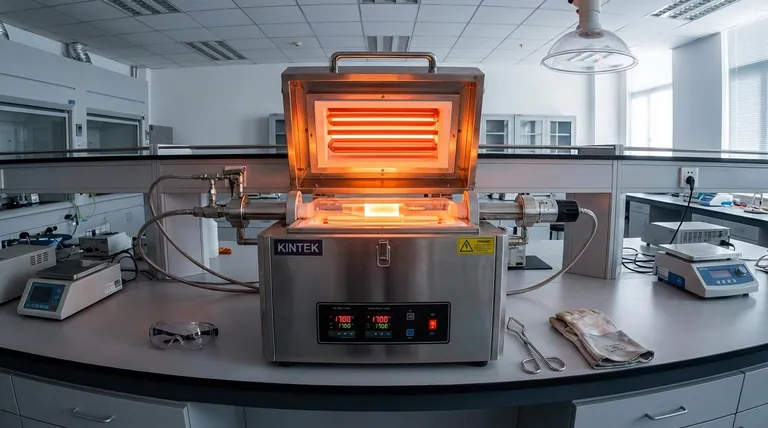
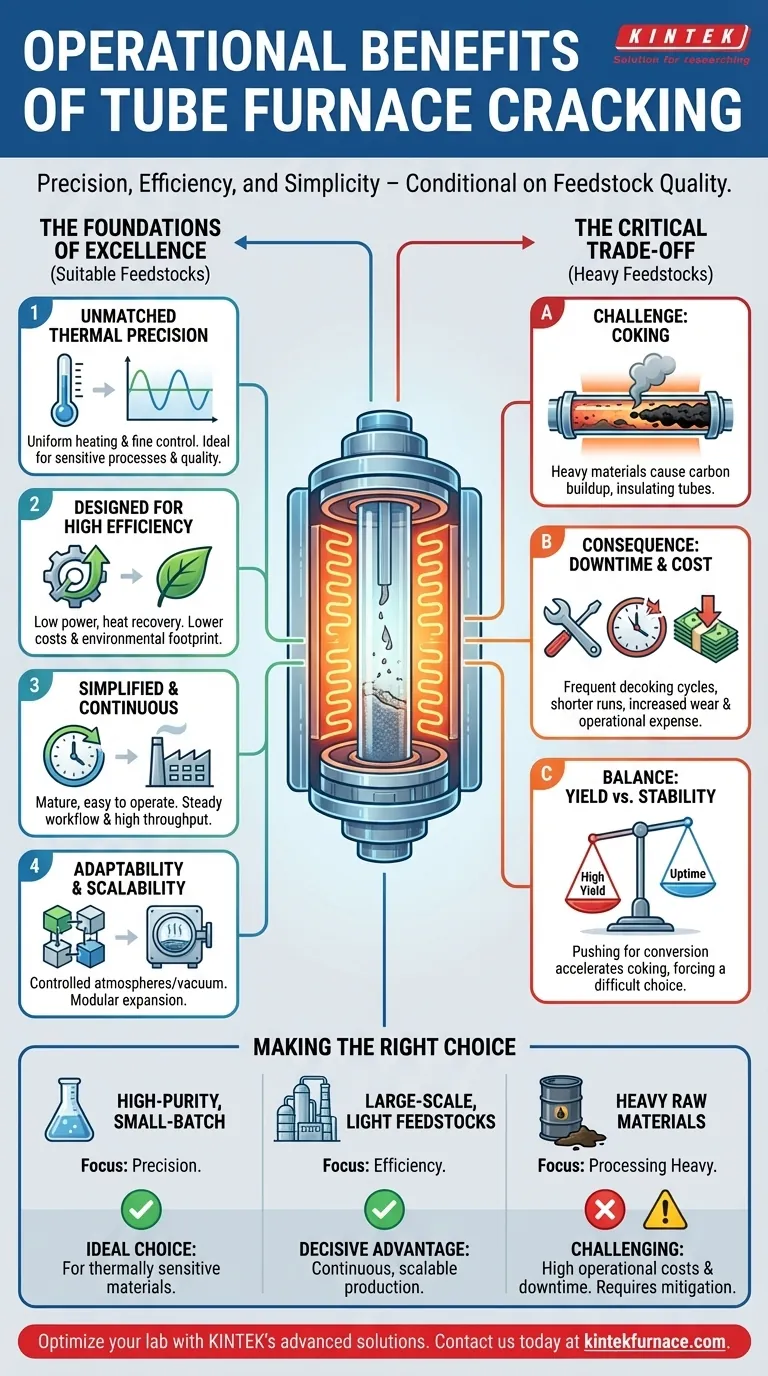
The primary operational benefits of tube furnace cracking stem from its precise control, high efficiency, and operational simplicity. This mature technology offers exceptional temperature management, continuous production capabilities, and high thermal efficiency, making it a powerful tool for converting specific raw materials into high-value products like ethylene and propylene.
While tube furnace cracking is celebrated for its precise thermal control and high efficiency, its true operational advantage is unlocked only when the process is paired with suitable raw materials. The choice of feedstock is the single most critical factor determining whether the furnace operates as a highly efficient asset or a high-maintenance liability.

The Foundations of Operational Excellence
Tube furnace cracking is a cornerstone technology because it excels in several key operational domains. These benefits are a direct result of its fundamental design and mature engineering principles.
Unmatched Thermal Precision and Control
The cylindrical geometry of a tube furnace provides unmatched thermal uniformity. This design allows for exceptionally fine adjustments to temperature, ensuring the material inside is heated evenly and consistently.
This level of control is critical for sensitive thermal processes where precise temperature profiles dictate product yield and quality. The ability to heat quickly and maintain a stable atmosphere or vacuum makes it highly adaptable.
Designed for High Efficiency
Tube furnaces are engineered for high thermal efficiency and low power consumption. The design allows for the effective recovery and use of heat from both the cracked gas and the flue gas, minimizing energy waste.
This efficiency translates directly to lower operating costs and a smaller environmental footprint, as it avoids pollution associated with less controlled combustion processes.
Simplified and Continuous Operation
A key advantage is the technology's maturity and structural simplicity. These furnaces are relatively easy to operate and control, which reduces the need for highly specialized labor and minimizes the potential for error.
Furthermore, they are designed for continuous production. This allows for a steady, uninterrupted workflow, maximizing throughput and asset utilization when operating under ideal conditions.
Adaptability and Scalability
The inherent design of a tube furnace is adaptable to various process requirements, including those needing a controlled atmosphere or a vacuum. This makes it suitable for a wide range of chemical synthesis and materials processing applications.
For large-scale needs, multiple furnaces can be operated in parallel. This modular approach to scalability allows producers to expand capacity as demand grows without redesigning the core process.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
No technology is without limitations. The impressive operational benefits of tube furnace cracking are conditional and depend heavily on the raw materials being processed. Ignoring this context is the most common pitfall.
The Challenge of Heavy Raw Materials
The primary limitation of tube furnace cracking is its performance with heavy raw materials. These feedstocks have a strong tendency to cause coking—the formation of hard carbon deposits on the interior surfaces of the furnace tubes.
Coking acts as an insulator, severely impeding heat transfer and disrupting the cracking process. This single issue can negate many of the furnace's primary benefits.
The Consequence of Coking
When coking occurs, it triggers a cascade of negative operational consequences. The furnace must be taken offline frequently for decoking, a process that burns off the carbon deposits.
This leads directly to shorter operation cycles and reduced effective annual production time. It also increases wear and tear, impacting the lifespan of the furnace tubes, and drives up operational costs through lower raw material utilization and the production of low-value byproducts.
Balancing Yield vs. Uptime
There is a fundamental tension between cracking depth and operational stability when using heavier feedstocks. Attempting to increase the conversion rate (cracking depth) often accelerates coking, which in turn reduces uptime.
This forces a difficult choice: either operate at a lower efficiency to prolong the run time or push for higher yields and accept the significant cost and downtime of frequent decoking cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right technology requires a clear-eyed evaluation of your specific goals and constraints. The operational profile of a tube furnace makes it an excellent choice for some applications and a poor one for others.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, small-batch processing: The exceptional thermal uniformity and precise process control of a tube furnace make it the ideal choice, especially for thermally sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production with light feedstocks: The continuous operation, high efficiency, and scalability of tube furnace cracking offer a decisive competitive advantage.
- If you must process heavy raw materials: The significant operational costs and downtime associated with coking make a standard tube furnace a challenging option unless you can implement advanced mitigation technologies.
Ultimately, leveraging the full operational power of tube furnace cracking depends on a clear assessment of your specific raw materials and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Operational Benefit | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Thermal Precision | Unmatched uniformity, fine temperature adjustments, stable heating |
| High Efficiency | Low power consumption, heat recovery, reduced operating costs |
| Continuous Operation | Mature technology, easy control, steady workflow, high throughput |
| Adaptability | Controlled atmosphere/vacuum, scalable for various applications |
| Limitations | Coking with heavy feedstocks, requires decoking, affects uptime |
Ready to optimize your laboratory processes with advanced tube furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on high-purity small-batch processing or large-scale production, we can help you achieve superior efficiency and precision. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















