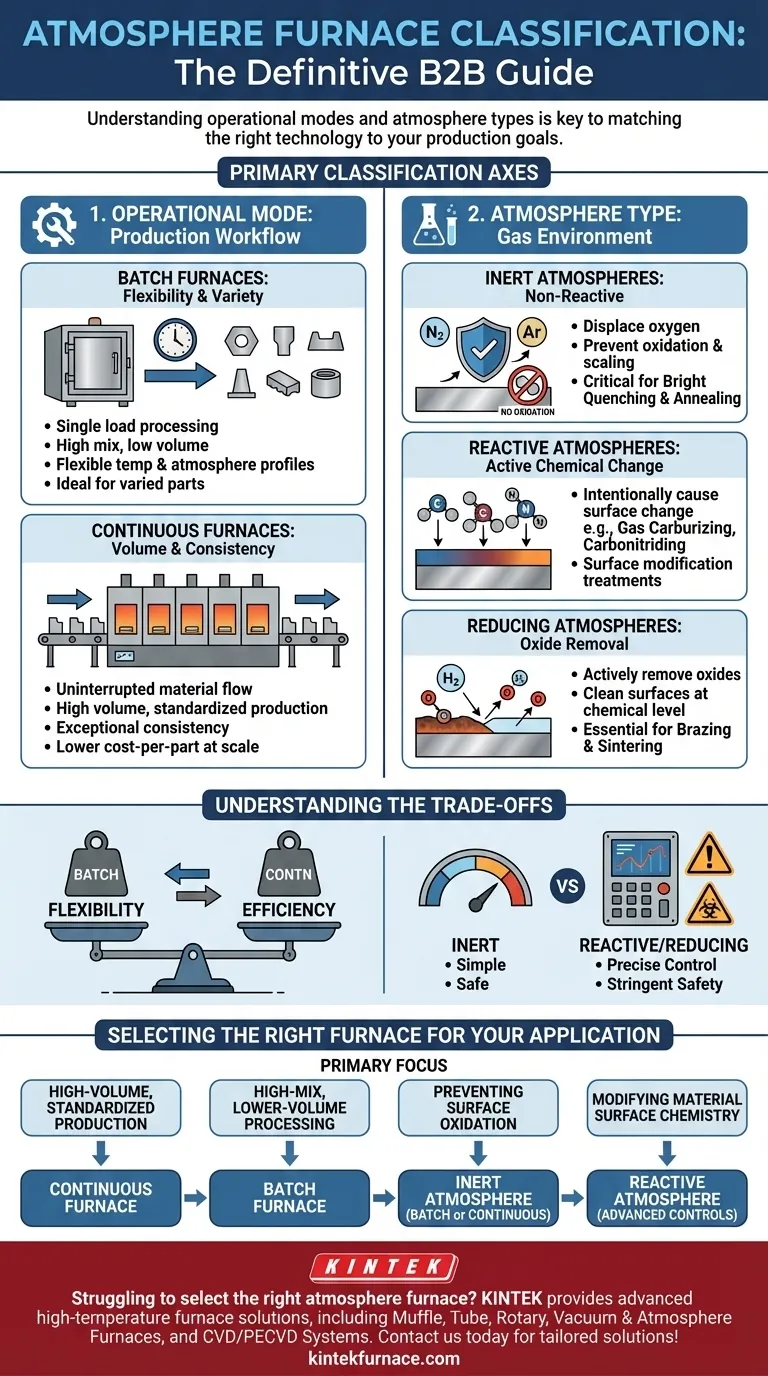
At its core, an atmosphere furnace is classified along two primary axes: its operational mode—how material moves through it—and the type of protective or reactive gas it contains. These classifications determine the furnace's suitability for different production volumes, material types, and desired heat treatment outcomes.
The classification of an atmosphere furnace is not merely a technical detail; it is the fundamental framework that dictates its capabilities. Understanding whether a furnace is batch or continuous and what type of atmosphere it uses is the first step in matching the right technology to your specific process and production goals.

Classification by Operational Mode
The most significant distinction in furnace design is based on the production workflow. This choice directly impacts throughput, flexibility, and cost.
Batch Furnaces: For Flexibility and Variety
A batch furnace processes a single load, or "batch," of material at a time. The entire thermal cycle—from heating to holding to cooling—is completed before the next batch is introduced.
This design is ideal for operations with a high mix of different parts, processes, or smaller production runs. It offers maximum flexibility to change temperature profiles and atmosphere compositions between cycles.
Continuous Furnaces: For Volume and Consistency
A continuous furnace processes materials in an uninterrupted flow. Parts move through different temperature and atmosphere zones on a conveyor belt or pusher mechanism.
These furnaces are the backbone of high-volume, standardized production. They deliver exceptional consistency and a lower cost-per-part at scale, but they lack the flexibility of batch systems and require significant initial investment.
Classification by Atmosphere Type
The "atmosphere" is the carefully controlled gas inside the furnace, which defines the chemical environment for the heat treatment process. This is the second key classification method.
Inert Atmospheres
An inert atmosphere, typically using gases like nitrogen or argon, is non-reactive. Its primary purpose is to displace oxygen and prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation and scaling on the material's surface.
This is critical for processes like bright quenching and bright annealing, where maintaining a clean, scale-free surface finish is paramount.
Reactive (or Active) Atmospheres
A reactive atmosphere is designed to intentionally cause a specific chemical change on the surface of the material. The gas composition actively participates in the process.
Common examples include gas carburizing (adding carbon to steel surfaces for hardening), carbonitriding (adding both carbon and nitrogen), and other surface modification treatments.
Reducing Atmospheres
A reducing atmosphere, often containing hydrogen, is used to actively remove oxides from a material's surface. This "cleans" the parts at a chemical level.
This type of atmosphere is essential for processes like brazing and sintering, where clean, oxide-free surfaces are required to ensure proper metallurgical bonding.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance, cost, and operational complexity. The classification directly informs these trade-offs.
Flexibility vs. Efficiency
The primary trade-off is between the flexibility of a batch furnace and the high-throughput efficiency of a continuous furnace. Batch systems are adaptable but less efficient for mass production, while continuous systems are highly efficient but inflexible.
Atmosphere Control and Safety
Inert atmospheres are relatively simple and safe to manage. In contrast, reactive and reducing atmospheres require precise monitoring of gas composition, pressure, and purity. Flammable gases like hydrogen demand stringent safety protocols and specialized equipment.
Operational Complexity
The complexity of the furnace system directly impacts operational requirements. Continuous furnaces and those using reactive atmospheres demand more sophisticated control systems, regular maintenance, and highly skilled operators to ensure both process quality and safety.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your choice should be driven by a clear understanding of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: A continuous furnace with a dedicated atmosphere is the most efficient and consistent solution.
- If your primary focus is high-mix, lower-volume processing: A batch furnace provides the essential process flexibility you need to handle varied parts and cycles.
- If your primary focus is preventing surface oxidation: An inert atmosphere (nitrogen or argon) is your goal, which can be implemented in either a batch or continuous system.
- If your primary focus is modifying material surface chemistry: You require a reactive atmosphere (e.g., for carburizing) and the advanced control systems needed to manage it safely.
Understanding these fundamental classifications empowers you to align your equipment strategy directly with your specific production goals.
Summary Table:
| Classification Type | Key Categories | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Mode | Batch Furnace | High-mix, low-volume, flexible processes |
| Operational Mode | Continuous Furnace | High-volume, standardized production |
| Atmosphere Type | Inert Atmosphere | Preventing oxidation, bright annealing |
| Atmosphere Type | Reactive Atmosphere | Surface hardening, carburizing |
| Atmosphere Type | Reducing Atmosphere | Oxide removal, brazing, sintering |
Struggling to select the right atmosphere furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your heat treatment efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab



















