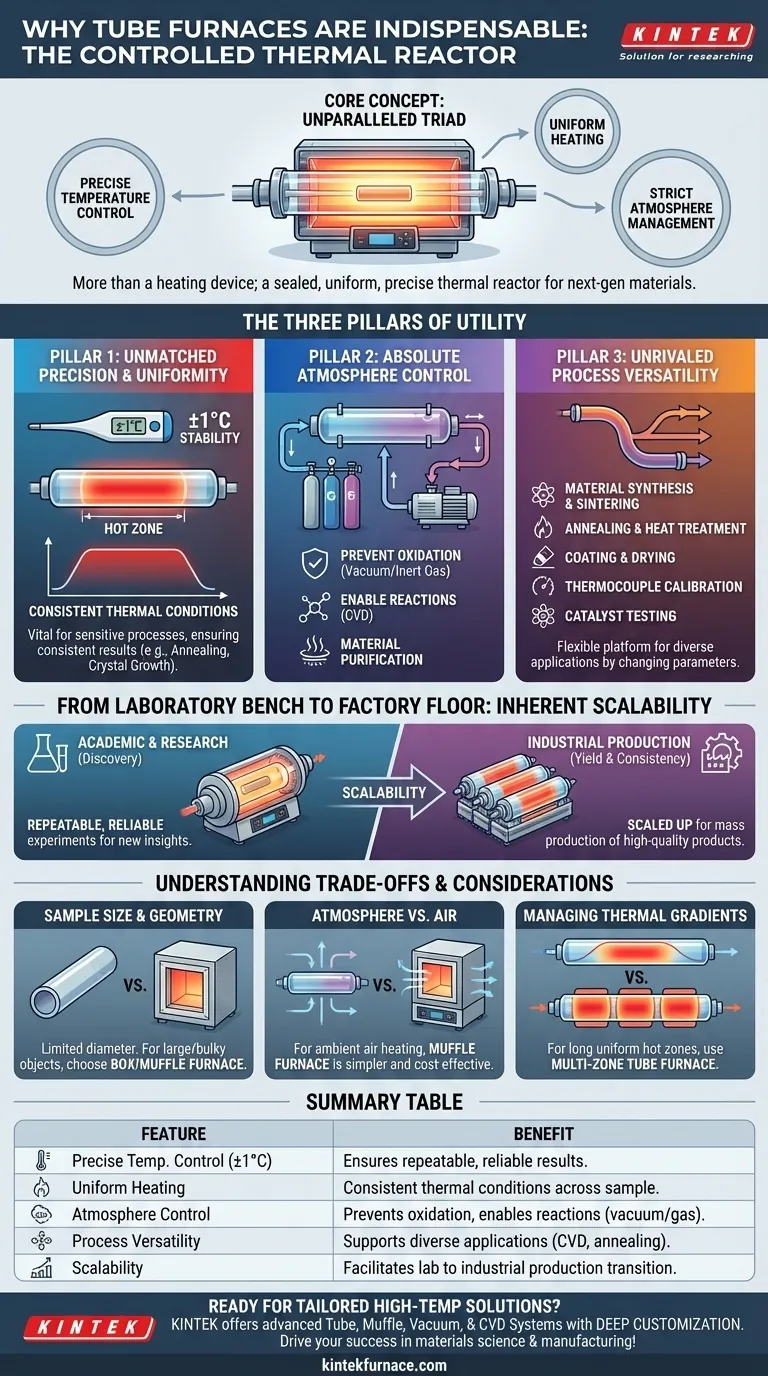
At its core, a tube furnace is indispensable because it offers an unparalleled combination of precise temperature control, uniform heating, and the ability to strictly manage the atmospheric environment around a sample. This unique triad makes it a foundational tool for advanced materials science and high-tech manufacturing, enabling processes that are impossible in a standard oven or muffle furnace.
A tube furnace is more than just a heating device; it is a controlled micro-environment. Its true value lies in providing a sealed, uniform, and precise thermal reactor, which is the fundamental requirement for developing, testing, and producing next-generation materials.

The Three Pillars of Tube Furnace Utility
The indispensability of a tube furnace rests on three core capabilities that work in concert: precise temperature, a controlled atmosphere, and process versatility.
Pillar 1: Unmatched Precision and Uniformity
A key advantage is the ability to achieve and maintain exact temperatures, often with a stability of ±1°C. This precision is vital for processes where even minor thermal deviations can compromise the outcome.
This control is paired with uniform heating along the length of the furnace's central "hot zone." Uniformity ensures that an entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions, which is critical for consistent results in applications like annealing or crystal growth.
Pillar 2: Absolute Atmosphere Control
This is arguably the most significant differentiator for a tube furnace. The tubular chamber can be sealed and connected to gas and vacuum systems, allowing for complete control over the processing atmosphere.
This enables several critical functions:
- Preventing Oxidation: Processing in a vacuum or under an inert gas (like Argon) protects sensitive materials from reacting with oxygen at high temperatures.
- Enabling Reactions: Introducing specific reactive gases is the basis for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a cornerstone of semiconductor manufacturing.
- Material Purification: Certain impurities can be vaporized and removed from a sample by heating it under a vacuum.
Pillar 3: Unrivaled Process Versatility
The combination of precise temperature and atmosphere control makes the tube furnace a flexible platform for a vast range of applications.
By simply changing the temperature profile, gas mixture, or the tube material itself (quartz for lower temperatures, alumina for high temperatures), the same furnace can be used for:
- Material Synthesis and Sintering
- Annealing and Heat Treatment
- Coating and Drying
- Thermocouple Calibration
- Catalyst Testing and Accelerated Aging
From Laboratory Bench to Factory Floor
The principles that make the tube furnace essential for research are the same ones that make it vital for industry, demonstrating its inherent scalability.
In Academic & Research Settings
For researchers, the tube furnace is an instrument of discovery. Its precision and control ensure that experiments are repeatable and reliable. It allows for the fundamental exploration of material properties under tightly controlled conditions, forming the basis for new scientific insights and technological breakthroughs.
In Industrial Production
In industry, the focus shifts to yield, consistency, and reliability. Tube furnaces deliver by allowing processes perfected in the lab to be scaled up for mass production.
Whether producing semiconductors, advanced ceramics, or battery components, the furnace's ability to maintain a uniform and stable process environment ensures high yields of consistent, high-quality products. Multiple furnaces can be run in parallel for continuous, large-scale output.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While incredibly powerful, a tube furnace is not the universal solution for all heating needs. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Sample Size and Geometry
The most obvious trade-off is the limited sample size dictated by the tube's diameter. For processing large, bulky, or irregularly shaped objects, a box or muffle furnace is often a more practical choice.
Atmosphere vs. Air: The Muffle Furnace Distinction
If your process simply requires heating a sample in ambient air, a tube furnace may be overly complex. A muffle furnace provides a similar high-temperature, uniform environment but without the sealed tube required for atmosphere control, often at a lower cost and with fewer geometric constraints.
Managing Thermal Gradients
While the central hot zone of a tube furnace is highly uniform, the temperature naturally drops off toward the ends of the tube. For processes requiring a very long and exceptionally uniform hot zone, a multi-zone tube furnace with independent heating elements is necessary to compensate for this effect.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing tool depends entirely on the requirements of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is materials synthesis, purification, or analysis requiring a non-air atmosphere: The precise atmospheric and temperature control of a tube furnace is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is simply heat-treating large parts in ambient air: A muffle or box furnace is likely the more efficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is scaling a specific chemical process from lab to production: The tube furnace's process consistency and scalability make it the ideal platform for reliable manufacturing.
Ultimately, understanding that a tube furnace is a controlled environmental reactor, not just an oven, empowers you to leverage its unique capabilities for success.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Precise Temperature Control (±1°C) | Ensures repeatable and reliable results for sensitive processes |
| Uniform Heating | Provides consistent thermal conditions across the sample for even treatment |
| Atmosphere Control | Allows vacuum or gas environments to prevent oxidation or enable reactions |
| Process Versatility | Supports applications like CVD, annealing, and material synthesis |
| Scalability | Facilitates transition from lab research to industrial production |
Ready to enhance your lab or production line with tailored high-temperature solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace systems like Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your success in materials science and manufacturing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- How do roller kilns and tube furnaces differ in their use of Alumina ceramic tubes? Compare Transport vs. Containment



















