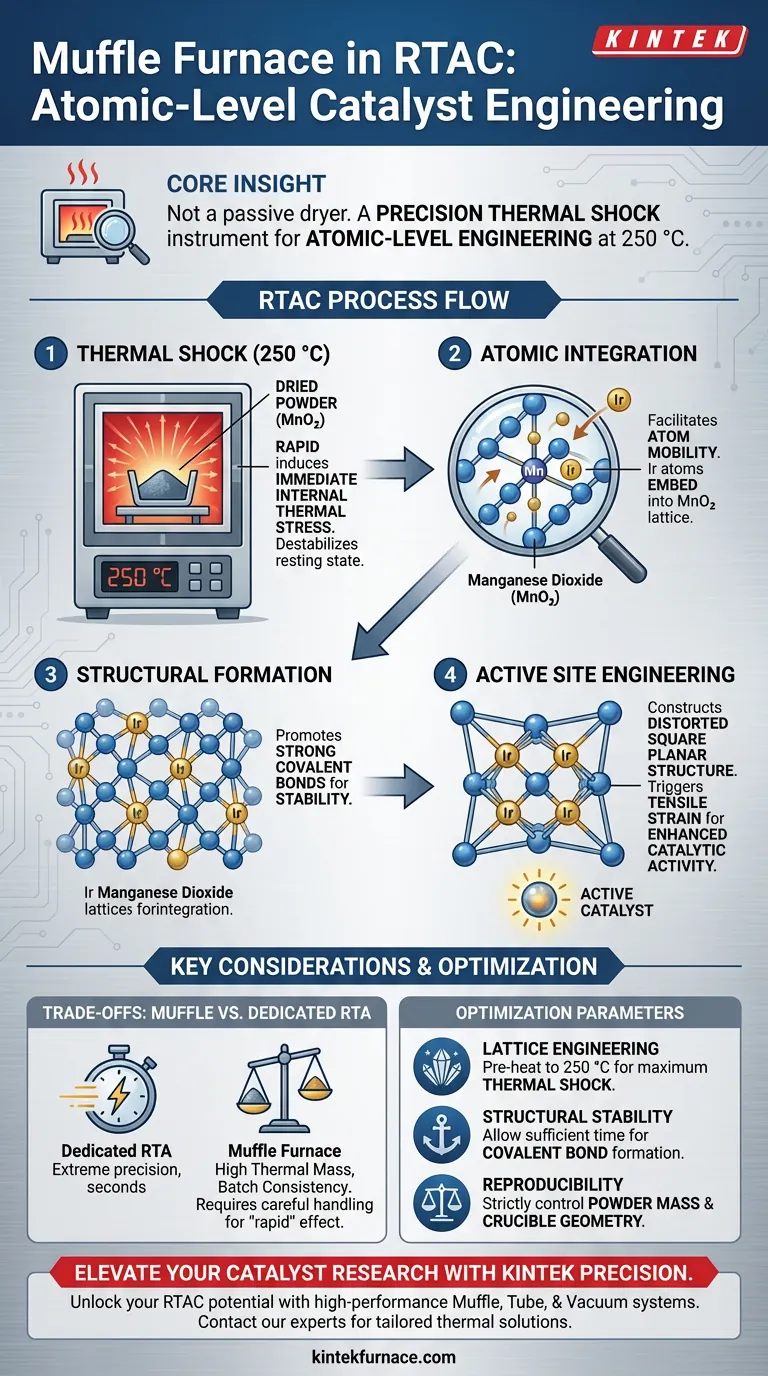
In the context of the Rapid Thermal Annealing-Cooling (RTAC) strategy, a muffle furnace functions as a precise thermal shock instrument rather than a passive drying oven. It is specifically utilized to rapidly heat dried powder to 250 °C, a critical temperature threshold that induces immediate internal thermal stress within the material.
Core Insight: The muffle furnace in this strategy is not just removing moisture; it is performing atomic-level engineering. By subjecting the material to a specific high-temperature shock, it forces the integration of active atoms into the support lattice, creating the physical strain necessary for enhanced catalytic activity.

The Mechanism of Atomic Integration
Inducing Thermal Stress
The primary function of the muffle furnace in this strategy is to generate controlled internal thermal stress.
By rapidly elevating the temperature of the dried powder to 250 °C, the furnace creates a thermodynamic environment that destabilizes the material's resting state. This stress is the catalyst for physical and chemical transformation.
Embedding Active Atoms
The thermal energy provided by the furnace facilitates the mobility of atoms.
Specifically, this process drives the embedding of iridium atoms into the lattice of manganese dioxide. This is not merely a surface coating; it is an integration of the active metal into the crystal structure of the support material.
Constructing the Active Site Architecture
Forming Covalent Bonds
The heat treatment within the muffle furnace moves beyond simple physical deposition to facilitate chemical bonding.
The high-temperature environment promotes the formation of strong covalent bonds between the embedded iridium and the manganese dioxide lattice. This bonding is essential for the long-term stability and durability of the catalyst.
Creating Tensile Strain
The ultimate goal of using the muffle furnace in this manner is to engineer a specific geometric distortion.
The annealing process constructs a distorted square planar structure. This specific architectural change triggers tensile strain at the active sites, which is the key factor that enhances the catalyst's performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Equipment Capability vs. Process Requirements
While this specific RTAC strategy utilizes a muffle furnace, it is important to distinguish this from standard Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA) systems.
Dedicated RTA systems (often laser or lamp-based) offer heating rates measured in seconds and extreme precision. A muffle furnace relies on high thermal mass and pre-heating to achieve "rapid" effects, which may offer less precise control over second-by-second temperature ramp rates compared to specialized RTA hardware.
Batch Consistency
The muffle furnace excels in thermal field stability, ensuring that the entire batch reaches the 250 °C target uniformly.
However, achieving the "rapid" heating effect requires careful handling. If the sample mass is too large, the heat transfer may be too slow to induce the necessary thermal stress, resulting in a standard calcination effect rather than the desired lattice distortion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To effectively utilize a muffle furnace for the RTAC strategy, consider the following parameters:
- If your primary focus is Lattice Engineering: Ensure the furnace is pre-heated to 250 °C before introducing the sample to maximize the thermal shock effect.
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Allow sufficient time at temperature to ensure the covalent bonds between the iridium and manganese dioxide are fully established.
- If your primary focus is Reproducibility: strictly control the mass of the powder and the geometry of the crucible to ensure the heating rate remains consistent across different batches.
Success in this strategy relies on viewing the muffle furnace not as a heater, but as a tool for inducing precise atomic stress.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Function of Muffle Furnace | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock | Rapid heating of dried powder to 250 °C | Induction of internal thermal stress |
| Atomic Integration | Facilitating mobility of active atoms | Embedding iridium into manganese dioxide lattice |
| Structural Formation | Promoting high-temperature chemical bonding | Creation of stable covalent bonds |
| Active Site Engineering | Inducing geometric distortion | Distorted square planar structure with tensile strain |
Elevate Your Catalyst Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock the full potential of your RTAC strategy with KINTEK’s high-performance muffle furnaces. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide the thermal precision required to induce the exact lattice strain your advanced materials demand. Whether you need standard Muffle, Tube, or Vacuum systems, or a customizable high-temp furnace tailored to your unique research parameters, KINTEK delivers the thermal stability and reliability essential for atomic-level engineering.
Ready to optimize your active site architecture? Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Hui Su, Qinghua Liu. Tensile straining of iridium sites in manganese oxides for proton-exchange membrane water electrolysers. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44483-6
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace required for determining the ash content of activated carbon? Purity Guide
- What are common high-temperature applications of muffle furnaces in laboratories? Unlock Precision in Material Testing and Synthesis
- What safety features should a muffle furnace have? Essential Protections for Your Lab's Safety
- What role does a high-temperature muffle furnace play in the pre-calcination of PZT ceramics? Essential Synthesis Guide
- Why is wearing appropriate clothing important when operating a benchtop furnace? Essential Safety Tips to Prevent Burns and Fires
- What role does a muffle furnace play in SCS of catalysts? Optimize Thermal Initiation for Manganese-Nickel Synthesis
- What is the necessity of the annealing process using a muffle furnace for ZnCo2O4? Boost Phase Purity and Conductivity
- Why is an industrial muffle furnace required to process sugar beet samples at 550 °C for crude ash determination?



















