In essence, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used for a wide range of industrial and laboratory processes. Its primary uses involve subjecting materials to extreme heat in a controlled environment, including heat-treating metals, ashing organic samples for chemical analysis, firing ceramics and glass, and conducting advanced materials research.
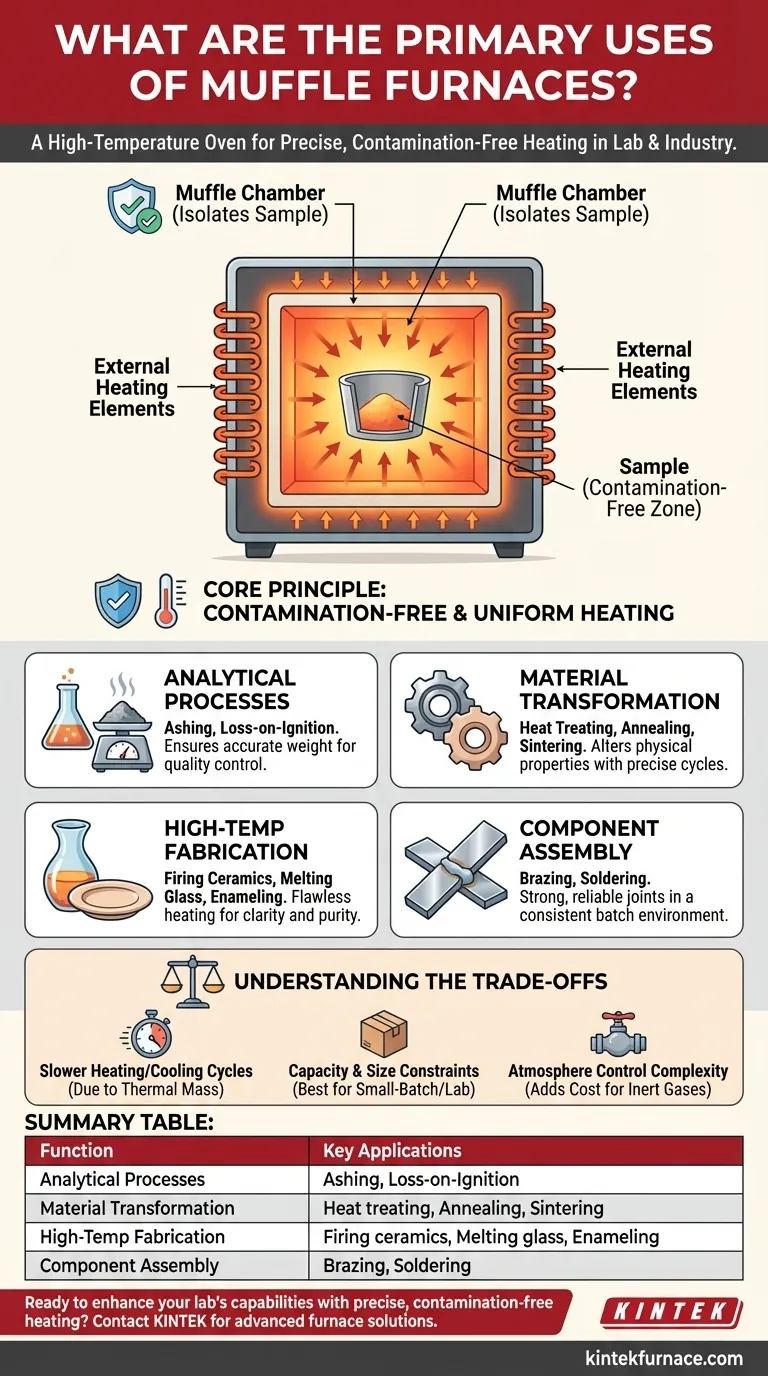
A muffle furnace's defining feature is not just its high heat, but its muffle—an insulating chamber that separates the material from the heating elements. This critical isolation is the key to achieving the clean, uniform, and precisely controlled thermal processing required in sensitive applications.
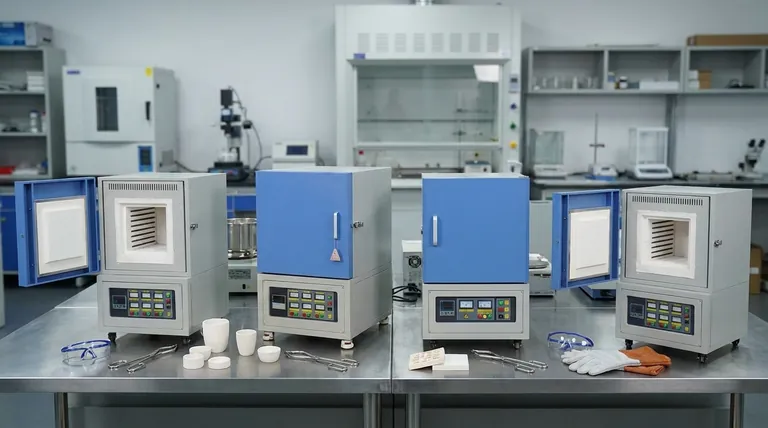

The Core Principle: Contamination-Free Heating
The "muffle" is the central concept that distinguishes this furnace. Understanding it reveals why it is chosen for specific tasks over other types of kilns or ovens.
What is a "Muffle"?
A muffle is a sealed inner chamber, typically made of high-temperature ceramic, that contains the workpiece or sample. Heating elements are positioned outside this chamber, heating the muffle, which then radiates thermal energy evenly inward.
Preventing Contamination
By isolating the sample, the muffle prevents any byproducts of combustion (if using a gas-fired model) or material flaking from the heating elements from contaminating the workpiece. This purity is essential for chemical analysis and creating high-quality materials.
Ensuring Uniform Heat
The muffle's walls heat up and radiate energy from all sides toward the center. This creates an exceptionally uniform thermal environment, eliminating the hot spots and uneven heating that can occur with direct exposure to a flame or heating element.
Key Applications by Function
The unique capabilities of a muffle furnace make it indispensable across several functional categories.
Analytical Processes: Ashing and Loss-on-Ignition
Many quality control and analytical chemistry procedures require ashing. This involves heating a sample to burn away all organic matter, leaving only the non-combustible inorganic ash.
A muffle furnace is ideal because its clean environment ensures that the final weight of the ash is accurate and not skewed by external contaminants. This is critical for environmental testing, pharmaceutical analysis, and the food industry.
Material Transformation: Heat Treating and Sintering
Metallurgy and materials science rely heavily on precisely altering the physical properties of a material.
Processes like annealing (softening metal and relieving stress), hardening (strengthening it), and sintering (fusing powdered materials into a solid mass) all depend on exact temperature cycles. The uniform, controlled heat of a muffle furnace allows for predictable and repeatable results.
High-Temperature Fabrication: Ceramics, Glass, and Enamels
Creating high-quality glass and ceramic objects requires flawless heating. The muffle furnace provides the stable temperatures needed for melting glass, firing technical ceramics, and fusing enamel coatings onto metal.
The absence of combustion byproducts ensures the clarity of glass and the purity of the ceramic or enamel color.
Component Assembly: Brazing and Soldering
Brazing and soldering are processes used to join metal components using a filler metal. A muffle furnace can provide a consistent, high-heat environment to perform these tasks on a batch scale, ensuring strong and reliable joints without introducing impurities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not the universal solution for all heating needs. Its design comes with inherent trade-offs.
Slower Heating and Cooling Cycles
The same ceramic muffle that provides thermal uniformity also acts as a significant thermal mass. This means muffle furnaces generally take longer to heat up and cool down compared to direct-fired kilns, which can affect process throughput.
Capacity and Size Constraints
Muffle furnaces are most common in laboratory and small-batch production settings. While large industrial models exist, the design is often better suited for processing smaller, high-value workpieces rather than large-scale, continuous manufacturing.
Atmosphere Control Adds Complexity
While standard models operate in air, some advanced processes require a controlled atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation. Incorporating gas-tight seals and control systems adds significant cost and complexity to the furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use a muffle furnace should be driven by the specific demands of your process.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: Use a muffle furnace for ashing, loss-on-ignition, or sample prep where preventing contamination is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is material property modification: It is the ideal tool for heat-treating, annealing, and sintering materials that require precise and uniform temperature profiles.
- If your primary focus is high-quality fabrication: Leverage its clean, even heating for crafting glass, technical ceramics, or enamel coatings that demand a flawless finish.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is the definitive tool when your process demands high heat without compromise.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Analytical Processes | Ashing, Loss-on-Ignition for chemical analysis |
| Material Transformation | Heat treating, Annealing, Sintering of metals and powders |
| High-Temperature Fabrication | Firing ceramics, Melting glass, Enameling |
| Component Assembly | Brazing, Soldering metal joints |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise, contamination-free heating? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and deep customization, we tailor solutions to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are precision stirring and drying equipment necessary for photocatalytic materials? Master Microstructure Control
- Why is a muffle furnace used to determine the ash content of biochar? Master Your Material Purity Analysis
- How does a muffle furnace contribute to kaolin-modified biochar? Optimize Pyrolysis & Mineral Integration
- What is the primary role of a muffle furnace in the annealing process of AlCrTiVNbx alloys? Enhance Alloy Strength
- What role does a muffle furnace play in analyzing the combustion residues? Optimize Your Composite Char Analysis



















