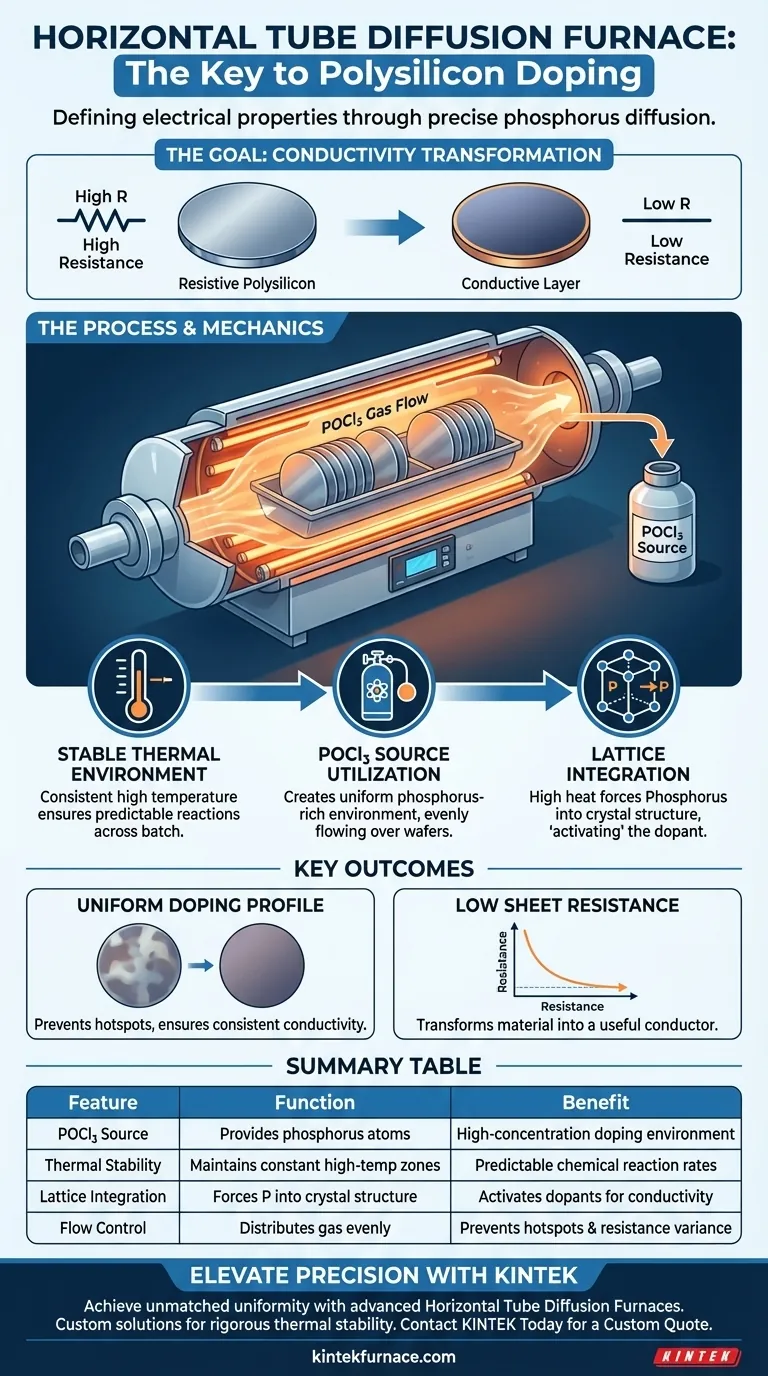
A Horizontal Tube Diffusion Furnace is the critical instrument used to define the electrical properties of polysilicon layers. It utilizes a Phosphorus Oxychloride (POCl3) source to drive phosphorus atoms into the material. By maintaining a highly stable high-temperature environment, the furnace ensures these atoms integrate uniformly into the polysilicon crystal lattice to create a conductive layer.
The primary purpose of this furnace is to facilitate the uniform diffusion of phosphorus atoms into the polysilicon structure, ensuring the active doping profile necessary for low sheet resistance.

The Mechanics of Diffusion Doping
Creating a Stable Thermal Environment
The doping process relies heavily on thermal energy. The Horizontal Tube Diffusion Furnace provides a consistent, high-temperature environment.
This stability is non-negotiable. It allows the chemical reaction to proceed at a predictable rate across the entire batch of wafers.
Utilizing POCl3 as a Source
The process specifically employs Phosphorus Oxychloride (POCl3) as the doping agent.
Inside the heated tube, the POCl3 creates an environment rich in phosphorus. The furnace's design ensures this gas flows evenly over the deposited polysilicon layers.
Achieving Electrical Performance
Lattice Integration
Mere exposure to phosphorus is not enough; the atoms must become part of the material structure.
The high heat forces phosphorus atoms to migrate and integrate into the polysilicon crystal lattice. This structural integration is what "activates" the dopant.
Uniformity of the Doping Profile
For a semiconductor to function correctly, conductivity must be consistent.
The furnace ensures that the phosphorus diffusion is uniform throughout the layer. This prevents hot spots or areas of high resistance that could cause device failure.
Lowering Sheet Resistance
The ultimate goal of this process is to alter the electrical resistance of the material.
By achieving an active doping profile through heat and proper integration, the process results in low sheet resistance. This transforms the polysilicon from a resistive material into a useful conductor.
Operational Considerations and Trade-offs
The Necessity of High Temperatures
Achieving lattice integration requires significant thermal energy.
While effective, this high-temperature requirement dictates a strict "thermal budget" for the manufacturing process to avoid damaging other structures on the wafer.
Dependency on Stability
The process is highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
Any instability in the furnace's heat profile can lead to uneven doping. This results in variable sheet resistance, rendering the polysilicon layer inconsistent and potentially unusable.
Optimizing the Doping Process
To ensure the best results when doping polysilicon layers, consider your specific performance targets.
- If your primary focus is Conductivity: Prioritize the furnace's temperature stability to ensure maximum phosphorus activation and the lowest possible sheet resistance.
- If your primary focus is Consistency: Ensure the POCl3 flow and temperature zones are perfectly calibrated to achieve a uniform active doping profile across the crystal lattice.
The Horizontal Tube Diffusion Furnace remains the standard for converting raw polysilicon into a highly conductive, functional component.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Polysilicon Doping | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| POCl3 Source | Provides phosphorus atoms for diffusion | Creates high-concentration doping environment |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains constant high-temperature zones | Ensures predictable chemical reaction rates |
| Lattice Integration | Forces phosphorus into crystal structure | Activates dopants for electrical conductivity |
| Flow Control | Distributes gas evenly across wafer batch | Prevents localized hotspots and resistance variance |
Elevate Your Semiconductor Precision with KINTEK
Ready to achieve unmatched uniformity in your doping profiles? KINTEK’s advanced Horizontal Tube Diffusion Furnaces are engineered for the rigorous thermal stability required for POCl3 diffusion and polysilicon activation.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory or production needs. Don't let temperature fluctuations compromise your sheet resistance—trust the experts in high-temperature lab solutions.
Contact KINTEK Today for a Custom Quote
Visual Guide
References
- Pradeep Padhamnath, Armin G. Aberle. Investigation of Contact Properties and Device Performance for Bifacial Double-Side Textured Silicon Solar Cells With Polysilicon Based Passivating Contacts. DOI: 10.52825/siliconpv.v2i.1295
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of using a vacuum tube furnace for S53P4-NO2 glass? Achieve 100% Amorphous Results
- What are the main characteristics of vertical tube furnaces? Optimize Your Lab with Space-Saving, Uniform Heating
- What are the limitations of tube furnaces when handling larger samples? Overcome Size and Heat Transfer Challenges
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in the carbonization of nitrogen-doped carbon? Optimize Your Material Synthesis
- Why are drop tube furnaces essential tools in high-temperature processes? Unlock Precision in Combustion and Material Research
- What role do tube plugs and thermal fixtures play in vertical tube furnaces? Enhance Temperature Control and Versatility
- What role does a Tube Furnace play in the solution treatment of titanium alloys? Master Material Integrity.
- What is the three-step heating process in graphite furnace atomization? Master Precise Trace Metal Analysis



















