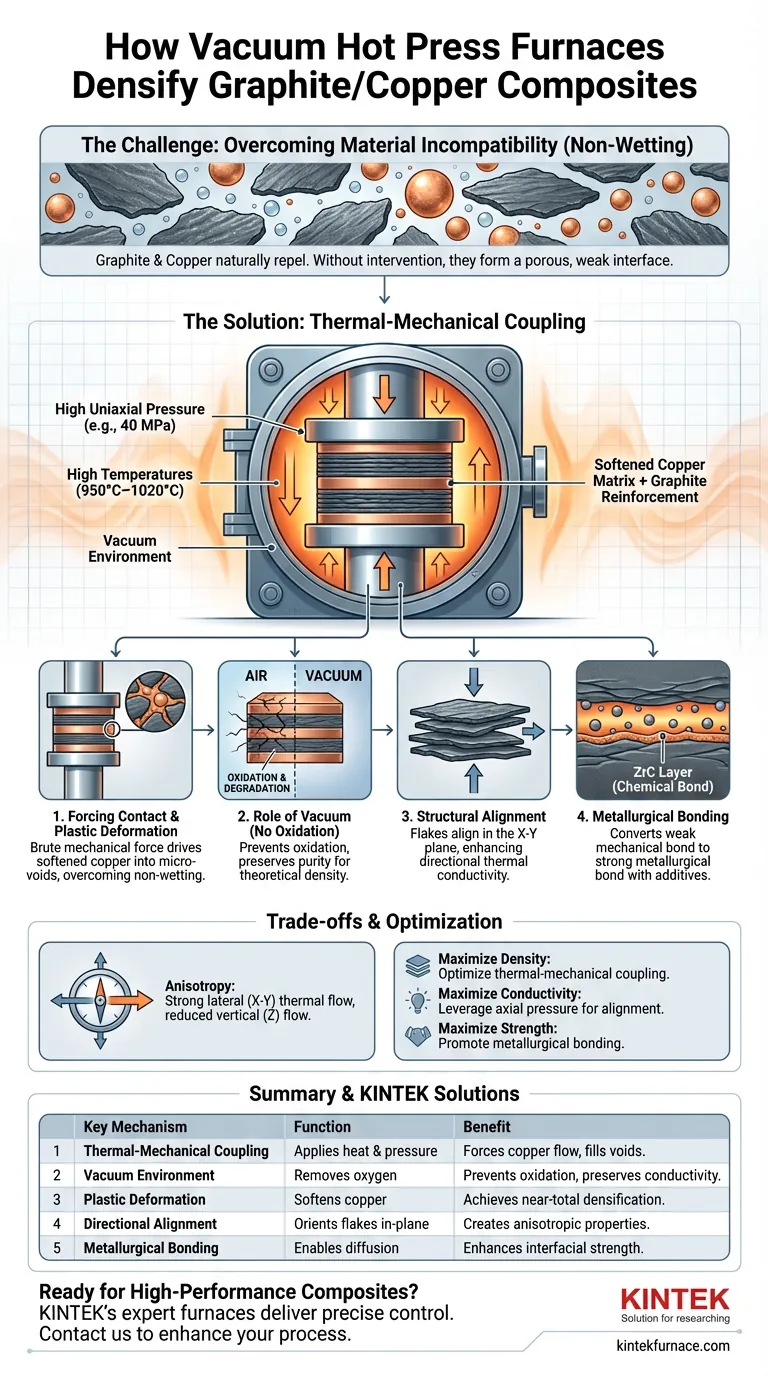
A vacuum hot press furnace promotes densification through a process known as thermal-mechanical coupling. By simultaneously applying high uniaxial pressure (e.g., 40 MPa) and high temperatures (950°C–1020°C) within an oxygen-free environment, the system forces the softened copper matrix to physically deform. This mechanical force overcomes the natural surface tension between the materials, compelling the copper to fill the microscopic voids between graphite flakes that heat alone could not penetrate.
The fundamental challenge in manufacturing graphite/copper composites is the "non-wetting" nature of the two materials—they naturally repel rather than bond. Vacuum hot pressing solves this by substituting chemical affinity with brute mechanical force, ensuring a dense, void-free interface while preventing the oxidation that destroys thermal performance.

Overcoming Material Incompatibility
Forcing Contact Despite Non-Wetting
Copper and graphite possess a natural resistance to bonding, known as non-wetting behavior. Under normal atmospheric pressure, molten or softened copper will simply sit on top of graphite without penetrating its surface irregularities.
The vacuum hot press overcomes this by applying significant mechanical pressure (e.g., 40 MPa). This external force physically pushes the copper matrix into tight contact with the graphite particles, effectively eliminating interfacial gaps regardless of the materials' chemical reluctance to bond.
Inducing Plastic Deformation
To achieve high density, the copper matrix must flow into every microscopic crevice. The furnace creates a high-temperature environment that softens the copper, while the continuous axial pressure induces plastic deformation.
This forces the copper powder to undergo plastic flow, squeezing it into the micro-voids and micropores between the graphite structures. This mechanical filling is critical for achieving near-total densification, especially in composites with a high volume of graphite reinforcement.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
Prevention of Oxidation
Both copper and graphite are susceptible to degradation when heated in air. Oxygen creates oxides on the copper surface and can cause the graphite to deteriorate, both of which ruin thermal conductivity.
The vacuum environment ensures that high temperatures (up to 1020°C) can be reached without these chemical reactions. This pristine environment preserves the purity of the matrix and reinforcement, allowing the material to approach its theoretical density.
Facilitating Liquid Phase Sintering
In specific formulations, such as those including boron, the vacuum environment supports the formation of a liquid phase (e.g., a copper-boron liquid). The vacuum allows the material to reach the necessary melting points without vaporizing or oxidizing.
This liquid phase significantly improves fluidity. When combined with pressure, this liquid acts as a lubricant and filler, moving easily over rough graphite surfaces to plug even the smallest internal pores.
Structural Alignment and Bonding
Directional Alignment of Flakes
When using flake-shaped fillers, the physics of hot pressing introduces a distinct structural advantage. The continuous high axial pressure does not just compress the material; it reorients the graphite flakes.
This pressure induces a directional alignment of the flakes along the X-Y plane (perpendicular to the pressing direction). This alignment creates anisotropic properties, resulting in superior thermal conductivity along the plane of the composite.
Transitioning to Metallurgical Bonding
Beyond simple mechanical interlocking, the furnace provides the thermal energy required for chemical diffusion. For example, if additives like Zirconium are present, the heat drives these atoms to the interface.
This facilitates a reaction with the graphite to form a distinct layer, such as Zirconium Carbide (ZrC). This converts a weak mechanical bond into a strong metallurgical bond, further enhancing the material's integrity and thermal transfer capabilities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Anisotropy Management
While aligning graphite flakes improves performance in one direction (the X-Y plane), it often reduces performance in the Z-axis (through the thickness). Engineers must account for this directionality; the component effectively conducts heat laterally but may act as an insulator vertically.
Process Complexity and Throughput
Vacuum hot pressing is a batch process that requires precise control over temperature, pressure, and atmosphere simultaneously. Unlike continuous casting methods, this approach prioritizes precision and quality over high-volume speed, making it best suited for high-performance applications where material integrity cannot be compromised.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a vacuum hot press furnace for your specific composite application:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Density: Prioritize the optimization of the "thermal-mechanical coupling" to ensure pressure is applied exactly when the matrix reaches peak plasticity.
- If your primary focus is Thermal Conductivity: Leverage the axial pressure to maximize the directional alignment of the graphite flakes along the primary heat transfer path.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Strength: Utilize the thermal energy capabilities to promote the diffusion of carbide-forming additives (like Zr) to create metallurgical bonds.
By precisely controlling the interplay of heat and pressure in a vacuum, you transform a naturally incompatible mixture into a cohesive, high-performance composite.
Summary Table:
| Key Mechanism | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal-Mechanical Coupling | Applies heat and pressure simultaneously | Forces copper to fill voids, overcoming non-wetting |
| Vacuum Environment | Removes oxygen during heating | Prevents oxidation, preserves thermal conductivity |
| Plastic Deformation | Softens copper under pressure | Achieves near-total densification |
| Directional Alignment | Orients graphite flakes in-plane | Creates anisotropic thermal properties |
| Metallurgical Bonding | Enables diffusion and carbide formation | Enhances interfacial strength and integrity |
Ready to develop high-performance graphite/copper composites?
Our vacuum hot press furnaces are engineered to deliver the precise thermal-mechanical coupling required to overcome material incompatibility and achieve maximum densification. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, including customizable lab high-temp furnaces tailored for advanced materials processing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your composite manufacturing process and meet your unique performance goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is vacuum press technology indispensable in modern metalworking? Unlock Precision and Quality in Metal Forming
- What are the common applications of vacuum hot pressing? Essential for High-Performance Materials
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density
- How does vacuum hot pressing equipment enhance the matrix quality of diamond tools through improved wettability? Unlock Superior Diamond Retention
- How do the temperature and pressure conditions in a vacuum hot-pressing furnace facilitate the densification of AMC?
- What is the impact of precise temperature control in a sintering furnace? Optimize Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs Composites
- What role does a hot-press sintering furnace play in Y2O3-YAM composite ceramics? Achieve 100% Density & Control Grains
- What are the advantages of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) systems? Superior High-Entropy Carbide Ceramic Fabrication



















