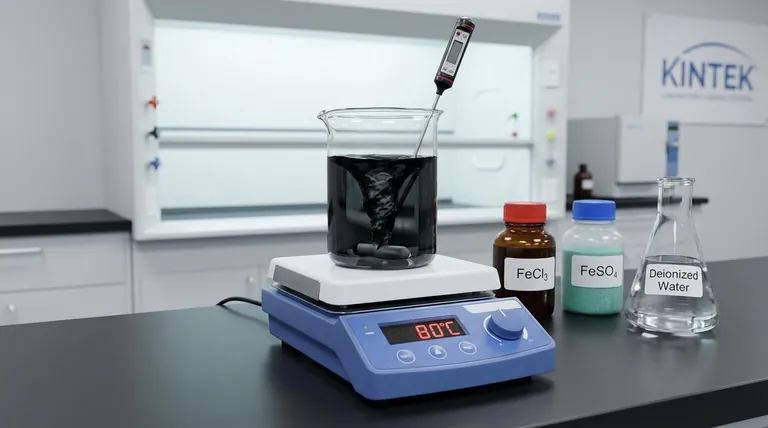
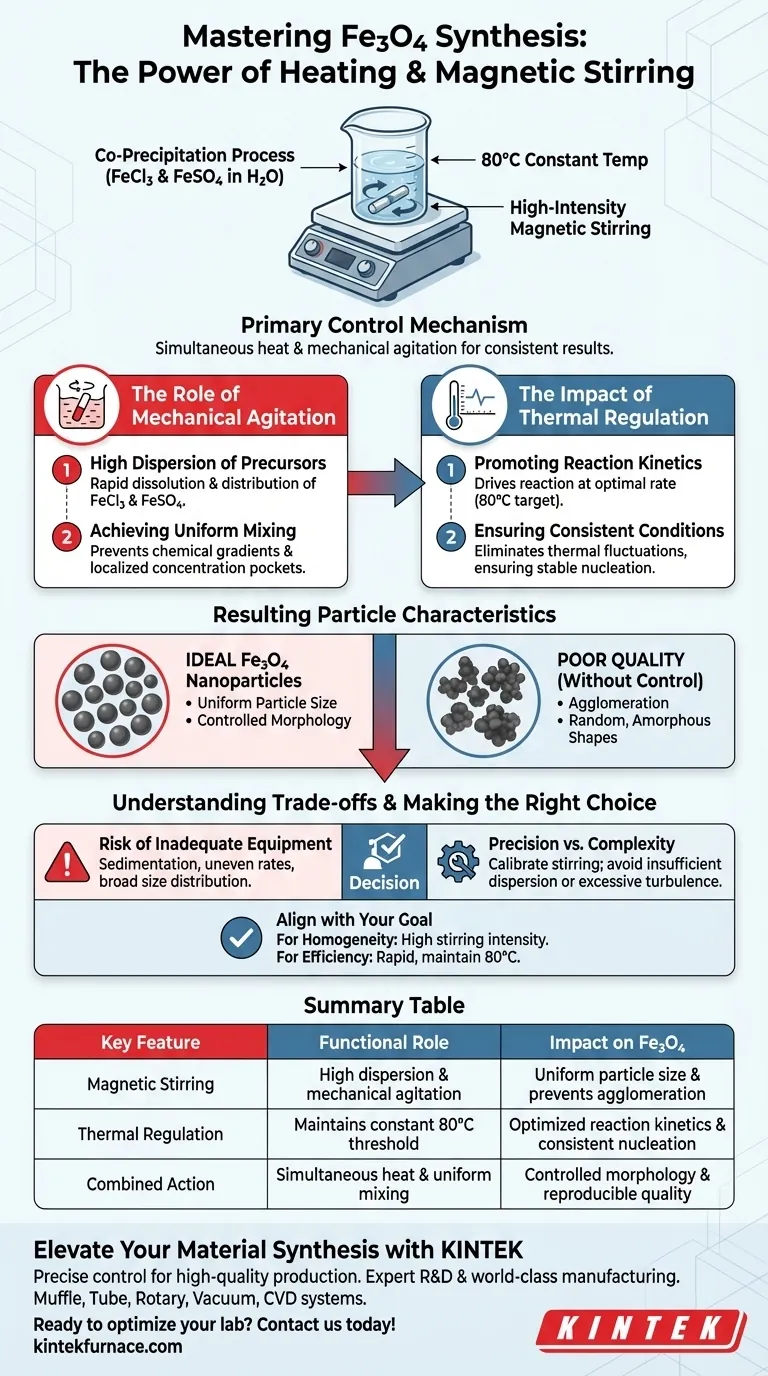
Heating equipment with magnetic stirring functions as the primary control mechanism for the successful co-precipitation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. By simultaneously maintaining a constant temperature of 80°C and providing high-intensity mechanical agitation, this equipment ensures that the iron precursors—FeCl3 and FeSO4—are fully dispersed and react under uniform conditions to produce consistent results.
In nanoparticle synthesis, the physical environment dictates the chemical outcome. The simultaneous application of heat and stirring is essential to drive reaction kinetics while preventing agglomeration, resulting in particles with controlled morphology and uniform size.

The Role of Mechanical Agitation
High Dispersion of Precursors
The primary function of the magnetic stirring element is to ensure the high dispersion of iron salts in the solvent.
Specifically, it facilitates the rapid dissolution and distribution of FeCl3 and FeSO4 within the deionized water base.
Achieving Uniform Mixing
Without rigorous mechanical intervention, chemical gradients can form within the solution.
High-intensity mechanical stirring guarantees that the reactants are mixed uniformly, preventing localized areas of high or low concentration that could lead to inconsistent particle growth.
The Impact of Thermal Regulation
Promoting Reaction Kinetics
The heating element is responsible for driving the chemical reaction forward at an optimal rate.
Maintaining the solution at a specific temperature of 80°C promotes the kinetics of the reaction, ensuring the co-precipitation process occurs efficiently.
Ensuring Consistent Conditions
Temperature stability is just as critical as reaching the target heat.
The equipment maintains a constant heating condition, which eliminates thermal fluctuations that could otherwise alter the nucleation process and degrade the quality of the final product.
Resulting Particle Characteristics
Uniform Particle Size
The combination of consistent heat and uniform mixing directly influences the size distribution of the nanoparticles.
When precursors are evenly distributed and heated, nucleation occurs simultaneously throughout the solution, leading to a uniform particle size.
Controlled Morphology
The physical shape, or morphology, of the nanoparticles is dictated by the reaction environment.
By strictly controlling the agitation and temperature, the equipment ensures the generated Fe3O4 nanoparticles exhibit the desired structural characteristics rather than random, amorphous shapes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Inadequate Equipment
Using standard heating without magnetic stirring often results in sedimentation or uneven reaction rates.
If the precursors settle or mix unevenly, the resulting particles may suffer from broad size distributions or significant agglomeration.
Precision vs. Complexity
While this equipment adds a layer of operational complexity, it removes the variability found in manual methods.
However, users must ensure the stirring intensity is calibrated correctly; insufficient stirring fails to disperse precursors, while excessive turbulence could potentially introduce air bubbles or shear stress depending on the scale.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your Fe3O4 synthesis, align your equipment settings with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Particle Homogeneity: Ensure your magnetic stirring is set to a high intensity to prevent concentration gradients during the nucleation phase.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Efficiency: Prioritize equipment that can rapidly reach and strictly maintain the 80°C threshold to optimize chemical kinetics.
Consistency in your physical controls is the single most important factor in reproducible nanoparticle synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Functional Role in Synthesis | Impact on Fe3O4 Nanoparticles |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Stirring | High dispersion & mechanical agitation | Uniform particle size & prevents agglomeration |
| Thermal Regulation | Maintains constant 80°C threshold | Optimized reaction kinetics & consistent nucleation |
| Combined Action | Simultaneous heat & uniform mixing | Controlled morphology & reproducible quality |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise control over thermal and mechanical variables is the foundation of high-quality nanoparticle production. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides advanced laboratory solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to meet your unique research requirements.
Whether you are scaling up Fe3O4 synthesis or developing complex thin-film materials, our high-temperature furnaces ensure the thermal stability and uniformity your work demands.
Ready to optimize your lab's performance? Contact us today to find the perfect equipment for your needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Meenakshi Sundaram Sharmila, Gurusamy, Annadurai. Biogenic fabrication of biochar-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles using Miscanthus sinensis for oxytetracycline removal and toxicological assessment. DOI: 10.12692/jbes/27.2.10-20
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What type of pump is used in water circulating vacuum pumps and how is it installed? Discover Robust Fluid-Based Vacuum Solutions
- How do high-precision mass flow controllers assist in the formation of superlattice structures? Mastery of 2D CVD
- What are the requirements for high-temperature heating equipment and quartz crucibles in incineration ash pretreatment?
- What are the thermal properties of alumina tubes? Discover Their High-Temp Durability and Stability
- What is the function of alumina crucibles in YBCO synthesis? Ensure Purity & Stability in Superconductor Production
- What is the function of a graphite crucible in synthesis? Ensure Purity in Sn0.50Ag0.25Bi0.25Se0.50Te0.50 Production
- What roles do the Stockbarger method and vacuum-sealed quartz ampoules play in NaCl:Li and KCl:Na crystal growth?
- Why are laboratory precision stirrers and heating devices essential for synthesizing magnetic precursor solutions?



















