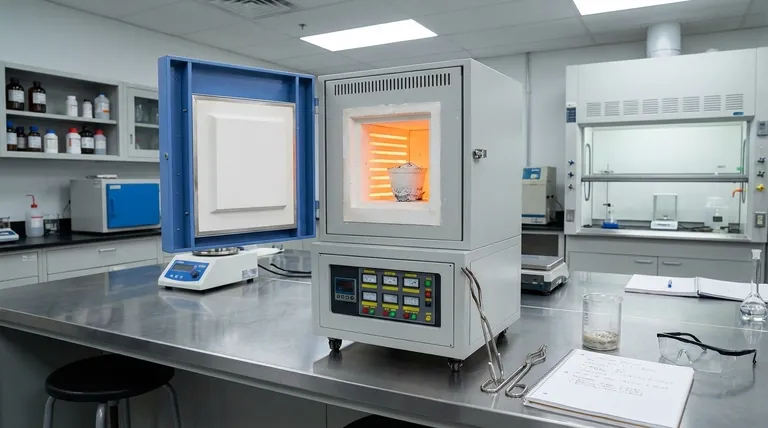
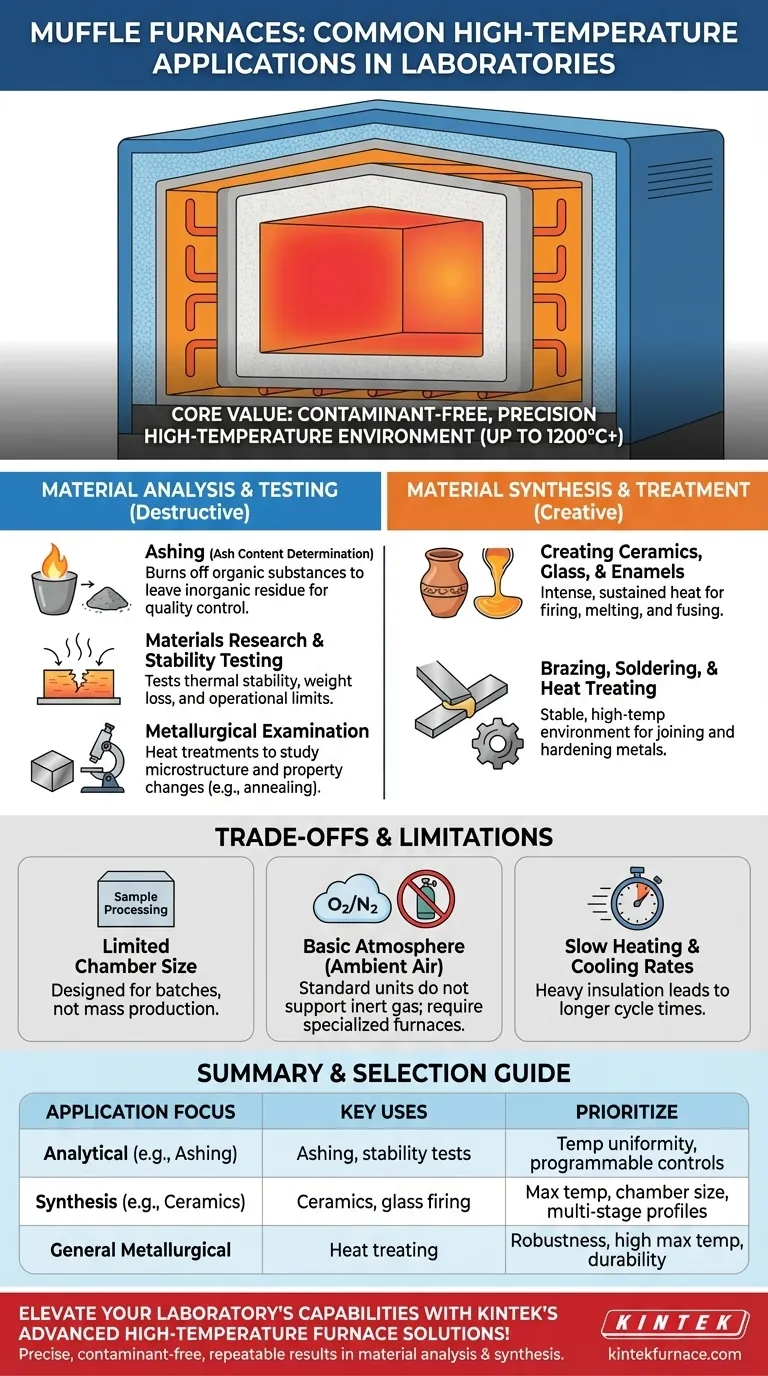
In a laboratory setting, a muffle furnace is primarily used for two categories of high-temperature work: analytical testing that breaks down materials, and synthetic processes that create or alter them. Common applications include determining the ash content of a sample (ashing), testing how materials withstand extreme heat, creating technical ceramics, and heat-treating metals.
A muffle furnace's core value is its ability to heat samples in a chamber that is isolated from direct contact with the heating elements. This provides a contaminant-free, precisely controlled high-temperature environment essential for obtaining repeatable and accurate results in both materials testing and synthesis.

What Defines a Muffle Furnace?
Before diving into applications, it's crucial to understand what makes this device unique. Its primary advantage lies in its construction.
The "Muffle" Principle
A muffle furnace contains an insulated outer cabinet and an inner refractory chamber, known as the "muffle."
The heating elements heat the muffle from the outside. This design isolates the material being processed from any harmful byproducts of fuel or electric heating, ensuring a clean environment.
Precision High-Temperature Control
These furnaces are engineered to reach and maintain very high temperatures—often up to 1200°C (2192°F) or higher—with a high degree of accuracy. This control is critical for scientific procedures that depend on specific temperature profiles.
Core Application: Material Analysis and Testing
A primary function of a muffle furnace is to subject materials to extreme heat to analyze their properties. This is a form of destructive testing that reveals a material's composition or performance limits.
Determining Ash Content (Ashing)
Ashing is one of the most common applications. It involves heating a sample to a high temperature to burn off all organic substances, leaving only the inorganic residue, or "ash."
This is vital for quality control in industries like food science, polymer manufacturing, and environmental testing (e.g., water quality analysis) to determine the percentage of non-combustible material.
Materials Research and Stability Testing
Muffle furnaces are used to test the thermal stability of materials like polymers, plastics, and composites.
By exposing a material to a specific temperature for a set duration, researchers can observe its degradation, measure weight loss, and determine its operational limits before failure.
Metallurgical Examination
In metallurgy, furnaces are used to perform heat treatments on small metal samples. This allows analysts to study how processes like annealing or tempering affect a metal's microstructure and physical properties.
Core Application: Material Synthesis and Treatment
The other major use for a muffle furnace is to use heat to create new materials or modify existing ones. The controlled environment is key to achieving the desired outcome.
Creating Ceramics, Glass, and Enamels
The furnace provides the intense, sustained heat needed for firing technical ceramics, melting glass, or fusing enamel coatings onto metal.
The precise temperature control allows for complex heating and cooling cycles, which are essential for developing the desired hardness, durability, and finish in these materials.
Brazing, Soldering, and Heat Treating
The furnace provides a stable, high-temperature environment for joining metal components through brazing or soldering.
It is also used for a variety of heat treatments that alter the properties of metals, such as hardening steel parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, muffle furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Limited Chamber Size
Laboratory muffle furnaces are designed for sample processing, not mass production. Their chamber sizes are relatively small, making them suitable for batch work or one-off tests.
Basic Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace isolates the sample from combustion byproducts but operates in an ambient air atmosphere. For processes that require an inert or reactive gas environment (like argon or nitrogen), a more specialized furnace with atmosphere control is necessary.
Heating and Cooling Rates
The heavy insulation required to reach high temperatures means that muffle furnaces often heat up and cool down slowly. This must be factored into the total processing time for any procedure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the right tool, you must match its capabilities to your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical testing (e.g., ashing): Prioritize a furnace with certified temperature uniformity and programmable controls to ensure compliance with standardized test methods (like ASTM).
- If your primary focus is materials synthesis (e.g., ceramics): Focus on the maximum achievable temperature, chamber dimensions, and the ability to program multi-stage heating and cooling profiles.
- If your primary focus is general metallurgical work: A robust furnace with a high maximum temperature and good durability will serve you well for various heat-treating tasks.
By understanding these distinct applications, you can effectively leverage a muffle furnace for precise and repeatable high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Key Uses | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Material Analysis | Ashing, thermal stability testing, metallurgical examination | Up to 1200°C or higher |
| Material Synthesis | Ceramics, glass firing, brazing, heat treating | Up to 1200°C or higher |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with precision tools like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for contaminant-free, repeatable results in material analysis and synthesis. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















