The Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) serves as a critical decarbonization tool by fundamentally shifting steel production from extraction to recycling. By utilizing steel scrap as its primary raw material, the EAF significantly lowers carbon emission intensity compared to the traditional blast furnace-converter route, enabling immediate reductions in industrial $CO_2$ output.
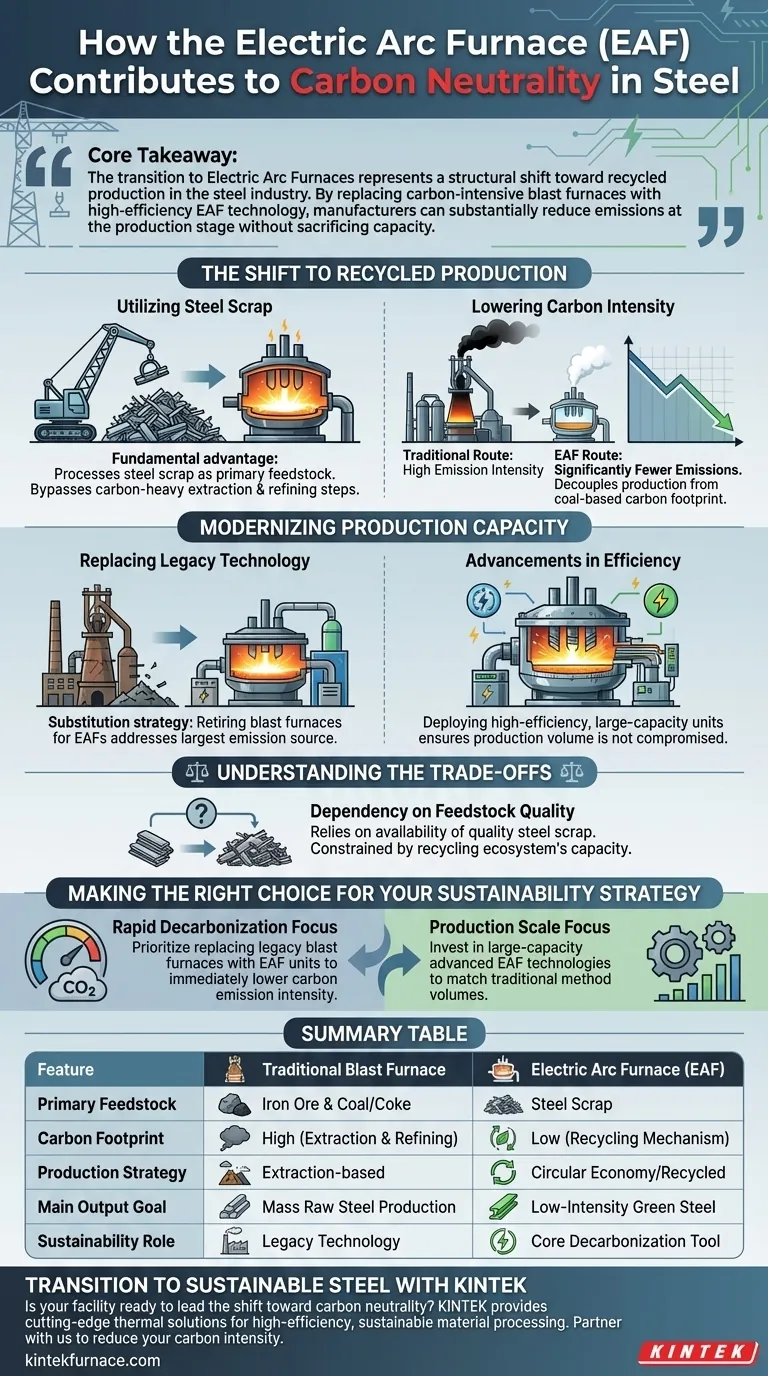
Core Takeaway The transition to Electric Arc Furnaces represents a structural shift toward recycled production in the steel industry. By replacing carbon-intensive blast furnaces with high-efficiency EAF technology, manufacturers can substantially reduce emissions at the production stage without sacrificing capacity.

The Shift to Recycled Production
Utilizing Steel Scrap
The fundamental advantage of the EAF is its ability to process steel scrap as the primary feedstock.
Unlike traditional methods that rely on processing raw iron ore, the EAF functions as a recycling mechanism. This approach bypasses the carbon-heavy extraction and refining steps required in the conventional steelmaking cycle.
Lowering Carbon Intensity
This reliance on recycled material results in a dramatic reduction in carbon emission intensity.
When compared to the traditional blast furnace-converter route, the EAF process generates significantly fewer emissions per unit of steel produced. It effectively decouples steel production from the immense carbon footprint associated with coal-based iron reduction.
Modernizing Production Capacity
Replacing Legacy Technology
To achieve carbon neutrality, the industry is actively moving to replace existing blast furnace capacity with EAF technology.
This is not merely an addition to existing lines but a substitution strategy. By retiring blast furnaces in favor of EAFs, producers address the largest source of emissions in the steel value chain.
Advancements in Efficiency
Modern strategies involve deploying high-efficiency, large-capacity advanced EAF technologies.
These advancements ensure that the shift to greener steel does not compromise production volume. Large-capacity units allow for the industrial-scale handling of scrap, making the decarbonization of the sector economically and operationally viable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Dependency on Feedstock Quality
While the EAF route reduces emissions, it introduces a reliance on the availability of steel scrap.
Because the process utilizes scrap as the primary raw material, consistent production depends heavily on a steady and quality supply chain of recycled metal. Unlike blast furnaces, which utilize abundant raw iron ore, the EAF model is constrained by the recycling ecosystem's capacity to provide input material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Sustainability Strategy
Adopting EAF technology requires aligning your environmental goals with your operational capabilities.
- If your primary focus is rapid decarbonization: Prioritize replacing legacy blast furnace operations with EAF units to immediately lower your carbon emission intensity.
- If your primary focus is production scale: Invest in large-capacity advanced EAF technologies to ensure your recycled production lines can match the volume of traditional methods.
Transitioning to electric arc furnaces is currently the most effective method for reducing carbon dioxide emissions at the production stage of steel manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Traditional Blast Furnace | Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Feedstock | Iron Ore & Coal/Coke | Steel Scrap |
| Carbon Footprint | High (Extraction & Refining) | Low (Recycling Mechanism) |
| Production Strategy | Extraction-based | Circular Economy/Recycled |
| Main Output Goal | Mass Raw Steel Production | Low-Intensity Green Steel |
| Sustainability Role | Legacy Technology | Core Decarbonization Tool |
Transition to Sustainable Steel with KINTEK
Is your laboratory or production facility ready to lead the shift toward carbon neutrality? KINTEK provides the cutting-edge thermal solutions necessary for high-efficiency, sustainable material processing.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside specialized lab high-temp furnaces. Every unit is fully customizable to meet your unique metallurgical and recycling research needs, ensuring you achieve the highest efficiency in green production.
Partner with us to reduce your carbon intensity. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our advanced furnace technology can empower your sustainability strategy.
Visual Guide
References
- The Technical Society, The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan. Production and Technology of Iron and Steel in Japan during 2024. DOI: 10.2355/isijinternational.65.7app_i
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What pre-treatment procedures are required for a Stainless Steel Reactor? Maximize Metal Hydride Reaction Success
- What is the purpose of preheating low carbon steel molds to 300 °C before the casting of Mg-Zn-xSr alloys?
- How does the aluminum precursor coating process modify high-purity quartz? Enhancing Thermal Stability and Viscosity
- Why is a standard constant temperature and humidity curing box used for magnesium slag mortar? Key Pre-treatment Facts
- What is an industrial oven and which industries use it? Discover Versatile Thermal Processing Solutions
- How does temperature control precision affect c-BAs crystal growth? Ensure Lattice Integrity in Two-Week Cycles
- Why is industrial-grade isostatic pressing necessary for zirconia? Achieve Uniform Density & Structural Integrity
- What is the significance of applying full displacement constraints at fixed entry points? Ensure Thermal Accuracy



















