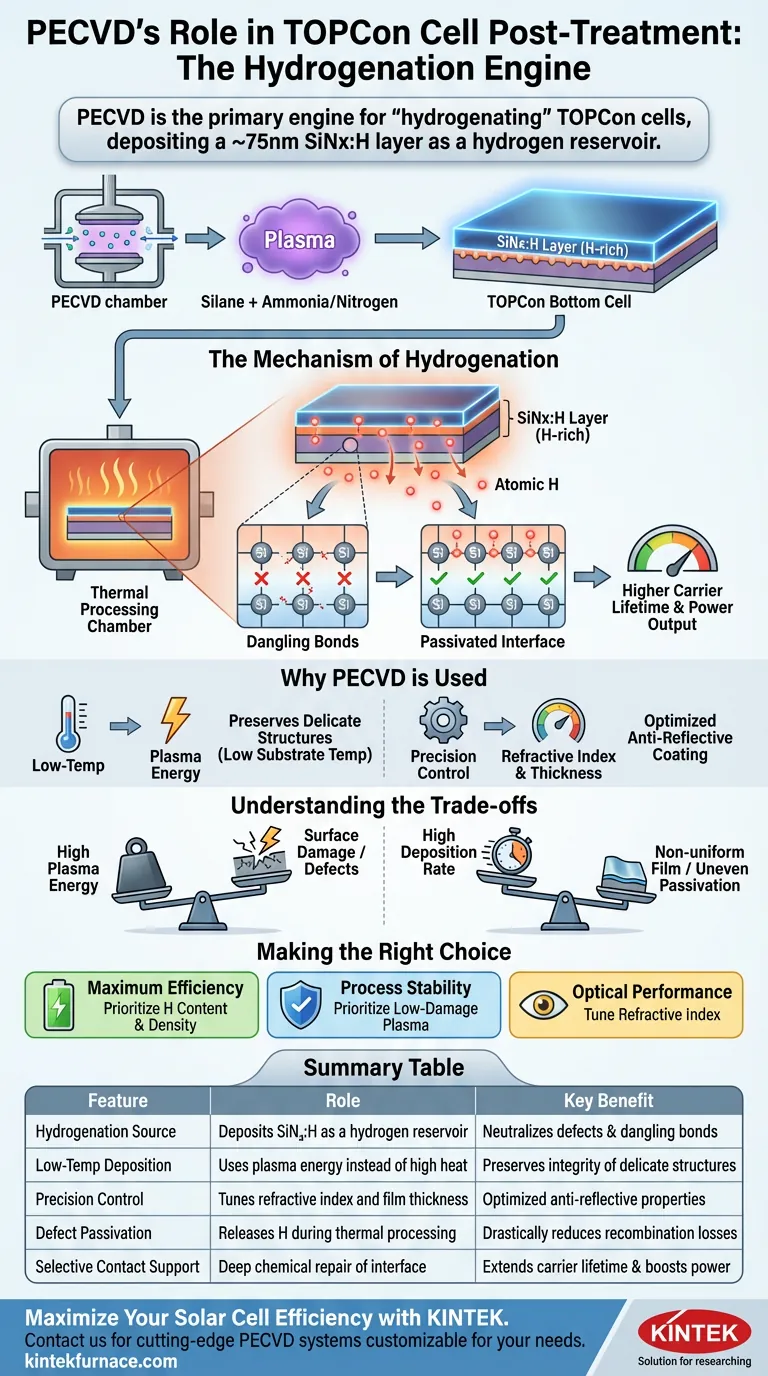
PECVD equipment is the primary engine for "hydrogenating" TOPCon cells, a critical post-treatment step that maximizes efficiency. It functions by depositing a layer of hydrogenated silicon nitride (SiNx:H), approximately 75 nanometers thick, onto the surface of the bottom cell.
The core function of this SiNx:H layer is to act as a hydrogen reservoir. During subsequent thermal steps, this film releases atomic hydrogen into the underlying silicon interface, neutralizing defects and significantly extending the carrier lifetime of the cell.

The Mechanism of Hydrogenation
The contribution of PECVD to post-treatment is chemical rather than structural. It prepares the cell for a process known as hydrogen passivation, which is essential for high-performance photovoltaics.
Creating the Hydrogen Source
The PECVD equipment introduces reactant gases, typically silane and ammonia or nitrogen, into a vacuum chamber.
By ionizing these gases into a plasma, the equipment deposits a thin, uniform film of hydrogenated silicon nitride (SiNx:H).
Crucially, this layer is engineered to trap a high concentration of hydrogen atoms within its structure during deposition.
Activation via Thermal Processing
The PECVD process itself is the setup; the payoff occurs during the subsequent thermal processing (firing) steps.
When the cell is heated, the SiNx:H film releases its stored hydrogen.
This atomic hydrogen diffuses downward into the carrier-selective contact interface of the TOPCon cell.
Enhancing Carrier Lifetime
Once the hydrogen reaches the silicon interface, it bonds with "dangling bonds"—atomic defects that would otherwise trap electrons and reduce efficiency.
By satisfying these bonds, the hydrogen passivates the interface, drastically reducing recombination losses.
This results in a higher carrier lifetime, meaning the cell can hold onto the electrical charge longer, directly translating to higher power output.
Why PECVD is Used for This Step
While the primary goal is hydrogenation, the specific capabilities of PECVD equipment make it the ideal tool for this sensitive application.
Low-Temperature Deposition
Standard thermal deposition requires high heat, which could damage the delicate structures already formed on the solar cell.
PECVD uses plasma energy rather than thermal energy to drive chemical reactions.
This allows the protective SiNx:H coating to be applied at lower substrate temperatures, preserving the integrity of the underlying layers.
Precision Film Control
PECVD equipment offers exceptional control over the stoichiometry (chemical balance) of the deposited film.
Manufacturers can precisely tune the refractive index and thickness of the layer.
This ensures the film not only provides hydrogen but also serves as an effective anti-reflective coating, further boosting light absorption.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PECVD is standard, it introduces specific challenges that must be managed to ensure cell quality.
Plasma Damage Risks
The same high-energy ions that allow for low-temperature deposition can physically bombard the cell surface.
If the plasma energy is too high, it can cause surface damage or lattice defects, effectively creating new problems while trying to solve old ones.
Uniformity vs. Throughput
High deposition rates are desirable for manufacturing speed, but they can compromise the uniformity of the hydrogen content.
A non-uniform film leads to uneven passivation, resulting in cells with variable efficiency across their surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The effectiveness of your post-treatment strategy depends on how you tune the PECVD parameters.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Efficiency: Prioritize the hydrogen content and density of the SiNx:H film to ensure deep, thorough passivation of interface defects.
- If your primary focus is Process Stability: Prioritize low-damage plasma recipes to minimize ion bombardment, ensuring the underlying passivation layers remain intact.
- If your primary focus is Optical Performance: Tune the refractive index of the SiNx:H layer to optimize light trapping while maintaining sufficient hydrogen levels.
Ultimately, PECVD equipment transforms a standard silicon wafer into a high-performance device by turning a simple coating step into a deep chemical repair mechanism.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in TOPCon Post-Treatment | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogenation Source | Deposits SiNx:H layer as a hydrogen reservoir | Neutralizes atomic defects & dangling bonds |
| Low-Temp Deposition | Uses plasma energy instead of high heat | Preserves integrity of delicate cell structures |
| Precision Control | Tunes refractive index and film thickness | Optimizes anti-reflective properties and light absorption |
| Defect Passivation | Releases hydrogen during thermal processing | Drastically reduces recombination losses |
| Selective Contact Support | Deep chemical repair of the silicon interface | Extends carrier lifetime and boosts power output |
Maximize Your Solar Cell Efficiency with KINTEK
Are you looking to optimize your TOPCon cell production with precision hydrogenation? Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers cutting-edge PECVD systems and lab high-temp furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum CVD systems—all customizable for your unique solar and semiconductor needs. Our advanced technology ensures low-damage plasma recipes and superior film uniformity to help you achieve market-leading carrier lifetimes.
Ready to elevate your lab's performance? Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Rasmus Nielsen, Peter C. K. Vesborg. Monolithic Selenium/Silicon Tandem Solar Cells. DOI: 10.1103/prxenergy.3.013013
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- In which fields is PECVD commonly used? Essential Thin-Film Tech for Electronics, Optics, and More
- What is PECVD used for? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Advanced Manufacturing
- What is a common application of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, Solar Cells, and More
- Why is PECVD considered indispensable in high-tech industries? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does the PECVD process work in single wafer chambers? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of Inline PECVD in solar cell passivation? Maximize Efficiency with Precision Thin-Film Layers
- What are gas barrier films, and how is PECVD involved in their creation? Discover Advanced Packaging Solutions
- What is the process of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















