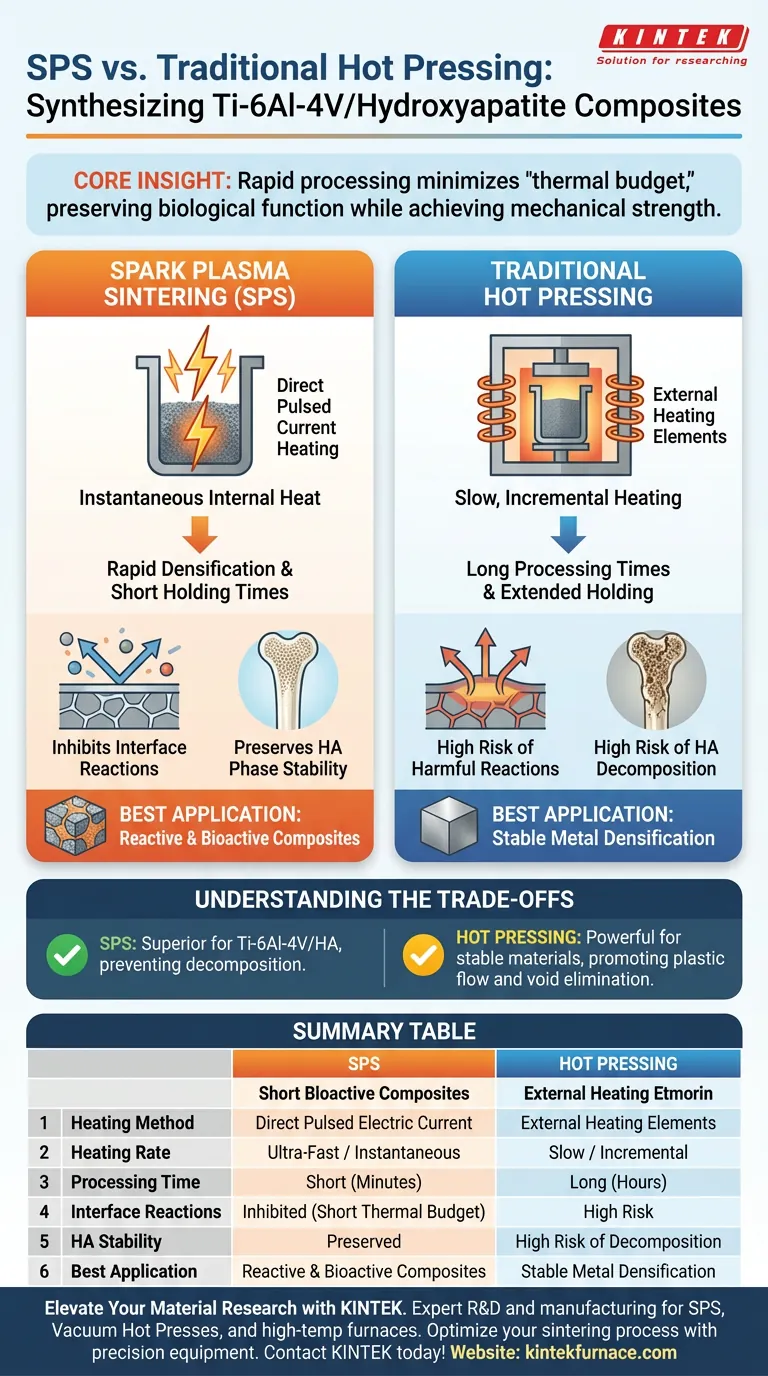
The primary advantage of laboratory-grade spark plasma sintering (SPS) is its ability to utilize direct pulsed current heating to achieve significantly higher heating rates and shorter holding times. For Ti-6Al-4V/hydroxyapatite composites specifically, this rapid processing is crucial. It allows for full densification before the high temperatures can trigger harmful chemical reactions between the titanium matrix and the bioceramic reinforcement.
Core Insight: The success of synthesizing this composite relies on strict thermal management. SPS succeeds where traditional methods struggle because it minimizes the "thermal budget"—the total time the material spends at peak temperature—thereby preserving the biological function of the hydroxyapatite while achieving the mechanical strength of the titanium.

The Mechanism of Rapid Densification
Direct Heating via Pulsed Current
Unlike traditional hot pressing, which relies on external heating elements to slowly warm the chamber, SPS passes a pulsed electric current directly through the powder (or the die).
This generates internal heat instantaneously, allowing the system to reach sintering temperatures rapidly.
Shortened Holding Times
Because the heating is direct and intense, the material requires a much shorter "holding time" at maximum temperature to bond.
This contrasts sharply with traditional methods, which often require extended periods to ensure heat penetrates the material and promotes plastic flow.
Solving the Ti-6Al-4V/Hydroxyapatite Conflict
Inhibiting Interface Reactions
The central challenge with Ti-6Al-4V/hydroxyapatite composites is that titanium is highly reactive with ceramics at elevated temperatures.
SPS completes the densification process so quickly that these harmful interfacial reactions are effectively inhibited.
preventing Bioceramic Decomposition
Hydroxyapatite (HA) is prone to excessive decomposition when exposed to high heat for long periods.
By slashing the process time, SPS preserves the phase stability of the HA, ensuring it retains the bioactive properties required for medical implants.
Balancing Strength and Bioactivity
The ultimate goal of this composite is to combine the load-bearing strength of titanium with the bone-growth properties of hydroxyapatite.
SPS maintains this delicate balance by sintering the metal matrix to full density without thermally degrading the ceramic phase embedded within it.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Strengths of Traditional Hot Pressing
While SPS is superior for this specific reactive composite, traditional vacuum hot pressing remains a powerful technique for other materials.
Supplementary data indicates that traditional hot pressing excels at promoting plastic flow and diffusion bonding through long-duration thermal-mechanical coupling.
When Time is Not a Factor
For stable materials like copper or aluminum alloys, the extended time and vacuum environment of hot pressing allow for the breaking of oxide films and near-total void elimination without the risk of decomposition.
However, for the specific chemistry of Ti-6Al-4V and hydroxyapatite, this "slow and steady" approach is detrimental, making the speed of SPS the decisive factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine which furnace technology aligns with your project requirements, consider the chemical stability of your constituents:
- If your primary focus is preserving a reactive bioceramic phase: Choose Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) to achieve densification before chemical decomposition or adverse interface reactions can occur.
- If your primary focus is strictly mechanical densification of stable metals: Consider Vacuum Hot Pressing, as the longer dwell times allow for extensive plastic flow and void elimination in non-reactive matrices.
For Ti-6Al-4V/hydroxyapatite composites, speed is not just an efficiency metric; it is the only way to ensure the material remains biologically functional.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) | Traditional Hot Pressing |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct Pulsed Electric Current | External Heating Elements |
| Heating Rate | Ultra-Fast / Instantaneous | Slow / Incremental |
| Processing Time | Short (Minutes) | Long (Hours) |
| Interface Reactions | Inhibited via short thermal budget | High risk of harmful reactions |
| HA Stability | Preserved phase stability | High risk of decomposition |
| Best Application | Reactive & Bioactive Composites | Stable Metal Densification |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Are you struggling to balance mechanical strength and bioactivity in your composites? Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) systems, Vacuum Hot Presses, and customizable lab high-temp furnaces designed to solve your most complex thermal processing challenges.
Whether you need to inhibit interfacial reactions or achieve full densification of stable alloys, our team provides the precision equipment required to ensure your materials remain functional and high-quality.
Ready to optimize your sintering process? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique needs with our technical specialists!
Visual Guide
References
- Reinhold Schneider, Christof Sommitsch. Partitioning Phenomena During the Heat Treatment of Martensitic Stainless Steels. DOI: 10.1515/htm-2025-0014
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment important in hot pressing? Essential for Purity and High-Density Materials
- What are the common applications of hot press furnaces? Unlock High-Density Material Solutions
- How does a Vacuum Hot Press (VHP) furnace facilitate the fabrication of bulk nanostructured Al-4Cu alloys?
- What is the primary role of a vacuum hot press furnace? Synthesis of Ti-Al3Ti Laminated Composites Explained
- What are some applications of hot pressing in the field of ceramics? Unlock Superior Performance in Advanced Ceramics
- Why is an industrial hot press critical for lunar ceramic components? Achieve Maximum Density and Impact Resistance
- What role does a vacuum hot press sintering furnace play in Ti/Al2O3 processing? Achieve 99% Density
- What are the advantages of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)? Enhance Cu2Se Densification and Thermoelectric Performance



















