At their core, drop tube furnaces are essential because they uniquely combine extremely high temperatures with precise control over the processing atmosphere and heating duration. This design allows researchers and engineers to accurately simulate and study rapid, high-temperature industrial processes—like combustion or gasification—on a small, manageable scale.
The true value of a drop tube furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its power to isolate and control every critical variable. It transforms complex, large-scale industrial phenomena into a repeatable and observable laboratory experiment.

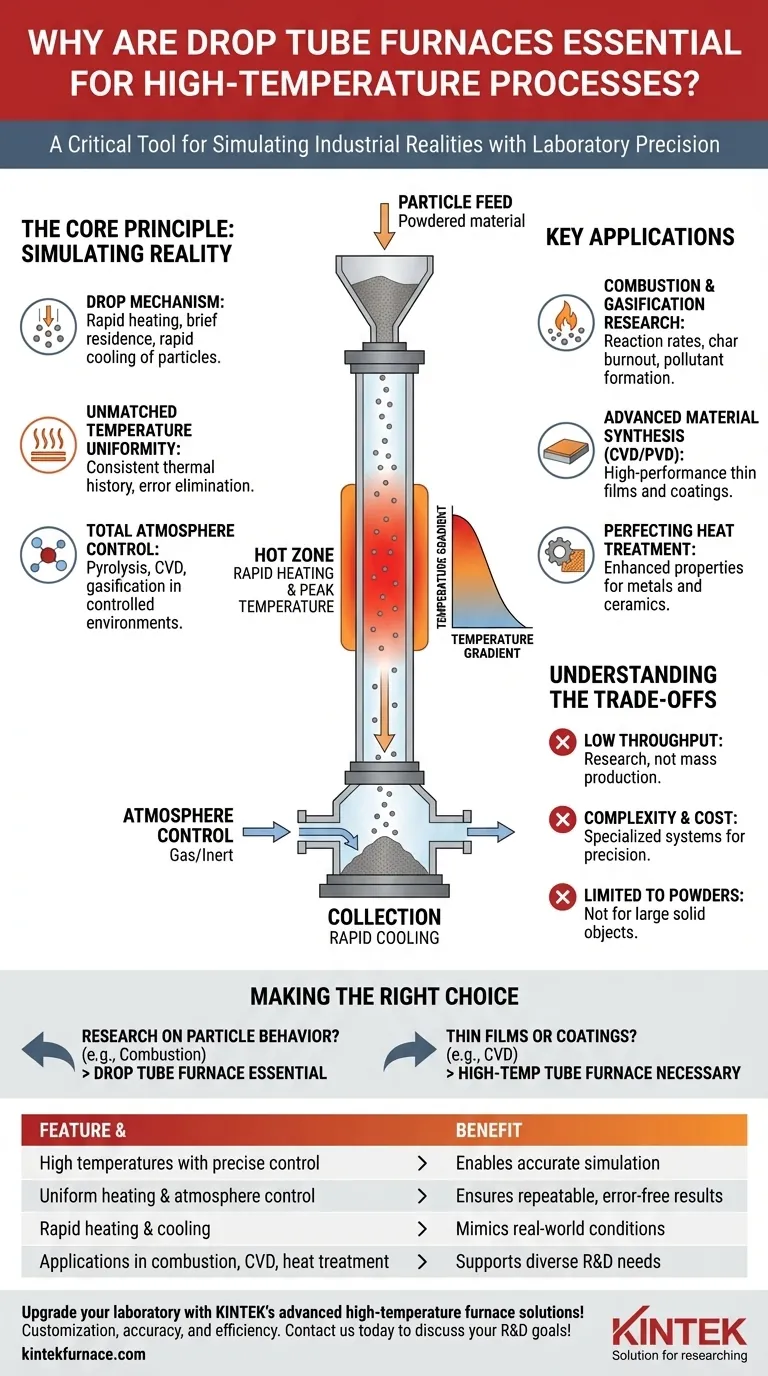
The Core Principle: Simulating Reality with Precision
A drop tube furnace’s design is deceptively simple, but it is this simplicity that provides its power. It is fundamentally a vertical tube heated to a specific temperature profile.
The "Drop" Mechanism
The key to its function is the "drop." Small particles of a material—such as coal, biomass, or a powdered chemical—are dropped into the top of the heated tube.
As they fall, the particles experience extremely rapid heating, a brief residence time at a peak temperature, and then rapid cooling as they exit the hot zone and are collected. This perfectly mimics the conditions particles face in large industrial combustors, gasifiers, or reactors.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The long, heated tubular chamber, known as the "hot zone," is engineered to provide an exceptionally uniform and stable temperature.
This uniformity is critical. It ensures that every particle passing through the furnace experiences the exact same thermal history, eliminating temperature variation as a source of error and leading to highly consistent and repeatable results.
Total Atmosphere Control
Because the process occurs within a sealed tube, operators have complete control over the gaseous environment.
This allows for processes that are impossible in open air. Researchers can conduct pyrolysis in an inert (oxygen-free) atmosphere, study gasification with controlled levels of steam and oxygen, or perform Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) in a high-vacuum environment to create advanced coatings.
Key Applications Driven by Furnace Capabilities
The unique combination of rapid heating and environmental control makes drop tube furnaces indispensable for several advanced applications.
Advancing Combustion and Gasification Research
Drop tube furnaces are the gold standard for studying how solid fuels behave. By analyzing the particles before and after their drop, researchers can determine reaction rates, char burnout efficiency, and pollutant formation under precisely controlled conditions.
Enabling Advanced Material Synthesis
Processes like CVD and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) are used to create high-performance thin films and coatings. These processes require a high-temperature, oxygen-free environment to deposit functional layers onto a substrate, a task for which a high-temperature tube furnace is perfectly suited.
Perfecting Heat Treatment
The precise temperature and atmospheric control offered by tube furnaces are vital for enhancing the properties of materials like metals and ceramics. These treatments can improve hardness, durability, and other critical characteristics with a high degree of reliability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the drop tube furnace is a specialized tool with specific limitations. Understanding them is key to its proper application.
Throughput is for Research, Not Production
The design is inherently low-throughput. It is intended for studying small batches of material with high precision, not for large-scale industrial manufacturing. Its value is in generating data and optimizing processes, not in mass production.
Higher Complexity and Cost
The systems required for precise temperature profiling, gas handling, and particle feeding make these furnaces more complex and expensive than simpler box or batch furnaces. They are sophisticated scientific instruments.
Limited to Powders and Small Particles
The "drop" mechanism is only effective for materials that can be processed as a powder or a stream of fine particles. It is not suitable for heat-treating large, solid objects or components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding if a drop tube furnace is the right tool depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is research on particle behavior (e.g., combustion, pyrolysis): The drop tube furnace is the essential tool for simulating industrial reactor conditions with laboratory-level precision.
- If your primary focus is developing thin films or coatings (e.g., CVD): A high-temperature tube furnace (often in a horizontal configuration) is necessary for its absolute atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is bulk heat treatment of components: A simpler and larger-capacity batch or box furnace will be a more practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, the drop tube furnace serves as a critical bridge, connecting theoretical understanding with real-world industrial performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High temperatures with precise control | Enables accurate simulation of industrial processes |
| Uniform heating and atmosphere control | Ensures repeatable, error-free results |
| Rapid heating and cooling | Mimics real-world conditions for particle studies |
| Applications in combustion, CVD, and heat treatment | Supports diverse research and development needs |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide drop tube furnaces and other systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in combustion, material synthesis, and more. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature research and development goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















