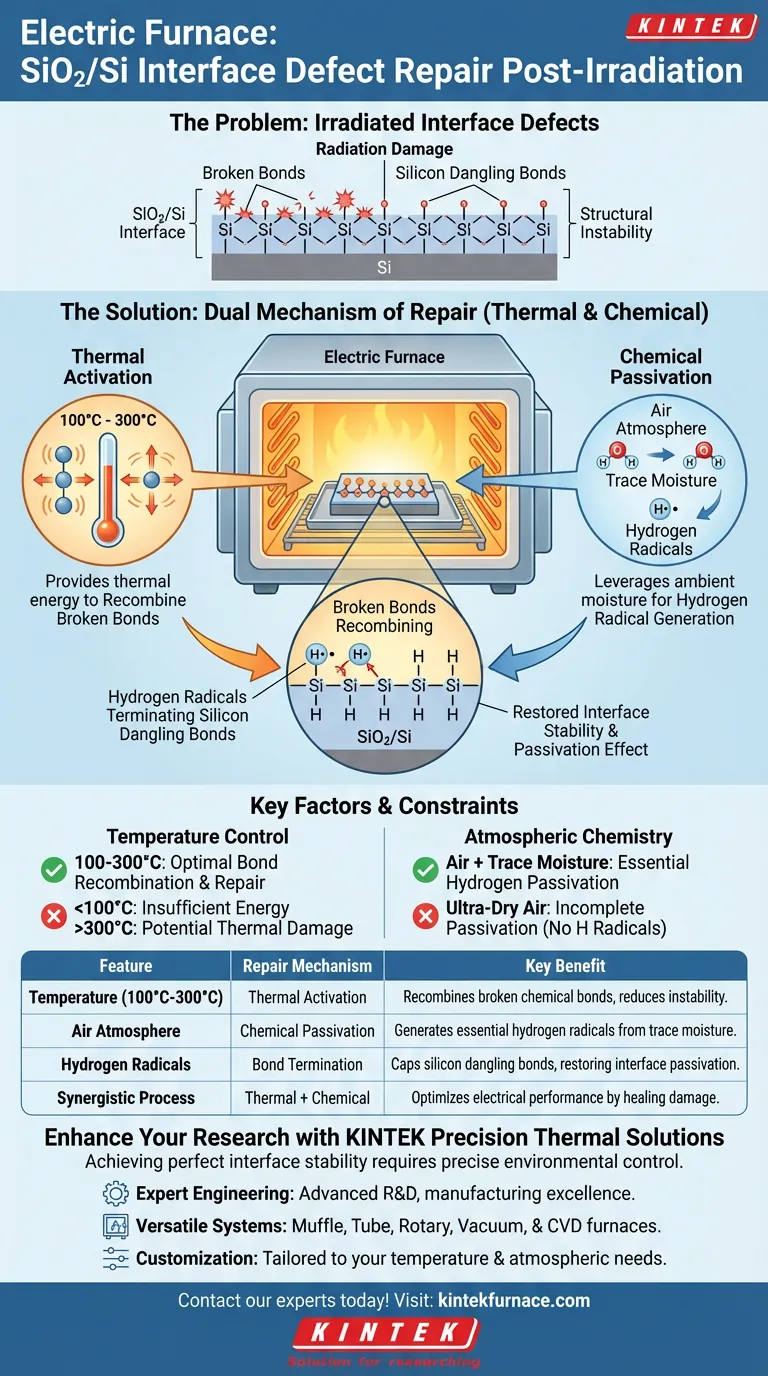
An Electric Furnace facilitates defect repair primarily through a dual mechanism of thermal activation and chemical passivation. By operating typically between 100°C and 300°C in an air atmosphere, the furnace provides the thermal energy required to recombine broken chemical bonds. Simultaneously, it leverages trace moisture naturally present in the air to generate hydrogen-related radicals, which actively terminate silicon dangling bonds and restore interface stability.
Post-irradiation annealing is not merely a thermal process; it is a chemical restoration of the material's structure. The Electric Furnace uniquely utilizes the ambient environment to deliver hydrogen passivation, effectively healing the critical SiO2/Si interface defects caused by radiation.

The Mechanism of Thermal Repair
Providing Essential Activation Energy
The primary function of the Electric Furnace is to supply thermal energy to the irradiated sample. Radiation damage often breaks chemical bonds at the interface, creating structural instability.
The furnace creates an environment where atoms and electrons create sufficient energy to move and reorganize. This thermal agitation promotes the recombination of chemical bonds that were severed during irradiation.
Target Temperature Range
The specific operating window for this process is typically between 100°C and 300°C.
This range is carefully selected to be high enough to stimulate bond repair but controlled enough to avoid inducing further thermal stress. Within this window, the elimination of interface defects becomes thermodynamically favorable.
The Role of Atmospheric Chemistry
Utilization of Ambient Air
Unlike vacuum annealing systems, the Electric Furnace operates in an air atmosphere. This is a strategic feature, not a lack of control.
The presence of air is critical because it introduces chemical components necessary for the repair process that mere heat cannot supply.
Trace Moisture as a Reactant
The key active ingredient in this atmosphere is trace amounts of moisture. Even low levels of humidity in the air play a vital chemical role during the annealing process.
Under the thermal conditions of the furnace, this moisture acts as a source for hydrogen-related radicals.
Restoring the Passivation Effect
These hydrogen radicals are essential for targeting silicon dangling bonds—unsatisfied valency bonds at the SiO2/Si interface that act as electrical defects.
The radicals attach to these dangling bonds, effectively "capping" or terminating them. This process restores the interface passivation effect, significantly improving the electrical performance of the structure.
Understanding the Constraints and Variables
Dependence on Environmental Conditions
Because the process relies on ambient air, the repair mechanism is inherently linked to the composition of the atmosphere.
If the air is completely devoid of moisture (e.g., in an ultra-dry environment), the supply of hydrogen radicals may be insufficient. This would limit the furnace's ability to terminate silicon dangling bonds, leaving the passivation incomplete.
The Limits of Thermal Recombination
While heat promotes bond recombination, it cannot fix all defects on its own.
Thermal energy moves the lattice toward a lower energy state, but without the chemical agent (hydrogen), certain interface states will remain active. The synergy between the heat and the moisture is the defining factor of success.
Optimizing the Annealing Process
To maximize defect repair in SiO2/Si structures, you must balance thermal precision with environmental chemistry.
- If your primary focus is Bond Recombination: Maintain the furnace temperature strictly within the 100°C to 300°C range to provide adequate activation energy without thermal damage.
- If your primary focus is Interface Passivation: Ensure the annealing takes place in an air atmosphere containing trace moisture to ensure a sufficient supply of hydrogen radicals for dangling bond termination.
Successful post-irradiation repair requires viewing the Electric Furnace not just as a heater, but as a reactor that facilitates essential chemical healing at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Repair Mechanism | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (100°C-300°C) | Thermal Activation | Recombines broken chemical bonds and reduces structural instability. |
| Air Atmosphere | Chemical Passivation | Leverages trace moisture to generate essential hydrogen radicals. |
| Hydrogen Radicals | Bond Termination | Caps silicon dangling bonds to restore interface passivation. |
| Synergistic Process | Thermal + Chemical | Optimizes electrical performance by healing irradiation-induced damage. |
Enhance Your Semiconductor Research with Precision Thermal Solutions
Achieving perfect interface stability requires more than just heat—it requires precise environmental control. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal equipment designed to meet the rigorous demands of post-irradiation annealing and materials science.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert Engineering: Backed by advanced R&D and manufacturing excellence.
- Versatile Systems: We offer a full range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems.
- Customization: Every furnace can be tailored to your specific temperature and atmospheric requirements.
Ready to optimize your defect repair process? Contact our experts today to find the perfect customizable furnace for your laboratory’s unique needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Shota Nunomura, Masaru Hori. O2 and Ar plasma processing over SiO2/Si stack: Effects of processing gas on interface defect generation and recovery. DOI: 10.1063/5.0184779
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heat Treatment
- What is the primary role of high-precision muffle furnaces in the sintering process of high-entropy alloys?
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace in g-C3N4/Bi2WO6 preparation? Expert Guide to Thermal Synthesis
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace required for coal gangue activation? Unlock Maximum Material Reactivity
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the synthesis of Si@Al adsorbents? Master Precise Thermal Transformation
- What are the primary uses of muffle furnaces? Essential for Contamination-Free High-Temp Processing
- How does a high-temperature box resistance furnace synthesize WC/C@N-S nanocatalysts? Precision Thermal Control
- Why is a controlled environment important in a muffle furnace? Ensure Precise, Contamination-Free Results



















