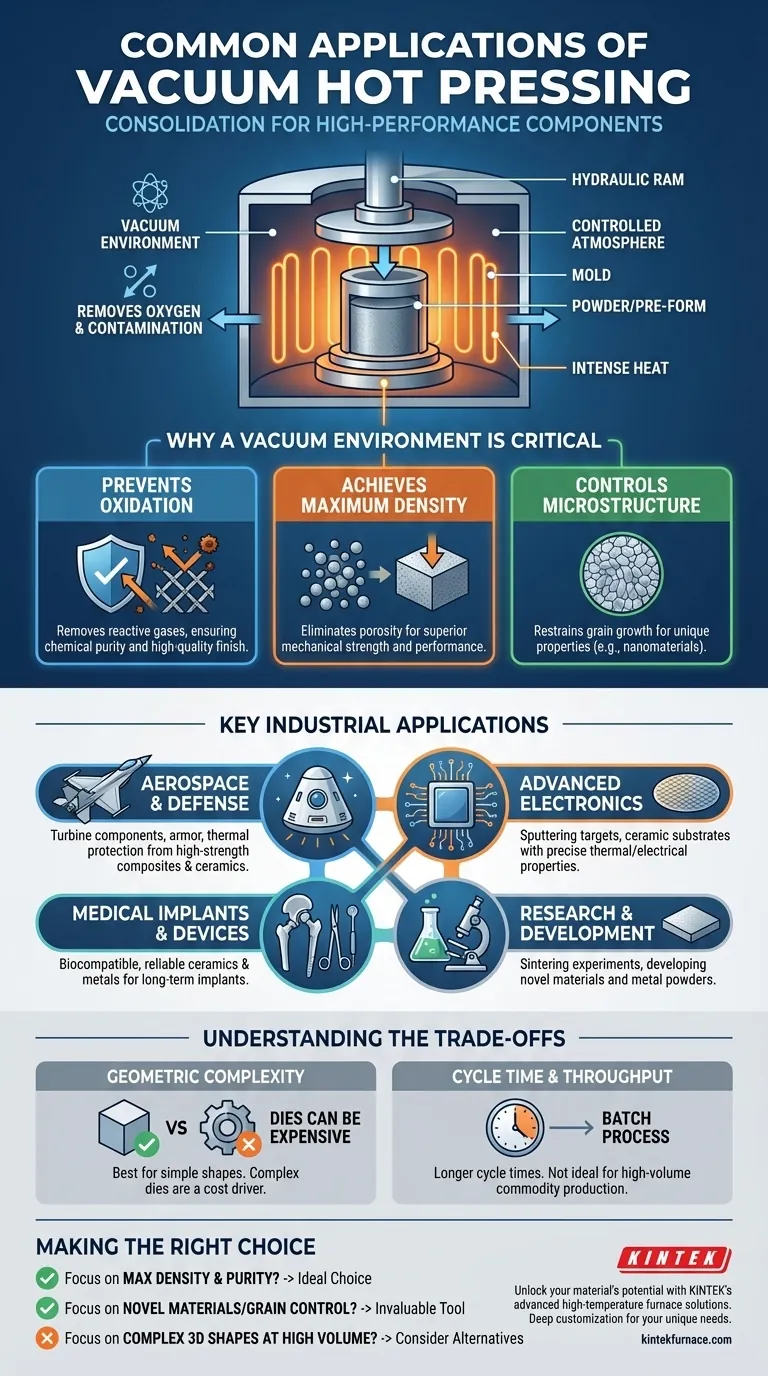
Fundamentally, vacuum hot pressing is a material consolidation process used to create highly dense, pure, and high-performance components. It combines intense heat and mechanical pressure inside a vacuum chamber to transform powders or pre-forms into solid parts. Its applications are concentrated in manufacturing advanced ceramics, refractory metals, powder metallurgy components, and specialized composites for demanding industries.
Vacuum hot pressing is not just about heating and squeezing a material; it is about doing so in a controlled vacuum. This prevents oxidation and contamination, enabling the production of materials with superior density and microstructural control that are often impossible to achieve with conventional sintering methods.

Why a Vacuum Environment is Critical
The defining feature of this process is the vacuum. This controlled atmosphere is directly responsible for the unique properties of the final components.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Many advanced materials, such as certain metals and functional ceramics, are highly sensitive to air exposure at high temperatures.
The vacuum environment removes oxygen and other reactive gases, preventing the formation of undesirable oxides. This ensures the material retains its intended chemical purity and achieves a high-quality finish.
Achieving Maximum Density
The simultaneous application of high temperature and uniaxial pressure forces the material particles together, effectively eliminating porosity.
This results in a final product that is highly compacted and near its theoretical maximum density. This density is critical for superior mechanical strength and other performance characteristics.
Controlling Material Microstructure
The precise control over temperature and pressure allows for the manipulation of the material's internal structure.
For example, the process can restrain the growth of crystal grains. This is particularly valuable for producing nanometer-scale materials, where maintaining a fine grain size is essential for achieving unique properties.
Key Industrial Applications
Vacuum hot pressing is chosen when material performance and purity are non-negotiable. It is a go-to process in several high-technology sectors.
Aerospace and Defense
This industry requires lightweight components that can withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stress.
Vacuum hot pressing is used to fabricate parts from high-strength composites, refractory metals, and advanced ceramics for applications like turbine components, armor, and thermal protection systems.
Advanced Electronics
The electronics industry needs components with highly specific thermal and electrical properties.
The process is used to create parts like sputtering targets for semiconductor manufacturing and ceramic substrates that require precise thermal conductivity and electrical insulation.
Medical Implants and Devices
Biocompatibility and reliability are paramount for any material placed inside the human body.
Vacuum hot pressing produces highly pure and dense ceramics and metals for use in surgical tools and long-term implants, where material integrity and inertness are critical for patient safety.
Research and Development
The versatility of the process makes it an essential tool in materials science.
Academic and industrial labs use vacuum hot presses for sintering experiments and developing novel materials, including nonmetals, carbon composites, and metal powders, under tightly controlled conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum hot pressing is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Geometric Complexity
Simple shapes like plates, blocks, and cylinders are straightforward and cost-effective to produce.
However, manufacturing more complex geometries requires highly sophisticated and expensive pressing dies. The design and fabrication of these dies can be a significant engineering challenge and cost driver.
Cycle Time and Throughput
Vacuum hot pressing is a batch process. The time required to pump down the vacuum, heat the material, press it, and cool it down results in longer cycle times compared to continuous processes.
This makes it less suitable for high-volume, low-cost commodity production and better suited for high-value, lower-volume components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material density and purity: Vacuum hot pressing is an ideal choice, especially for materials that are sensitive to oxidation.
- If your primary focus is producing complex 3D shapes at high volume: You should explore alternatives like additive manufacturing or powder injection molding, as die complexity and cost can be prohibitive.
- If your primary focus is developing novel materials with controlled grain size: The precise control over pressure, temperature, and atmosphere makes this process invaluable for research and creating fine-grained or nanostructured materials.
Ultimately, vacuum hot pressing is the definitive choice when material performance and integrity cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Materials Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Turbine components, armor, thermal protection systems | High-strength composites, refractory metals, advanced ceramics |
| Advanced Electronics | Sputtering targets, ceramic substrates | Ceramics with precise thermal/electrical properties |
| Medical Implants & Devices | Surgical tools, long-term implants | Biocompatible ceramics and metals |
| Research & Development | Novel materials, sintering experiments | Nonmetals, carbon composites, metal powders |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored vacuum hot pressing systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior density, purity, and performance for applications in aerospace, electronics, medical devices, and beyond. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your projects and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- What role does a high-performance laboratory hot press machine play in curing? Unlock Superior Composite Strength
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory hot press for F-MWCNT films? Boost Power Factor by 400%
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What role do a laboratory pressure machine and a steel die-set play in the preparation of Mn2AlB2 compacts?



















