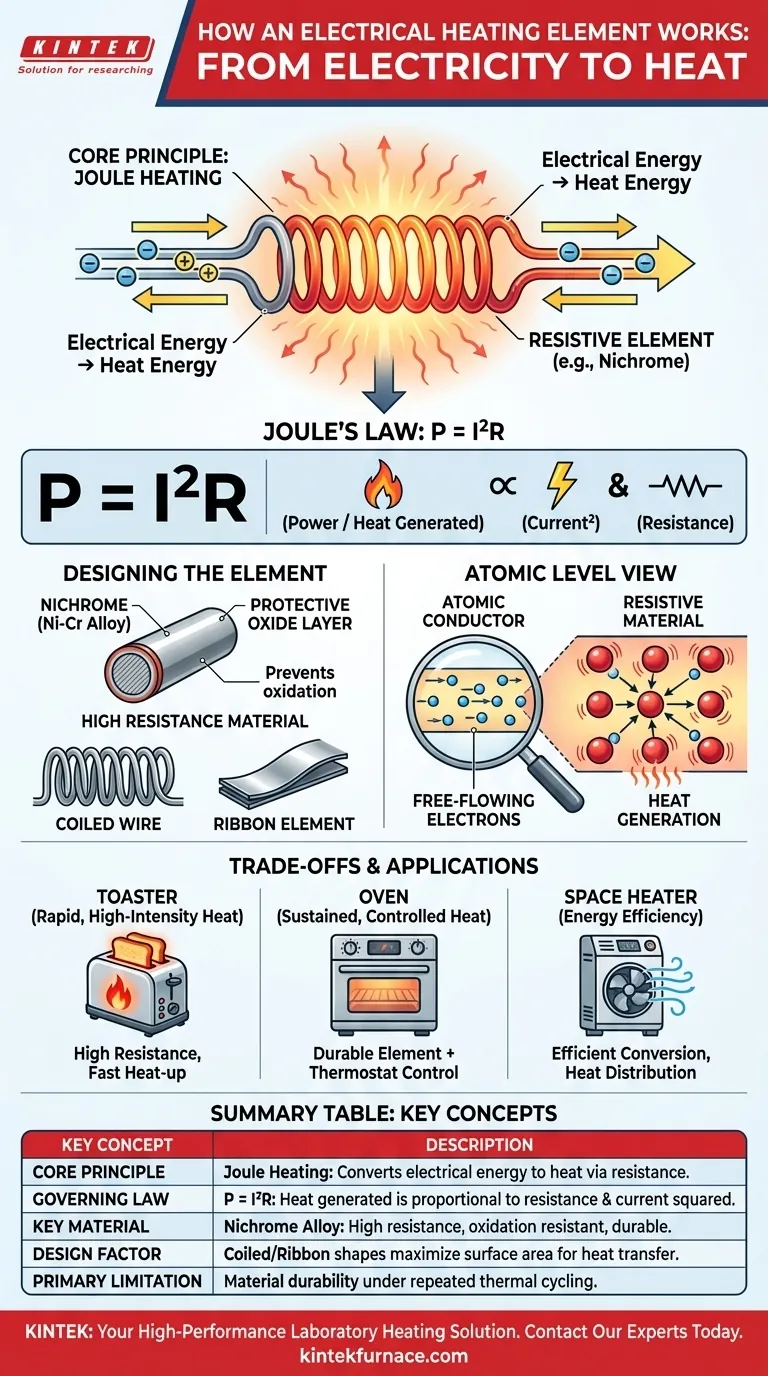
At its core, an electrical heating element works by converting electrical energy directly into heat through a process called Joule heating. When an electric current is sent through a material specifically chosen for its high electrical resistance, the material impedes the flow of that current. This opposition creates friction at an atomic level, manifesting as the intense heat used in everything from toasters to industrial furnaces.
The fundamental principle is not simply that electricity creates heat, but that heating elements are engineered with materials that intentionally resist the flow of electricity. This controlled resistance is what forces the conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy with very high efficiency.
The Core Principle: Joule Heating
To understand how a heating element works, you must first grasp the concepts of electrical current and resistance. These two factors are the foundation of Joule heating.
From Electricity to Heat
An electric current is simply the flow of electrons through a material. In an excellent conductor like copper wire, electrons flow easily with minimal opposition. A heating element, however, is made from a material that does the opposite.
The Role of Resistance
Resistance is a measure of a material's opposition to the flow of electric current. Instead of letting electrons pass freely, a resistive material forces them to work harder to get through. This is the key property exploited in a heating element.
An Atomic-Level View
As electrons are forced through the resistive material, they constantly collide with the atoms of that material. Each collision transfers kinetic energy from the electron to the atom, causing the atom to vibrate more rapidly. This widespread, increased atomic vibration is what we perceive and feel as heat.
Quantifying the Heat (Joule's Law)
This relationship is precisely described by Joule's first law, often expressed as P = I²R.
- P is power, which is the rate of heat generated.
- I is the electrical current flowing through the element.
- R is the element's resistance.
This formula shows that the heat produced is proportional to the resistance, but it increases with the square of the current. This means that even a small increase in current has a dramatic effect on the heat output.
Designing an Effective Heating Element
Not just any material can serve as a heating element. They are engineered from specific materials and formed into shapes that optimize heat generation and durability.
The Importance of High Resistance
The primary requirement is high electrical resistance. A material that conducts electricity too well would not generate sufficient heat; it would simply transmit the power. The goal is to find a material that effectively "fights" the current.
Common Materials: Nichrome
One of the most common materials used is nichrome, an alloy of nickel and chromium. Nichrome is ideal because it has high resistance and, critically, it forms a protective layer of chromium oxide when it heats up. This layer prevents it from oxidizing further, giving it a long service life at high temperatures.
Shape and Form Factor
You will often see heating elements shaped into coils, ribbons, or loops. This allows a very long length of resistive wire to be packed into a small, contained space, maximizing the surface area available for heat generation and transfer.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While Joule heating is a straightforward process, designing a real-world heating element involves balancing several critical factors.
Efficiency vs. Heat Loss
The conversion of electricity to heat within the element itself is nearly 100% efficient. However, the overall efficiency of an appliance depends on how well that heat is transferred to its target (e.g., water in a kettle, air in a room) versus how much is lost to the surrounding environment.
Material Durability
The material must be able to withstand extreme and repeated temperature changes—a phenomenon known as thermal cycling. A poorly chosen material would become brittle, crack, or melt after only a few uses.
Safety and Insulation
Because heating elements operate at very high temperatures, they must be properly insulated from the rest of the appliance and its user. This prevents electrical shorts, fire hazards, and accidental burns, ensuring the device operates safely.
How This Applies to Your Devices
Understanding this principle helps demystify how common appliances are designed for different heating tasks.
- If the goal is rapid, high-intensity heat (like a toaster): The design uses an element with very high resistance that can reach its target temperature in seconds.
- If the goal is sustained, controlled heat (like an oven): The system pairs a durable heating element with a thermostat, which switches the current on and off to precisely maintain a stable temperature.
- If the goal is energy efficiency (like a modern space heater): The design focuses on both the element's conversion efficiency and the device's ability (using fans or reflective surfaces) to effectively direct that heat into the living space.
By mastering the principle of controlled resistance, engineers can turn simple physics into the reliable heat that powers our daily lives.
Summary Table:
| Key Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Joule Heating: Converts electrical energy to heat via resistance. |
| Governing Law | P = I²R: Heat generated is proportional to resistance and the square of the current. |
| Key Material | Nichrome Alloy: High resistance and oxidation resistance for durability. |
| Design Factor | Coiled/ribbon shapes maximize surface area for effective heat transfer. |
| Primary Limitation | Material durability under extreme, repeated thermal cycling. |
Need a High-Performance Heating Solution for Your Laboratory?
Understanding the principles of Joule heating is just the first step. Applying this knowledge to create a robust, efficient, and precisely controlled heating system for your unique laboratory requirements is where KINTEK excels.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs.
Let us help you achieve superior thermal processing. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover the perfect heating solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















