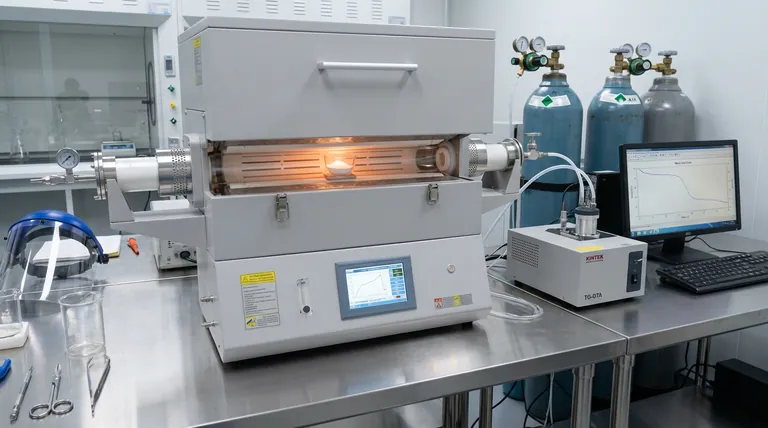
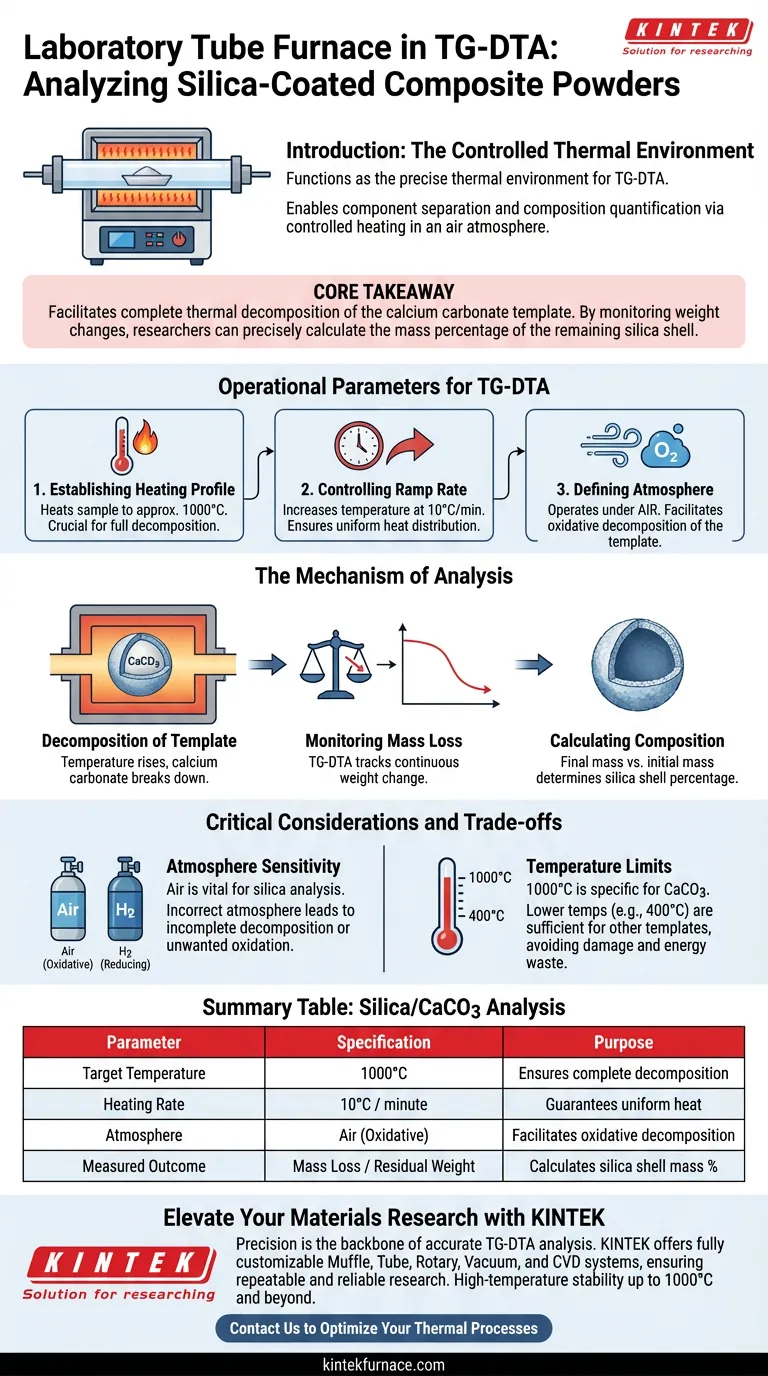
A laboratory tube furnace functions as the controlled thermal environment essential for performing thermogravimetric-differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA) on silica-coated composite powders. By subjecting the material to a precise heating regimen in an air atmosphere, the furnace enables the separation of the composite's components through thermal decomposition, allowing researchers to quantify the material's composition.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace allows for the precise calculation of the silica shell's mass percentage by facilitating the complete thermal decomposition of the inner calcium carbonate template. By monitoring the weight change before and after this process, researchers can isolate the mass of the remaining silica structure.

Operational Parameters for TG-DTA
Establishing the Heating Profile
To analyze silica-coated powders effectively, the tube furnace must adhere to a strict temperature ramp. The standard protocol involves heating the sample to approximately 1000°C.
Controlling the Ramp Rate
Precision is key to accurate DTA results. The furnace is programmed to increase temperature at a controlled rate, typically 10°C per minute. This gradual increase ensures uniform heat distribution and accurate recording of thermal events.
Defining the Atmosphere
For this specific analysis, the furnace operates under an air atmosphere. Unlike reduction processes that require hydrogen, the air environment is necessary to facilitate the oxidative decomposition of the template material.
The Mechanism of Analysis
Decomposition of the Template
The primary goal of the thermal cycle is the decomposition of the calcium carbonate template. As the temperature rises within the tube furnace, the calcium carbonate breaks down, leaving the thermally stable silica shell behind.
Monitoring Mass Loss
The TG-DTA setup continuously tracks the weight of the sample throughout the heating process. The furnace's stability allows for the detection of minute mass changes that correspond to the decomposition phases.
Calculating Composition
The final analysis relies on a comparison of mass. By calculating the difference in weight before and after the thermal treatment, researchers determine the mass percentage of the silica shell deposited on the original template.
Critical Considerations and Trade-offs
Atmosphere Sensitivity
It is vital to select the correct atmosphere for the specific chemical goal. While silica analysis requires an air atmosphere to decompose the carbonate, other processes—such as creating metallic copper/carbon nanotube composites—require a switch to a reducing atmosphere (like hydrogen). Using the wrong atmosphere will result in incomplete decomposition or unwanted oxidation.
The Role of Temperature Limits
The 1000°C threshold is specific to decomposing calcium carbonate. If analyzing different composites, such as those using ethyl cellulose templates, a lower temperature (e.g., 400°C) is sufficient. Applying excessive heat unnecessarily can damage the remaining nanostructures or waste energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of your laboratory furnace, align the operational parameters with your specific analytical objectives:
- If your primary focus is quantifying silica shell thickness: Ensure your furnace is set to an air atmosphere with a target temperature of 1000°C to fully decompose the calcium carbonate core.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing metallic composites: You must utilize a furnace capable of atmosphere switching to facilitate reduction (e.g., Hydrogen) rather than simple decomposition.
- If your primary focus is processing low-temp templates (like ethyl cellulose): A standard high-temperature box furnace set to 400°C is sufficient and may be more efficient than a high-spec tube furnace.
Select the thermal profile that strictly matches the chemical stability of your sacrificial template to ensure accurate compositional analysis.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Specification for Silica/CaCO3 Analysis | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Target Temperature | 1000°C | Ensures complete decomposition of calcium carbonate template |
| Heating Rate | 10°C / minute | Guarantees uniform heat distribution for accurate DTA results |
| Atmosphere | Air (Oxidative) | Facilitates the oxidative decomposition of the core material |
| Measured Outcome | Mass Loss / Residual Weight | Calculates the precise mass percentage of the silica shell |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK
Precision is the backbone of accurate TG-DTA analysis. At KINTEK, we understand that whether you are quantifying silica shells or synthesizing metallic composites, your thermal environment must be flawless.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs. From precise atmosphere switching to high-temperature stability up to 1000°C and beyond, our equipment ensures your research is both repeatable and reliable.
Ready to optimize your thermal processes? Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements with our technical specialists and discover how our high-performance lab furnaces can transform your results.
Visual Guide
References
- Hirokazu Katsui, Mikinori Hotta. Preparation of hollow silica particles by template method via chemical vapor deposition. DOI: 10.2109/jcersj2.23114
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes tube furnaces indispensable in academic and industrial settings? Unlock Precision Heating for Advanced Materials
- What is the function of a laboratory tube furnace in BiFeO3 nanopowder production? Master the Calcination Stage
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace in biochar production? Transform Waste Diaper Fibers with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace preferred for NRBBO:Eu2+ synthesis? Achieve Precise Atmosphere Control for Phosphors
- What industries commonly use horizontal furnaces? Unlock High-Temperature Processing for Your Sector
- What problems existed with early tube furnace designs? Discover the Flaws That Hindered Performance
- How does the sealing mechanism in Quartz Tube Furnaces differ from traditional systems? Discover Advanced Sealing for Reliable Results
- What conditions does a tube furnace provide for post-ion-implantation? Achieve Precise Microstructural Repair



















