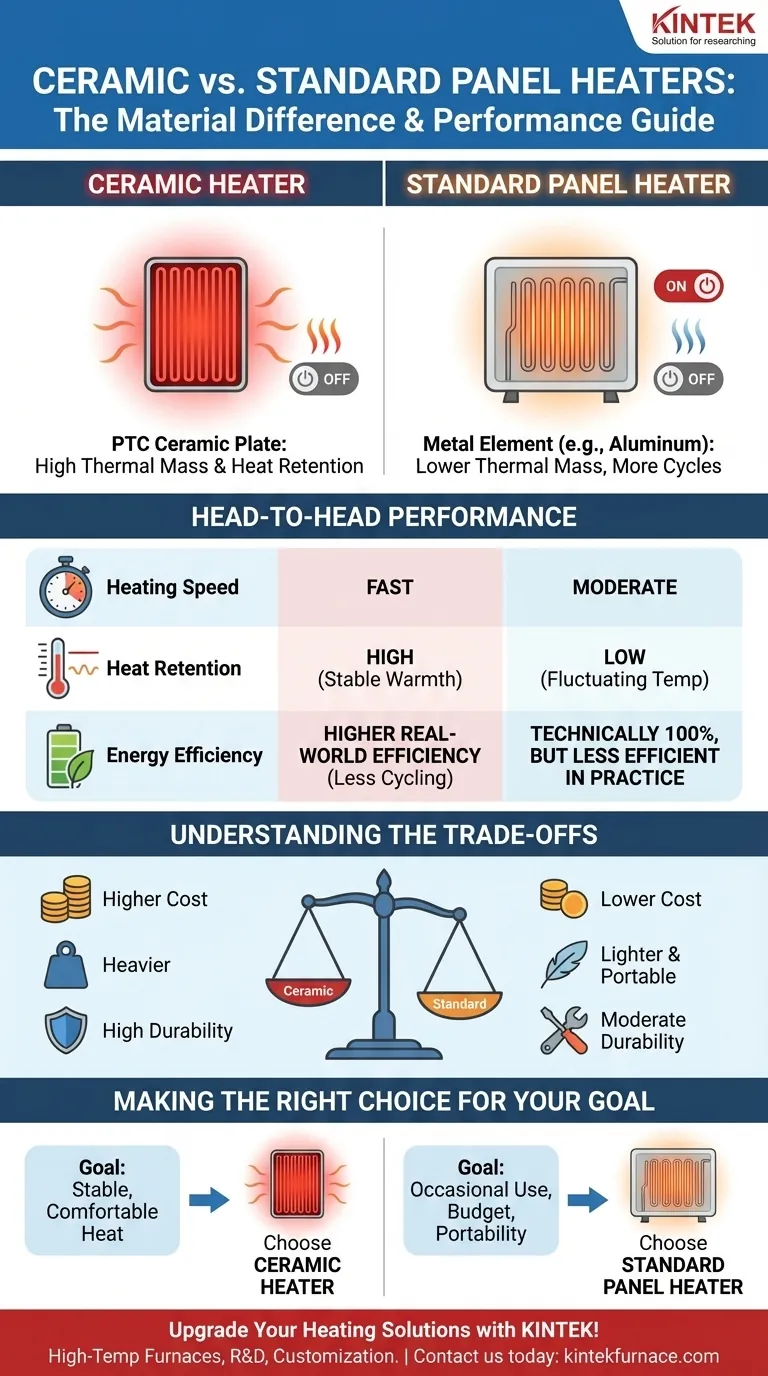
At their core, the fundamental difference between a ceramic heater and a standard panel heater is the material used for the heating element. While both are types of electric convection heaters, ceramic models use a Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) ceramic plate to generate warmth, whereas standard panel heaters typically use a metal element, such as aluminum. This single material difference dictates how each unit performs, retains heat, and distributes warmth throughout a room.
While both heater types convert electricity into heat with near-perfect efficiency, the choice between them comes down to a trade-off: a ceramic heater’s superior heat retention and speed versus a standard panel heater's lower initial cost and lighter weight.

How Each Heater Type Works
Both heater types operate on the principle of convection, meaning they heat the air around them, which then circulates to warm the entire space. The key distinction lies in how they manage that heat.
The Standard Panel Heater
A standard panel heater passes electricity through a resistive metal element, often made of aluminum. This element heats up quickly and begins to warm the air that passes over it.
This process creates a natural convection cycle: cool air is drawn into the bottom of the unit, heated by the element, and then rises out of the top, circulating throughout the room.
The Ceramic Heater
A ceramic heater functions on the same convection principle, but its ceramic element provides two distinct advantages. Ceramic has a high thermal mass, meaning it absorbs and stores heat extremely well.
When electricity is applied, the ceramic plate heats up very quickly. More importantly, it continues to radiate heat even after the thermostat turns the power off. This "heat storage" capability results in a more consistent room temperature with fewer on-off cycles.
A Head-to-Head Performance Comparison
Understanding the material science behind each heater helps clarify their practical differences in day-to-day use.
Heating Speed
Ceramic elements are designed for rapid heating. They typically reach their target temperature faster than the metal elements found in many standard panel heaters, providing warmth more quickly when you first turn them on.
Heat Retention and Stability
This is the most significant advantage of ceramic. Because the ceramic plate holds onto heat, it acts as a thermal buffer. This smooths out the heating cycle, providing a steady warmth and preventing the noticeable temperature drops that can occur when a standard heater's thermostat cycles off.
Energy Use
Technically, all-electric resistance heaters, whether ceramic or metal, are nearly 100% efficient at converting electricity into heat. A 1500-watt ceramic heater and a 1500-watt standard heater use the same amount of power to produce the same total amount of heat (BTUs).
However, the superior heat retention of a ceramic heater can lead to greater real-world efficiency. By cycling on and off less frequently to maintain a set temperature, it can ultimately reduce overall energy consumption in many scenarios.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is universally superior; each comes with its own set of considerations. Choosing the right one depends on your priorities.
Upfront Cost
Standard panel heaters with metal elements are generally less expensive to purchase. The technology is simpler and the materials are more common, making them a budget-friendly option for effective heating.
Weight and Portability
Ceramic is a denser, heavier material than the aluminum often used in standard panels. This makes standard panel heaters significantly lighter and often thinner, which can be an advantage if you plan to move the heater between rooms or mount it on a wall.
Durability
The ceramic PTC elements are incredibly durable and self-regulating. They are solid-state components that are not prone to overheating or corrosion, which can sometimes be a long-term concern with certain metal elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the best heater, analyze how you intend to use it and what you value most.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a stable, comfortable temperature in a frequently used room: A ceramic heater is the superior choice due to its excellent heat retention and faster warm-up time.
- If your primary focus is occasional use, portability, or the lowest initial purchase price: A standard metal-element panel heater provides effective convection heating at a more accessible cost.
By understanding these material differences, you can confidently select the heater that best aligns with your specific heating goals and budget.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ceramic Heater | Standard Panel Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Element | PTC Ceramic Plate | Metal (e.g., Aluminum) |
| Heating Speed | Fast | Moderate |
| Heat Retention | High (consistent warmth) | Low (more on-off cycles) |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher real-world due to less cycling | Technically 100%, but less efficient in practice |
| Upfront Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter and more portable |
| Durability | High (self-regulating, corrosion-resistant) | Moderate (prone to overheating/corrosion) |
Upgrade Your Heating Solutions with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored heating technologies can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
















