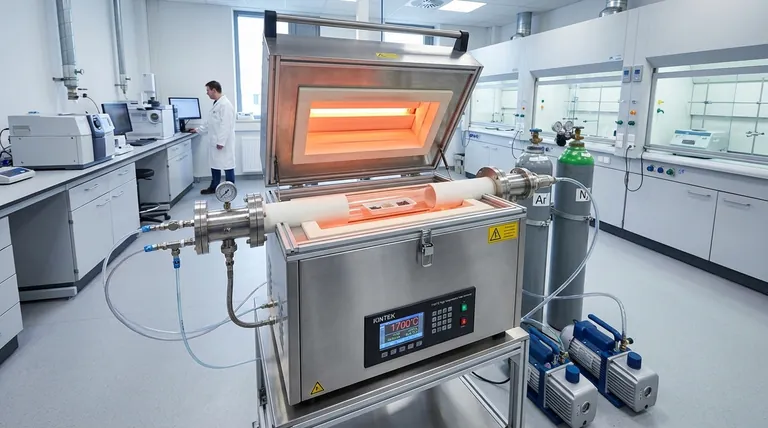
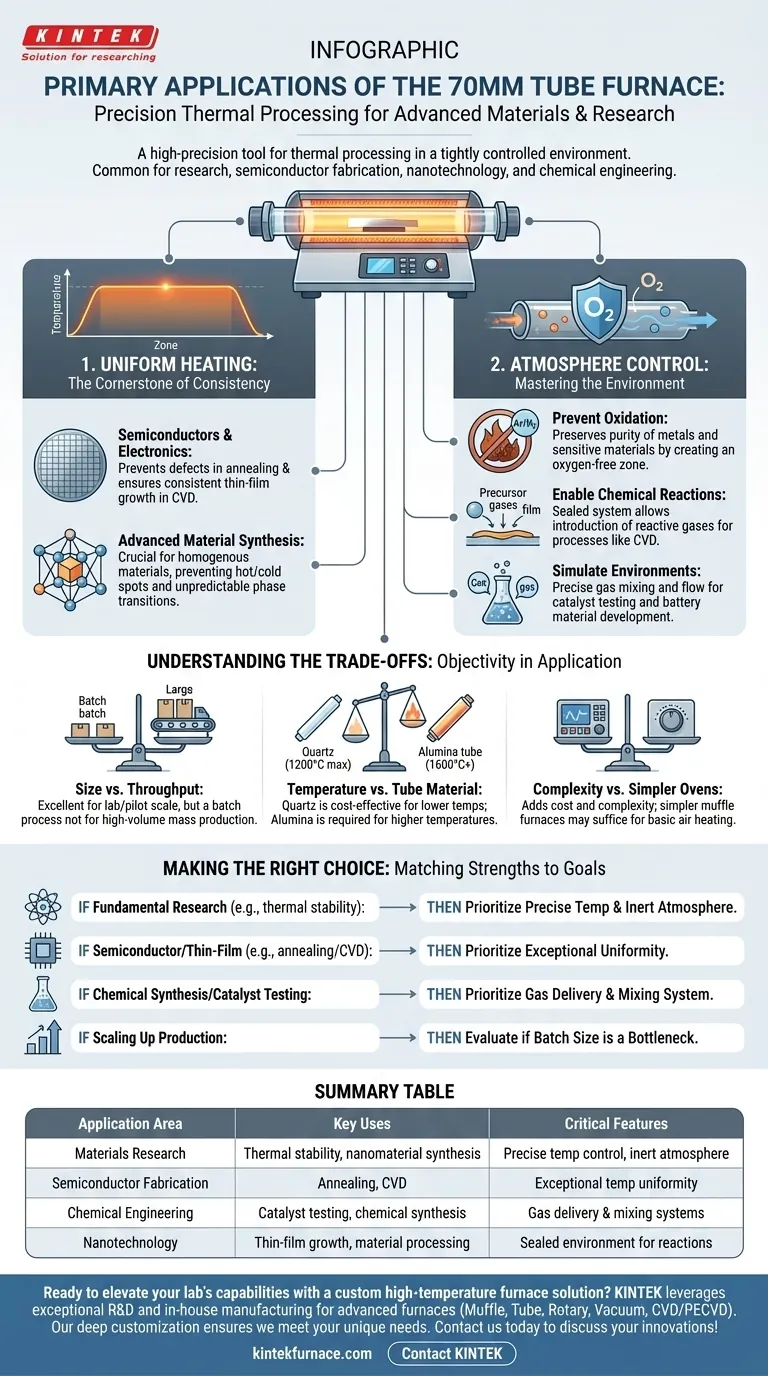
At its core, a 70mm tube furnace is a high-precision tool for thermally processing materials in a tightly controlled environment. Its primary applications span advanced materials research, semiconductor fabrication, nanotechnology, and chemical engineering. The 70mm inner diameter represents a common and versatile size, offering a good balance between sample capacity and the uniform heating characteristics essential for sensitive work.
The decision to use a tube furnace is driven by the need for two things: exceptional temperature uniformity and precise atmospheric control. Its value isn't just in getting hot, but in creating a perfect, repeatable thermal environment that is impossible to achieve with simpler ovens or furnaces.

Why Uniform Heating is the Cornerstone
The defining feature of a quality tube furnace is its ability to maintain a consistent temperature across the entire length of the sample. This uniformity is not a luxury; it is a fundamental requirement for many advanced processes.
For Semiconductor and Electronics Fabrication
In processes like annealing, slight temperature variations can create defects in a semiconductor wafer, ruining its electronic properties. Likewise, for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a uniform temperature ensures that thin films grow at a consistent rate and thickness.
For Advanced Material Synthesis
When creating novel alloys, ceramics, or nanomaterials, the final properties are directly linked to the processing temperature. Any "hot spots" or "cold spots" in the furnace will result in a non-homogenous material with inconsistent performance and unpredictable phase transitions.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
A tube furnace is a sealed system, which allows you to completely control the gaseous environment surrounding your sample. This is just as critical as the temperature itself.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Many materials, especially metals at high temperatures, will rapidly oxidize (or rust) in the presence of air. By flowing an inert gas like argon or nitrogen through the tube, you can create an oxygen-free environment, preserving the material's purity.
Enabling Chemical Reactions
Processes like CVD rely on introducing specific reactive gases (precursors) into the chamber. The high temperature causes these gases to decompose and deposit a solid thin film onto a substrate. The furnace's sealed nature is essential for this to work.
Simulating Specific Environments
In fields like catalyst research or battery material development, scientists need to test how materials behave under specific atmospheric conditions. A tube furnace allows for the precise mixture and flow of gases to simulate a target industrial or operational environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly powerful, a 70mm tube furnace is not the universal solution for all heating tasks. Objectivity requires understanding its limitations.
Size vs. Throughput
A 70mm diameter is excellent for lab-scale research, pilot studies, and processing small, high-value components. However, it is fundamentally a batch process and is not suitable for high-volume mass production, where larger, continuous, or specialized furnaces would be necessary.
Temperature vs. Tube Material
The maximum operating temperature is often limited by the process tube material. Quartz tubes are common and cost-effective but typically max out around 1100-1200°C. For higher temperatures (up to 1600°C or more), you must use more expensive and durable alumina (ceramic) tubes.
Complexity vs. Simpler Ovens
The gas management systems, vacuum pumps, and precise controllers add a layer of complexity and cost. If your process only requires heating a stable material in air and does not need perfect uniformity, a simpler and less expensive muffle furnace might be a more practical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if this is the right tool, match its core strengths to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is fundamental materials research (e.g., testing thermal stability): The precise temperature control and ability to work in an inert atmosphere are your most critical features.
- If your primary focus is semiconductor or thin-film processing (e.g., annealing or CVD): Prioritize exceptional temperature uniformity across the heated zone to ensure device and film consistency.
- If your primary focus is chemical synthesis or catalyst testing: The gas delivery and mixing system is as important as the furnace; ensure it meets the needs of your specific chemical process.
- If your primary focus is scaling up production: The 70mm furnace is an excellent pilot tool, but you must evaluate if its batch size is a bottleneck for your required throughput.
Ultimately, selecting a 70mm tube furnace is a decision to prioritize controlled, repeatable, and uniform thermal processing for high-value applications.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Critical Features |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Research | Thermal stability testing, nanomaterial synthesis | Precise temperature control, inert atmosphere |
| Semiconductor Fabrication | Annealing, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Exceptional temperature uniformity |
| Chemical Engineering | Catalyst testing, chemical synthesis | Gas delivery and mixing systems |
| Nanotechnology | Thin-film growth, material processing | Sealed environment for controlled reactions |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a custom high-temperature furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, whether for materials research, semiconductor processing, or chemical synthesis. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















