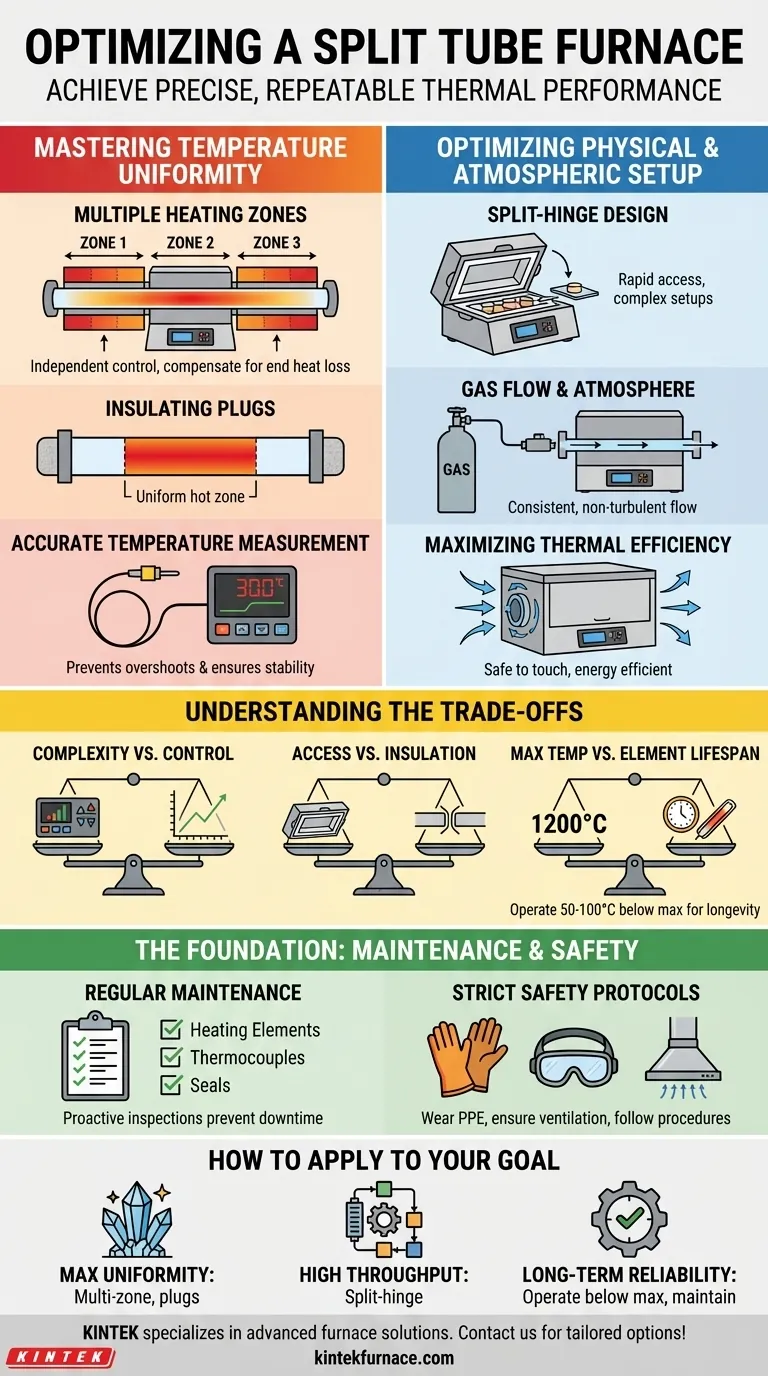
Ultimately, optimizing a split tube furnace is about achieving precise, repeatable thermal performance for your specific application. The key is to master three interconnected areas: precise temperature control across the furnace tube, an efficient physical and atmospheric setup, and disciplined operational procedures for maintenance and safety.
The core principle of optimization is not just about reaching a target temperature, but about creating a highly uniform and stable thermal environment. This is achieved by aligning the furnace’s design features, such as multiple heating zones and insulating plugs, with the specific requirements of your scientific or industrial process.
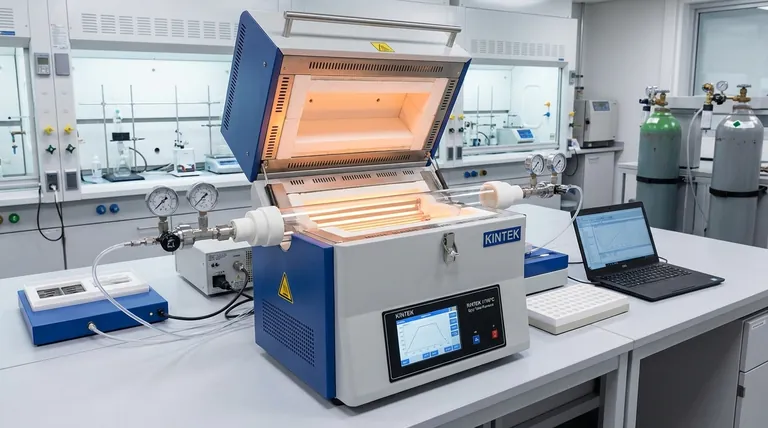

Mastering Temperature Uniformity and Control
The primary goal of any furnace is to deliver heat, but optimization demands that the heat is delivered with exceptional accuracy and uniformity.
The Role of Multiple Heating Zones
A furnace with multiple, independently controlled heating zones (e.g., 3 or 5 zones) offers superior performance over a single-zone model. This allows you to compensate for natural heat loss at the ends of the tube, creating a much longer and more stable uniform temperature zone in the center.
Leveraging Insulating Plugs
To further enhance temperature uniformity, always use insulating plugs at the ends of the process tube. These ceramic or quartz wool plugs act as barriers, significantly reducing heat loss and extending the length of the uniform hot zone.
Ensuring Accurate Temperature Measurement
Your control system is only as good as the data it receives. Ensure your thermocouples are correctly positioned, calibrated, and in good condition to provide accurate and responsive feedback to the temperature controller. This is critical for preventing temperature overshoots and maintaining stability.
Optimizing the Physical and Atmospheric Setup
How you configure the furnace and its internal environment is just as important as the temperature settings.
The Advantage of the Split-Hinge Design
The defining feature of a split tube furnace is its hinged, two-half body. True optimization means leveraging this for its intended purpose: rapid access. This design is ideal for experiments with complex setups inside the tube or for processes requiring quick sample changes, minimizing downtime.
Managing Gas Flow and Atmosphere
Many applications, like catalyst testing or annealing, require a specific atmosphere (e.g., inert gas) or vacuum. Optimizing gas flow involves ensuring a consistent, non-turbulent flow rate to maintain atmospheric purity without disturbing the thermal stability.
Maximizing Thermal Efficiency
The dual-layer, forced air-cooled casing is designed to keep the exterior safe to touch and minimize energy waste. Ensure ventilation around the furnace is unobstructed. This not only improves energy efficiency but also contributes to the longevity of the electronic components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Effective optimization requires acknowledging inherent design trade-offs.
Complexity vs. Control
A multi-zone furnace provides superior temperature control but adds complexity to programming and setup. You must invest the time to properly profile the furnace to take full advantage of its capabilities.
Access vs. Insulation
The split-hinge design offers unparalleled access but can be a potential source of minor heat loss or atmospheric leaks if the seals between the halves are not perfectly maintained. Regular inspection of these seams is crucial.
Maximum Temperature vs. Element Lifespan
While a furnace may be rated for 1200°C, consistently operating at the absolute maximum temperature will accelerate the degradation of the heating elements. For long-term reliability, it is often best to operate at 50-100°C below the maximum limit whenever possible.
The Foundation: Maintenance and Safety
No amount of technical optimization can succeed without a foundation of disciplined operation.
Implementing a Regular Maintenance Schedule
Create a simple checklist. Regularly inspect the condition of the heating elements (for cracking), thermocouples (for degradation), and the seals on the split-body. Proactive maintenance prevents failed experiments and costly downtime.
Adhering to Strict Safety Protocols
Optimization is impossible in an unsafe lab. Always wear heat-resistant gloves and eye protection when handling hot components. Ensure the work area is well-ventilated, and strictly follow all manufacturer-recommended startup and shutdown procedures.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your optimization strategy should be tailored to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity (e.g., crystal growth): Invest in a multi-zone furnace and master the use of insulating plugs to create the most stable hot zone possible.
- If your primary focus is high throughput or complex setups (e.g., in-situ analysis): Fully leverage the split-hinge design to minimize the time between experimental runs.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and efficiency: Operate below the furnace's absolute maximum temperature and adhere to a strict maintenance and safety schedule.
By applying these principles, you transform your split tube furnace from a simple heat source into a precision instrument capable of delivering consistent and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Optimization Area | Key Takeaways |
|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Use multiple heating zones, insulating plugs, and accurate thermocouples for uniform heat. |
| Physical Setup | Leverage split-hinge design for quick access; manage gas flow and ensure ventilation. |
| Trade-offs | Balance complexity vs. control, access vs. insulation, and temperature vs. element lifespan. |
| Maintenance & Safety | Regular inspections and strict protocols to ensure longevity and safe operation. |
Ready to optimize your lab's thermal processes with precision? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















