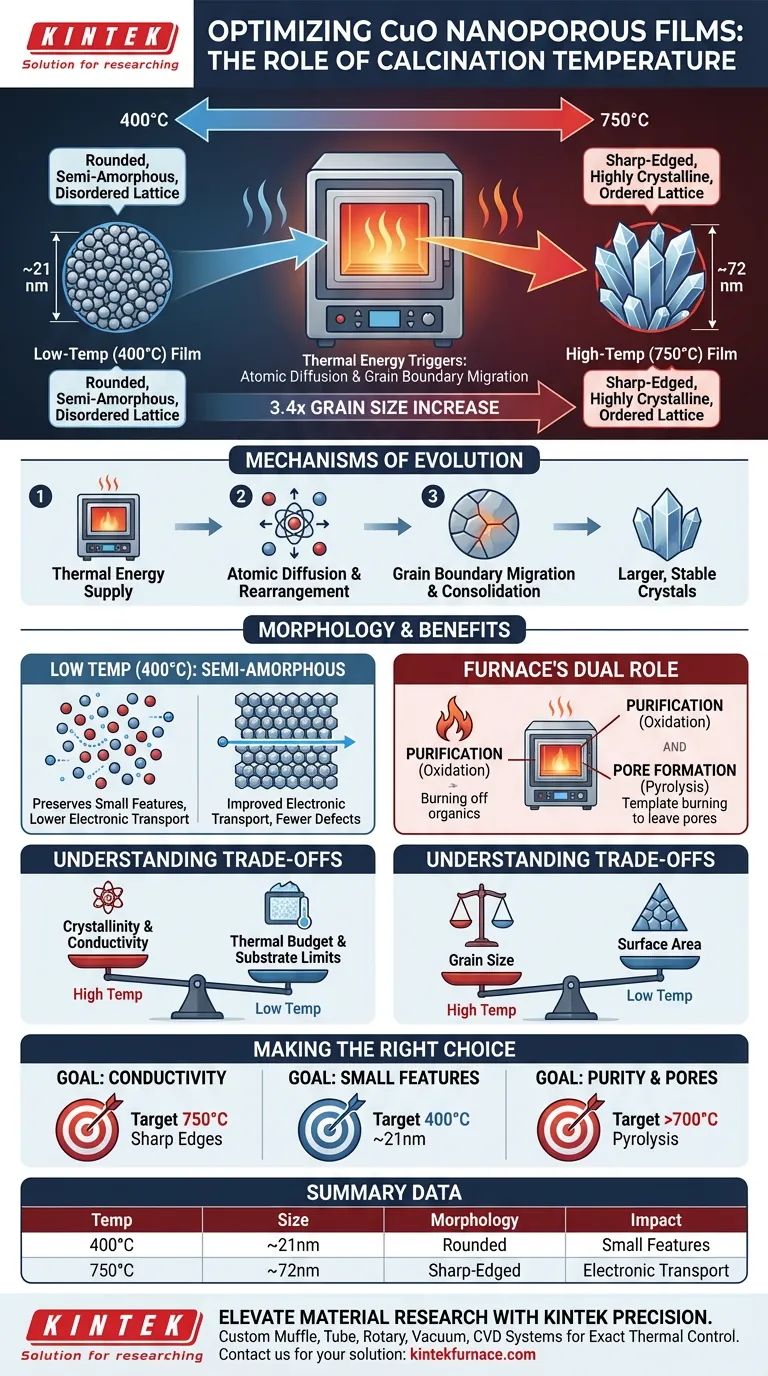
Calcination temperature acts as the primary driver for structural evolution in nanoporous copper oxide (CuO) films, directly dictating the size and quality of the microscopic grains. Specifically, increasing the temperature in a high-temperature muffle furnace from 400°C to 750°C causes the grains to more than triple in size, expanding from approximately 21 nm to 72 nm.
Core Takeaway: Thermal energy triggers atomic diffusion and grain boundary migration, fundamentally altering the material's microstructure. This process converts rounded, semi-amorphous particles into distinct, sharp-edged crystals, significantly enhancing the electronic transport quality of the film.
Mechanisms of Thermal Annealing
Driving Atomic Diffusion
The heat provided by the muffle furnace supplies the kinetic energy necessary for atomic diffusion.
At elevated temperatures, atoms within the copper oxide lattice gain enough energy to move and rearrange themselves. This movement allows the material to seek a lower energy state, which manifests as the growth of larger, more stable crystals.
Grain Boundary Migration
As diffusion accelerates, grain boundary migration occurs.
Smaller grains with higher surface energy merge into larger grains. This consolidation is the physical mechanism behind the observed size increase from roughly 21 nm at 400°C to 72 nm at 750°C.
Evolution of Crystal Morphology
Transition from Semi-Amorphous States
At lower calcination temperatures (closer to 400°C), the CuO grains tend to be rounded and semi-amorphous.
In this state, the crystalline structure is less defined. The lack of distinct edges indicates that the atoms have not yet fully settled into their optimal lattice positions.
Formation of Sharp Crystalline Edges
As the temperature approaches 750°C, the morphology undergoes a distinct transformation.
The grains develop sharp edges and clear crystalline structures. This geometric sharpening is visual evidence of high crystallinity, indicating that the lattice defects often found in amorphous materials have been annealed out.
Impact on Electronic Properties
The shift toward a highly crystalline structure has a direct functional benefit: improved electronic transport.
A well-ordered crystal lattice with fewer defects reduces scattering, allowing electrons to move more freely through the copper oxide film.
The Role of the Furnace Environment
Purity Through Oxidation
The high-temperature environment of the muffle furnace serves a critical dual purpose beyond grain growth: purification.
The continuous thermal oxidation reaction ensures the complete removal of residual organic surfactants and solvents (such as oleylamine or diphenyl ether).
Creating the Nanoporous Structure
For nanoporous films, this purification is the key to structure formation.
If pore-forming agents (like CTAB) are used, the furnace facilitates their high-temperature pyrolysis. This process burns away the organic template, leaving behind the desired ordered mesoporous structure within the nanoparticles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Crystallinity vs. Thermal Budget
While higher temperatures (750°C) yield superior crystallinity and electronic properties, they require a significantly higher thermal budget.
This increases energy consumption and limits the types of substrates you can use, as the substrate must also withstand these temperatures without degrading.
Grain Size vs. Surface Area
There is an inherent trade-off between grain size and specific surface area.
While larger grains (72 nm) improve conductivity, excessive growth can potentially reduce the total surface area available for chemical reactivity, which is often a key feature of nanoporous materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your copper oxide films, align the calcination temperature with your specific performance metrics:
- If your primary focus is electronic conductivity: Target higher temperatures (around 750°C) to maximize crystallinity, achieve sharp grain edges, and ensure the most efficient electron transport.
- If your primary focus is preserving small grain features: Maintain lower temperatures (closer to 400°C) to keep grains around 21 nm, though you must accept a more semi-amorphous structure.
- If your primary focus is purity and pore formation: Ensure the temperature is sufficient to fully pyrolyze any organic templates (often requiring at least 700°C) to prevent residual contamination from blocking the pores.
Select the temperature that balances the need for crystalline quality with the physical constraints of your nanoporous architecture.
Summary Table:
| Temperature (°C) | Average Grain Size | Morphology Characteristics | Primary Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 400°C | ~21 nm | Rounded, semi-amorphous | Preserves small grain features |
| 750°C | ~72 nm | Sharp-edged, high crystallinity | Maximizes electronic transport |
| Effect | 3.4x Increase | Structural Evolution | Purification & Pore Formation |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Unlock superior control over grain growth and crystallinity in your nanoporous films. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific thermal budget and atmospheric requirements.
Whether you are targeting precise atomic diffusion at 400°C or high-temperature pyrolysis at 750°C, our lab furnaces deliver the thermal stability your research demands.
Ready to optimize your calcination process? Contact us today to find your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Lukas Korell, Marcus Einert. On the structural evolution of nanoporous optically transparent CuO photocathodes upon calcination for photoelectrochemical applications. DOI: 10.1039/d4na00199k
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why is high-purity argon necessary for PVC dechlorination? Ensure Precise Reaction Control & Safety
- What are the advantages of using an acid oxidation bath? Accelerate Lignin Fiber Stabilization from Hours to Minutes
- What is the purpose of using nitrogen cylinders and flowmeters? Ensure Superior Carbon Fiber Recovery
- What is the role of high-purity argon gas in ultrafine magnesium powder production? Control Particle Size & Purity
- What role does thermal processing with precise temperature control and tensile stress play in PVDF fiber stabilization?
- Why is the mechanical mixing of precursor powders necessary for ITO thin films? Guide to Precision Growth
- What functions do high-strength graphite molds perform during SPS? Drive Efficiency & Precision in Material Bonding
- Why is a laboratory blast drying oven necessary for preparing Reduced Graphene Oxide precursors? Ensure Powder Quality



















