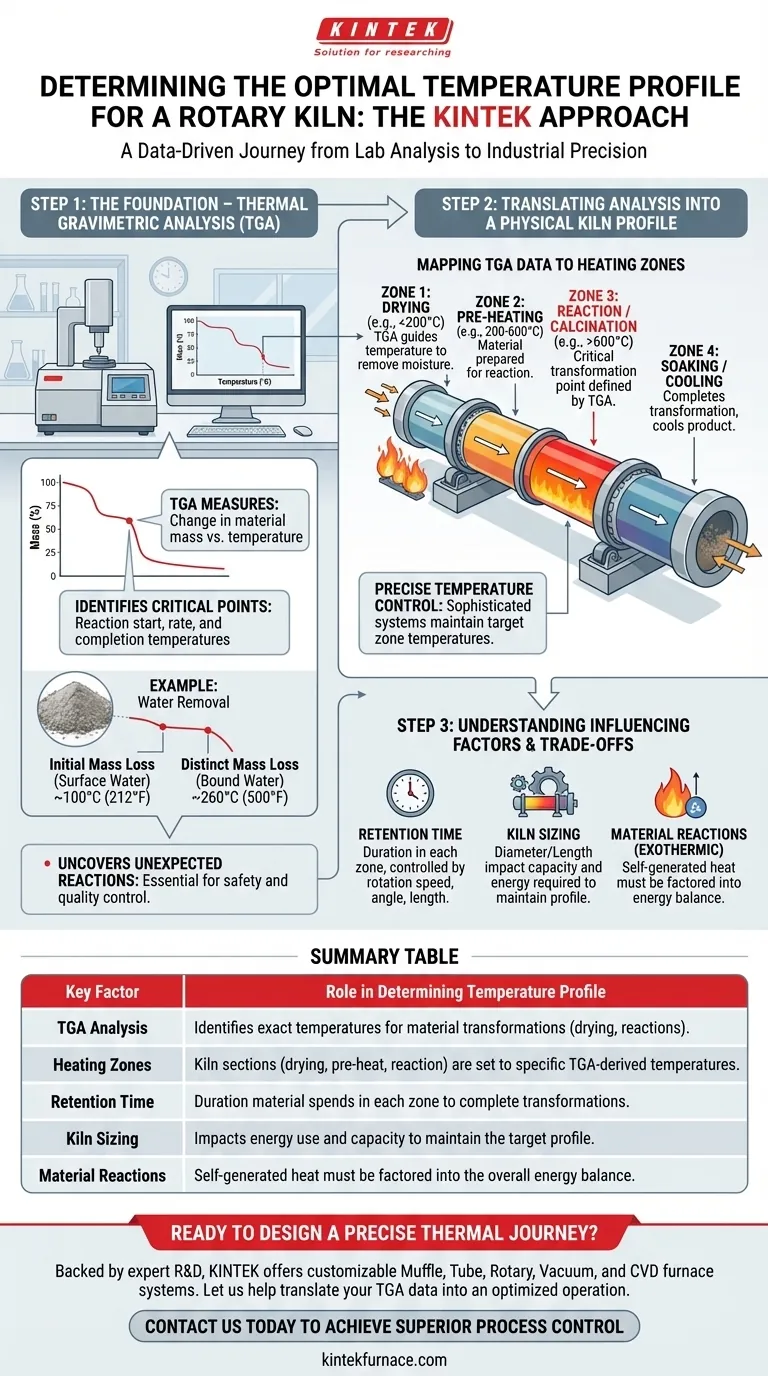
To determine the appropriate temperature profile for a rotary kiln, the foundational method used is Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA). This scientific analysis precisely measures changes in a material's mass as it is heated, identifying the exact temperature ranges where critical physical and chemical transformations—like drying or chemical reactions—occur. This data forms the blueprint for programming the kiln's heating zones.
The core principle is that a rotary kiln doesn't operate at a single temperature but guides material through a specific thermal journey. TGA provides the essential map for this journey, revealing the critical temperature milestones your material must reach to achieve its final, desired state.
The Foundation: Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
A successful kiln operation begins long before the material is loaded. It starts with a deep understanding of how that material behaves under heat, which is precisely what TGA provides.
What TGA Measures
Thermal Gravimetric Analysis is a laboratory technique that measures the change in a material's mass as a function of temperature. It essentially tells you at what temperature your material gains or, more commonly, loses weight.
Identifying Critical Temperature Points
This mass loss is the key indicator of a physical or chemical change. TGA clearly shows the temperature at which a reaction begins, the rate at which it proceeds, and the temperature at which it is complete.
A Practical Example: Water Removal
A simple TGA curve can differentiate between removing free moisture and chemically bound water. You might see an initial mass loss around 100°C (212°F) as surface water vaporizes, followed by another distinct mass loss event at a higher temperature, such as 260°C (500°F), as more tightly bound water molecules are released.
Uncovering Unexpected Reactions
Beyond planned transformations, a TGA can also reveal unpredicted side reactions. Identifying these reactions beforehand is critical for process control, safety, and ensuring the quality of the final product.
Translating Analysis into a Physical Profile
The data from the TGA is not just theoretical; it directly informs the physical setup and operation of the rotary kiln itself. The temperature curve from the lab becomes the temperature profile in the industrial unit.
The Concept of Heating Zones
Rotary kilns are not heated uniformly. They are engineered with multiple distinct heating zones along their length, each maintained at a specific temperature. Common zones include drying, pre-heating, reaction (or calcination), and soaking/cooling.
Mapping TGA Data to Kiln Zones
The temperature milestones identified by the TGA directly correspond to these zones. For example, the temperature range where free water is driven off dictates the temperature and length of the drying zone. The higher temperature where a chemical decomposition occurs defines the setpoint for the reaction zone.
The Role of Retention Time
The analysis also informs the necessary retention time—how long the material must spend in each zone to complete its transformation. This is controlled by the kiln's rotation speed, angle of inclination, and length.
Precise Temperature Control
To maintain this profile, kilns use sophisticated heating systems, such as external furnaces or internal direct-fired burners. These systems are precisely controlled to hold each zone at the target temperature derived from the initial TGA.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Influencing Factors
While TGA provides the ideal thermal map, successfully applying it depends on the kiln's physical characteristics and operational constraints.
The Impact of Kiln Sizing
The diameter and length of the kiln are critical. A larger kiln can process more material (capacity) but requires significantly more energy to maintain the temperature profile. The final size is a function of the required retention time and the desired fullness, or "bed depth," of the material.
Heat Generation from the Material
In some processes, the material's reaction is exothermic, meaning it generates its own heat. This must be factored into the energy calculations to avoid overheating and to maintain precise control over the temperature profile.
The Goal is a System, Not a Number
Ultimately, the temperature profile cannot be considered in isolation. It is one critical part of a system that includes feed rate, retention time, kiln dimensions, and the material's own chemical properties.
How to Apply This to Your Process
The correct temperature profile is entirely dependent on your material and your end goal. Using TGA as your starting point allows you to tailor the process with precision.
- If your primary focus is simple drying: Your TGA will guide a profile focused on a long, low-temperature zone to gently remove moisture without altering the material's chemistry.
- If your primary focus is complex calcination: Your TGA will reveal multiple, high-temperature reaction points, demanding a sophisticated, multi-zone profile with very precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and safety: A thorough TGA is non-negotiable to identify all reactions, account for their energy needs, and prevent unexpected events or incomplete processing within the kiln.
By starting with a rigorous thermal analysis, you transform the operation of a rotary kiln from estimation into a precise, data-driven science.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Determining Temperature Profile |
|---|---|
| Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA) | Identifies exact temperatures for material transformations (drying, reactions). |
| Heating Zones | Kiln sections (drying, pre-heat, reaction) are set to specific TGA-derived temperatures. |
| Retention Time | Duration material spends in each zone to complete transformations. |
| Kiln Sizing (Diameter/Length) | Impacts energy use and capacity to maintain the target profile. |
| Material Reactions (Exothermic) | Self-generated heat must be factored into the overall energy balance. |
Ready to design a precise thermal journey for your material?
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers advanced Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD furnace systems, all customizable for your unique processing needs. Our team can help you translate TGA data into an optimized, efficient kiln operation.
Contact us today to discuss your application and achieve superior process control!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency



















