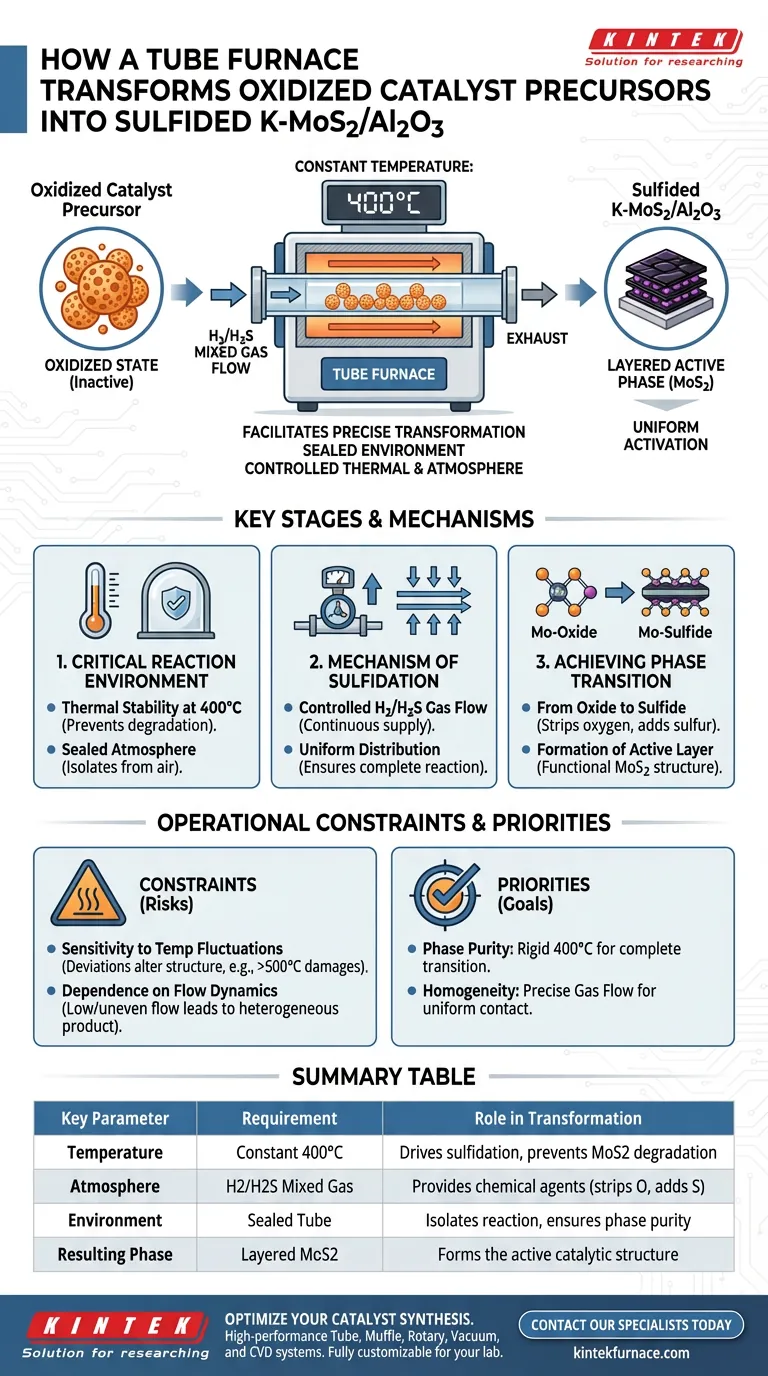
A Tube Furnace facilitates the precise transformation of oxidized catalyst precursors into sulfided K-MoS2/Al2O3 by maintaining a strictly controlled, sealed environment at a constant 400°C. Through the regulation of H2/H2S mixed gas flows, the furnace drives the chemical transition of molybdenum components from an oxidized state into a layered, active MoS2 phase.
The device's primary value lies in creating a uniform reaction environment that ensures complete sulfidation, preventing the uneven activation that often occurs in less controlled thermal settings.
Establishing the Critical Reaction Environment
To convert a catalyst precursor effectively, the physical environment must be rigorously stabilized. The tube furnace provides the isolation and thermal consistency required for this sensitive chemical process.
Thermal Stability at 400°C
The process requires a constant temperature environment specifically set to 400°C.
At this temperature, the energy is sufficient to drive the reaction without inducing unwanted thermal degradation.
The Sealed Atmosphere
The furnace utilizes a sealed reaction environment to isolate the precursor materials.
This isolation prevents external air from interfering with the chemistry, ensuring that the catalyst interacts only with the intended sulfiding agents.
The Mechanism of Sulfidation
The transformation from an inactive precursor to an active catalyst is driven by the interaction between the solid material and the gas phase.
Controlled Gas Flow
The core mechanism involves the strict control of H2/H2S mixed gases flowing through the tube.
By regulating this flow, the furnace ensures a continuous supply of reactants to the catalyst surface.
Uniform Distribution
The design of the tube furnace promotes uniform sulfidation across the entire batch of material.
This uniformity is critical, as it guarantees that every particle of the catalyst precursor is exposed to the same conditions, preventing partial activation.
Achieving the Phase Transition
The ultimate goal of using the tube furnace is a structural modification of the catalyst at the microscopic level.
From Oxide to Sulfide
The process targets the molybdenum components within the precursor, which start in an oxidized state.
The H2/H2S environment chemically strips oxygen and replaces it with sulfur.
Formation of the Active Layer
Successful treatment results in the transition to a layered MoS2 active phase.
This specific layered structure is the functional form of the catalyst required for its final application.
Understanding Operational Constraints
While the tube furnace is highly effective, it relies on strict adherence to process parameters.
Sensitivity to Temperature Fluctuations
The process is calibrated for 400°C; deviations can alter the crystalline structure of the MoS2.
Higher temperatures (such as the 500°C–650°C range used for sintering other materials like platinum) are not appropriate for this specific activation phase and could damage the K-MoS2 structure.
Dependence on Flow Dynamics
The quality of the final product is heavily dependent on the gas flow dynamics.
If the gas flow is too low or uneven, pockets of the precursor may remain oxidized, resulting in a heterogeneous and less effective catalyst.
Ensuring Successful Catalyst Activation
To maximize the effectiveness of the tube furnace for K-MoS2/Al2O3 production, focus on these operational priorities:
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Maintain the temperature rigidly at 400°C to ensure the molybdenum transitions completely to the layered MoS2 phase without degradation.
- If your primary focus is Homogeneity: Prioritize the precise regulation of the H2/H2S gas flow to ensure uniform contact with the entire catalyst bed.
By strictly controlling the thermal and atmospheric variables, you ensure the complete and uniform activation of the catalyst precursor.
Summary Table:
| Key Parameter | Requirement | Role in Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Constant 400°C | Drives sulfidation while preventing MoS2 degradation |
| Atmosphere | H2/H2S Mixed Gas | Provides the chemical agents to strip oxygen and add sulfur |
| Environment | Sealed Tube | Isolates reaction from air to ensure phase purity |
| Resulting Phase | Layered MoS2 | Forms the active catalytic structure required for applications |
Optimize Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK
Achieving perfect phase purity and homogeneity in catalyst activation requires precise thermal and atmospheric control. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of laboratory research.
Whether you are performing complex sulfidation or high-temperature sintering, our systems are fully customizable to fit your unique experimental needs.
Ready to elevate your lab's efficiency? Contact our specialists today to find the ideal furnace solution for your application!
Visual Guide
References
- Hao Wang, Yongming Luo. The Influence of Sulfurization and Carbonization on Mo-Based Catalysts for CH3SH Synthesis. DOI: 10.3390/catal14030190
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a continuous nitrogen flow required in a closed tube furnace during the solid-phase synthesis of LiMnO2 precursors?
- What are the specific operational benefits of tube furnace cracking? Unlock Efficiency and Precision in Material Processing
- Why is alumina ceramic tubing selected as the liner for a Drop Tube Furnace? Ensure Purity and High-Temp Stability
- Why is a Horizontal Tube Diffusion Furnace used for polysilicon doping? Master POCl3 Diffusion & Sheet Resistance
- How does a laboratory tube resistance furnace contribute to the thermal treatment stage of Bi2O3 precursors?
- Why are tubular furnaces valued in academic and research settings? Unlock Precision Heating for Your Experiments
- What are the key takeaways for optimizing a split tube furnace? Boost Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What are the specifications for three-zone and three-phase horizontal tube furnace models? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Lab



















