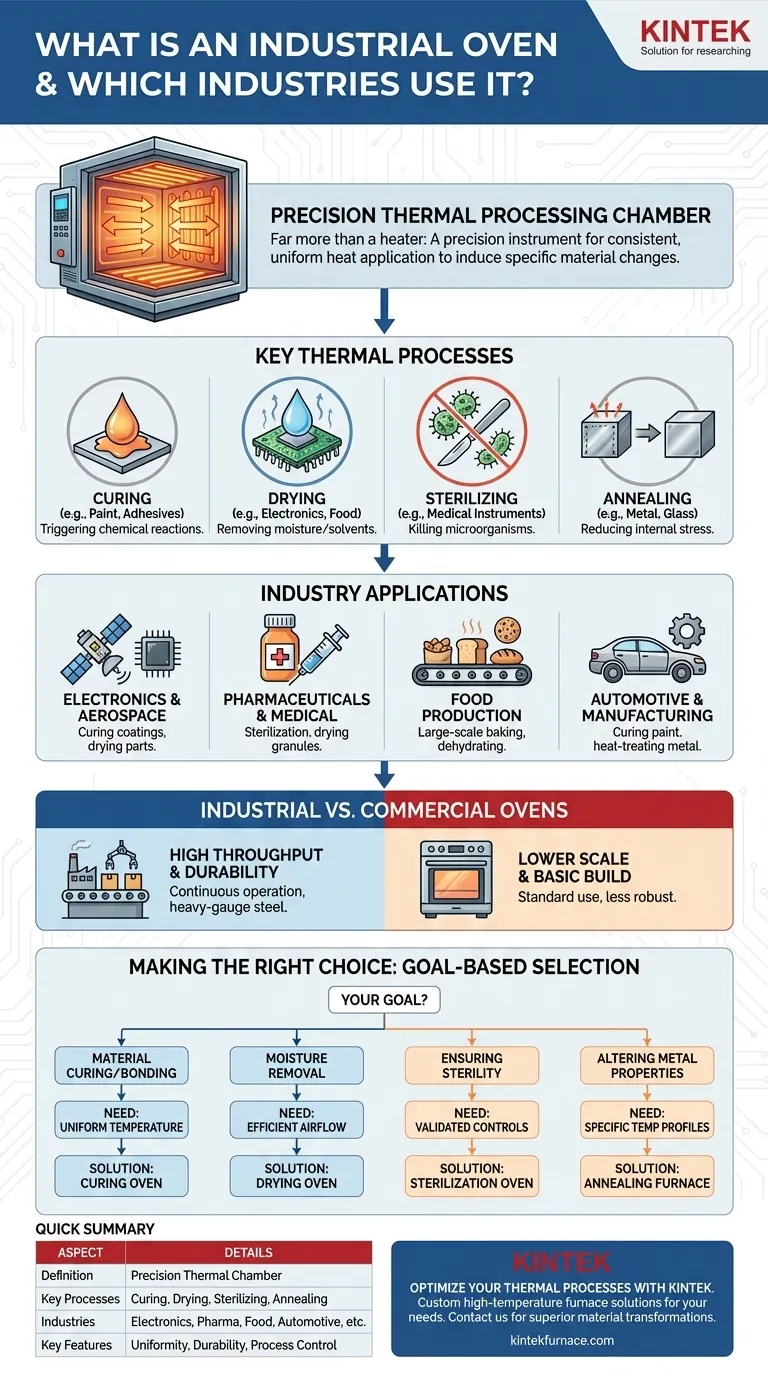
At its core, an industrial oven is a thermally insulated chamber engineered for high-temperature thermal processing. Far more than a simple heating device, it is a piece of precision equipment used across a vast range of sectors, including electronics, pharmaceuticals, food production, and heavy manufacturing, to induce specific chemical and physical changes in materials.
Industrial ovens are not defined by their size, but by their purpose. They are precision instruments designed to execute critical manufacturing processes—such as curing, drying, and sterilizing—where consistent and uniform heat application is essential for product quality, safety, and performance.

The Fundamental Purpose: Beyond Simple Heating
To understand the role of an industrial oven, you must look past the idea of just making something hot. The true function is to manage a controlled thermal process that transforms a material in a predictable and repeatable way.
Precision Temperature Control
The hallmark of an industrial oven is its ability to maintain uniform temperature throughout its chamber. This ensures that every part of a product receives the exact same thermal treatment, which is critical for consistent quality in mass production.
Specific Thermal Processes
These ovens are designed to perform a few key functions with high reliability. The most common processes include:
- Curing: Using heat to trigger a chemical reaction, such as hardening a paint, powder coating, or adhesive.
- Drying: Removing moisture or other solvents from a product, like drying components in electronics or dehydrating foods.
- Sterilizing: Using high heat to kill microorganisms on medical instruments or laboratory equipment.
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling metal or glass to remove internal stresses and improve its ductility.
Material Transformation
Ultimately, the goal is to change a material's properties. An oven might be used to make a coating more durable, a medical device safe for use, or a metal part less brittle. The oven is the tool that enables this essential transformation.
Key Applications Across Industries
While the processes are similar, the applications are highly specific to each industry's needs. The same basic technology is adapted to solve very different problems.
Electronics and Aerospace
In these fields, ovens are used for curing the epoxy, conformal coatings, and adhesives that hold sensitive components together and protect them from the environment. They are also used for drying parts after cleaning to prevent contamination.
Pharmaceuticals and Medical
Sterilization is the primary driver here. Ovens provide the dry heat needed to ensure that surgical instruments and glass vials are free of all contaminants. They are also used for drying granulated materials before they are compressed into tablets.
Food Production
Industrial ovens are essential for large-scale baking, roasting, and dehydrating. Conveyor ovens, for example, allow for a continuous flow of product, ensuring high throughput for items like bread, cookies, and snack foods.
Automotive and Manufacturing
The most visible application is curing paint and powder coatings on vehicle bodies and parts. This process creates the hard, durable, and cosmetically perfect finish required. Ovens are also used for heat-treating metal components to enhance their strength and longevity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Industrial vs. Commercial Ovens
Not all large ovens are "industrial." The distinction lies in their construction, control systems, and intended use case.
Scale and Throughput
Industrial ovens range from small benchtop units for R&D to massive conveyor systems that are integrated directly into an assembly line. They are built for high throughput and continuous or semi-continuous operation.
Durability and Construction
These ovens are built with heavy-gauge steel and high-quality insulation to withstand the rigors of a factory environment, often running 24/7. Their components, from hinges to heating elements, are designed for longevity and reliability.
Process Control
Unlike a simple commercial baking oven, an industrial oven often provides tight control over more than just temperature. Many models can manage airflow, humidity, or even maintain an inert atmosphere (using gases like nitrogen) to prevent oxidation during heating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the application of an industrial oven helps clarify its function in any manufacturing context. The right choice is always tied to the desired outcome of the thermal process.
- If your primary focus is material curing or bonding: You need an oven that guarantees exceptional temperature uniformity to ensure every part of the adhesive or coating reacts correctly.
- If your primary focus is moisture removal: The key feature is efficient airflow management to carry moisture away from the product, making drying or dehydration processes faster.
- If your primary focus is ensuring sterility: You need a high-temperature sterilization oven with validated controls that meet strict regulatory standards for medical or pharmaceutical use.
- If your primary focus is altering metal properties: You are looking for a furnace or annealing oven capable of reaching specific temperature profiles and controlled cooling rates.
Ultimately, selecting or specifying an industrial oven begins with a clear understanding of the specific material transformation your process requires.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Thermally insulated chamber for high-temperature thermal processing |
| Key Processes | Curing, drying, sterilizing, annealing |
| Industries | Electronics, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, medical, food production, automotive, manufacturing |
| Key Features | Precision temperature control, uniform heating, durability, process control (e.g., airflow, atmosphere) |
Ready to optimize your thermal processes with a custom industrial oven? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental and production requirements. Whether you're in electronics, pharmaceuticals, food, or heavy manufacturing, we can help you achieve superior material transformations. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your efficiency and quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How are a muffle furnace and ceramic crucible used for MoO3? Master High-Purity Synthesis Today
- Why is dual heat treatment required for SnO2 nanoparticles? Optimize Oxidation for Superior Performance
- What is a high-temperature vacuum furnace and where is it commonly used? Essential for Purity in Materials Science
- Why is it necessary to dry glassware in a 140 °C oven overnight before GTP? Ensure Precise Anhydrous Polymerization
- How does a box-type high-temperature furnace contribute to 6Mo stainless steel? Optimize Solution Treatment Now



















