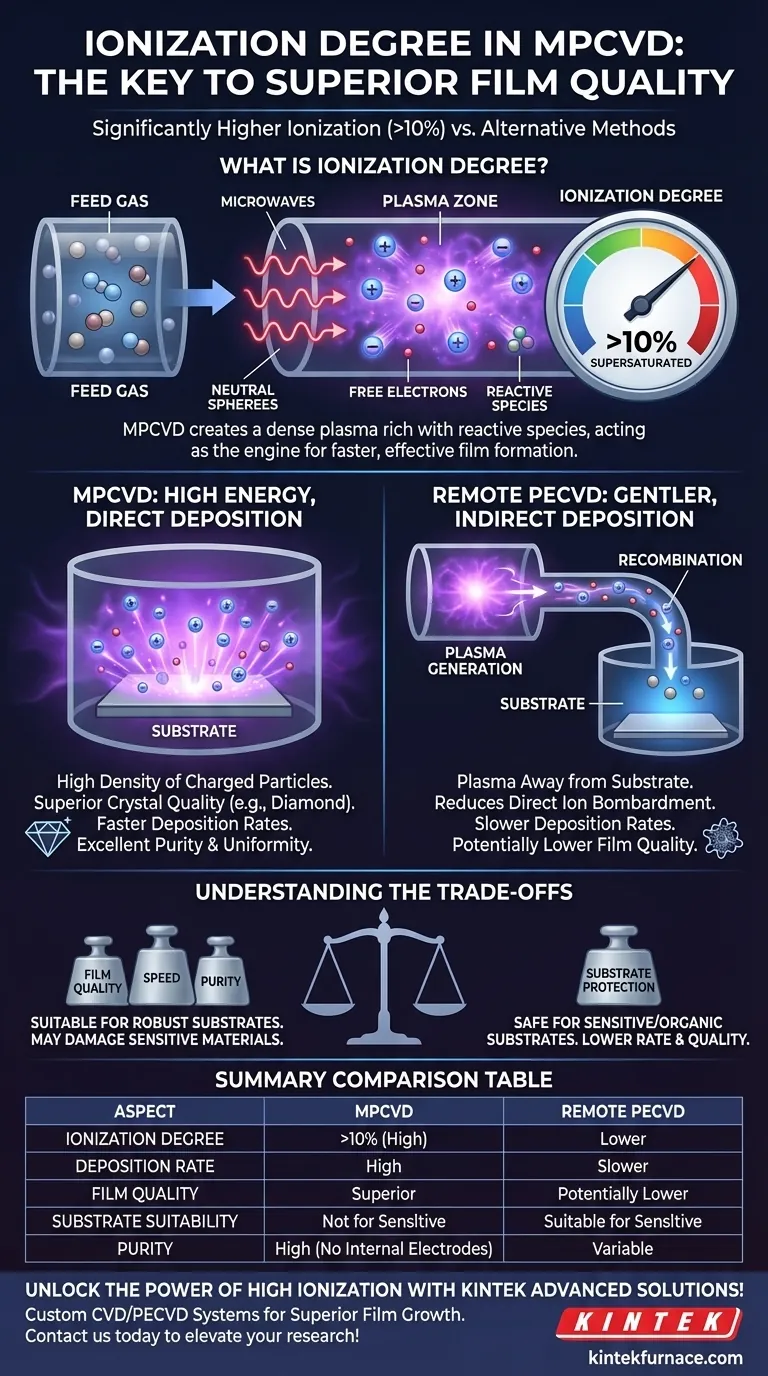
In short, Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD) has a significantly higher ionization degree compared to many alternative methods. The ionization of the feed gas in an MPCVD system can exceed 10%, creating a dense plasma environment rich with reactive species. This high degree of ionization is a primary reason MPCVD achieves superior deposition rates and higher quality films when compared to techniques like remote Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD).
The central decision between MPCVD and alternative methods hinges on a critical trade-off: MPCVD's high ionization degree delivers exceptional film quality and speed, but this high-energy environment can be unsuitable for sensitive substrates.

Why Ionization Degree is a Critical Metric
To understand the practical differences between deposition methods, you must first understand why the degree of ionization is so important. It directly dictates the efficiency and quality of the film growth process.
Defining Ionization in Deposition
Ionization is the process of energizing a gas until its atoms or molecules lose or gain electrons, turning them into charged ions and other reactive species. In MPCVD, microwaves energize the feed gas (e.g., hydrogen and a carbon source) into a highly reactive plasma state.
The Direct Impact of High Ionization
A high ionization degree, such as the 10%+ achievable with MPCVD, means the reaction chamber is filled with a supersaturated concentration of atomic hydrogen and carbon-containing groups. This high density of reactive building blocks is the engine behind MPCVD's performance, enabling faster and more effective film formation on the substrate.
How MPCVD Achieves High Plasma Density
MPCVD uses microwave energy to create a stable, non-polar discharge. This means there are no electrodes or hot filaments inside the chamber that could introduce contaminants. This method efficiently couples energy into the gas, leading to a large area of stable, high-density plasma.
A Direct Comparison: MPCVD vs. Remote PECVD
The contrast between MPCVD and remote PECVD clearly illustrates the impact of ionization degree on process outcomes.
MPCVD: High Energy, High Performance
MPCVD prioritizes creating the most reactive environment possible directly around the substrate. This results in a high density of charged particles that promotes the growth of high-purity, high-quality crystal structures, such as diamond films, with excellent homogeneity over large areas.
Remote PECVD: A Gentler Approach
In remote PECVD, the plasma is generated away from the substrate. The reactive species are then transported to the deposition region, which is kept plasma-free. This separation protects the substrate from direct ion bombardment and damage.
The downside is that many reactive species recombine or lose energy during transport. This results in a lower effective ionization degree at the substrate surface, which can lead to slower deposition rates and potentially lower film quality compared to MPCVD.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition technology is never about finding a single "best" method, but rather the one best suited for your specific requirements. MPCVD's advantages come with clear trade-offs.
Substrate Sensitivity
The primary drawback of MPCVD's high-energy plasma is its potential to damage sensitive substrates. The intense microwave and plasma environment is unsuitable for materials like certain polymers or delicate organic electronics that cannot withstand the energy exposure.
System Complexity and Cost
MPCVD systems are generally more complex and represent a higher initial investment compared to some other CVD setups. However, for applications demanding the highest purity and crystal quality, this cost is often justified by the consistent, high-quality results.
Purity and Control
The elimination of internal electrodes or filaments gives MPCVD a significant advantage in purity. Combined with stable temperature control and gas flow, it allows for exceptionally precise control over film thickness, purity, and crystal quality, which is harder to achieve in other systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of deposition method should be driven by a clear understanding of your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum film quality and deposition rate: MPCVD is the superior choice, as its high ionization degree provides the ideal conditions for growing dense, high-purity crystalline films.
- If your primary focus is depositing on sensitive or organic substrates: Remote PECVD is the safer option, as it protects the substrate from direct plasma damage, albeit at the cost of deposition speed and ultimate film quality.
- If your primary focus is large-area uniformity and purity: MPCVD offers excellent control and a stable, large-volume plasma, making it ideal for producing consistent films over a wide area without contamination.
Ultimately, understanding the role of ionization empowers you to select the deposition technique that best aligns with your material, substrate, and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | MPCVD | Remote PECVD |
|---|---|---|
| Ionization Degree | >10% | Lower |
| Deposition Rate | High | Slower |
| Film Quality | Superior | Potentially lower |
| Substrate Suitability | Not for sensitive materials | Suitable for sensitive substrates |
| System Complexity | Higher | Lower |
| Purity | High due to no internal electrodes | Variable |
Unlock the Power of High Ionization with KINTEK's Advanced Solutions!
Are you aiming for superior film quality, faster deposition rates, and high-purity results in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, ensuring optimal performance for applications like MPCVD.
Don't let substrate sensitivity or system complexity hold you back—let us help you achieve your goals with reliable, high-performance equipment. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can elevate your research and production processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the two main methods of synthetic diamond production? Discover HPHT vs. CVD for Lab-Grown Gems
- Can the reducing atmosphere be replaced with other gaseous mediums? Explore Advanced Surface Engineering Solutions
- What advantages do MPCVD diamond tools offer in industrial applications? Maximize Lifespan & Efficiency
- What is Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD)? Unlock Ultra-Pure Diamond Synthesis
- What are the key features of MPCVD single crystal diamond deposition equipment? Precision Control for High-Quality Growth



















