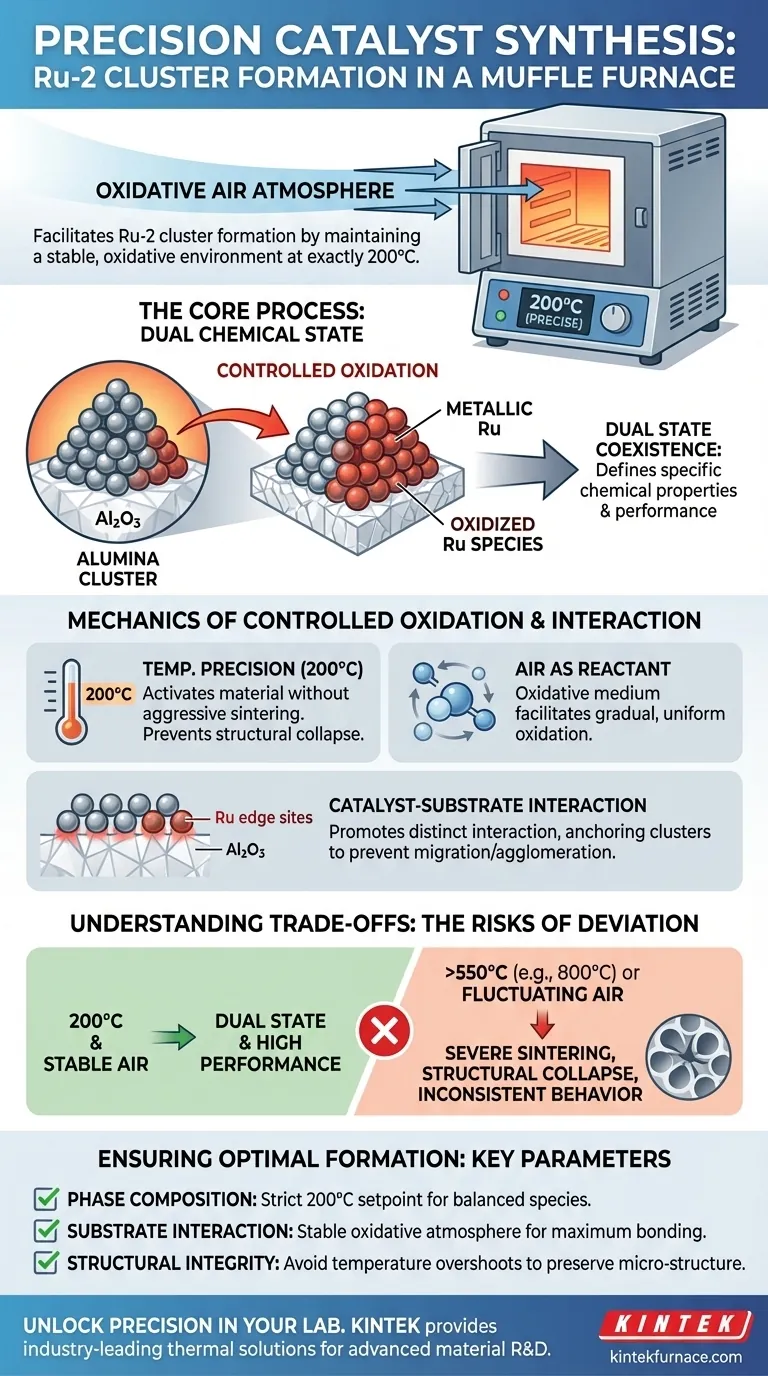
A Muffle Furnace facilitates the formation of ruthenium-2 (Ru-2) cluster catalysts by maintaining a stable, oxidative air atmosphere at a precise temperature of 200°C. This controlled environment drives a specific interaction between the ruthenium edge sites and the alumina (Al2O3) substrate, ensuring the catalyst develops the necessary chemical structure.
The core value of the muffle furnace in this process is its ability to foster the coexistence of metallic and oxidized ruthenium species within a single cluster. This dual state, achieved only through strictly controlled oxidation, is what defines the catalyst's specific chemical properties and performance.

The Mechanics of Controlled Oxidation
The Role of Temperature Precision
For Ru-2 clusters, the muffle furnace must be set to exactly 200°C. Unlike other calcination processes that require much higher heat (often 550°C or above), this specific low-temperature threshold is critical.
At this temperature, the furnace provides enough thermal energy to activate the material without causing aggressive sintering or structural collapse.
Air as an Oxidative Medium
The heated air inside the chamber does not merely transfer heat; it acts as a chemical reactant.
This oxidative medium facilitates the controlled oxidation of the ruthenium. It ensures the transition is gradual and uniform, preventing the metal from becoming fully oxidized and losing its catalytic potency.
Catalyst-Substrate Interaction
Activating Edge Sites
The thermal environment promotes a distinct interaction between the ruthenium cluster edge sites and the alumina (Al2O3) support.
This interfacial contact is vital for anchoring the clusters. It prevents them from migrating or agglomerating, which would otherwise reduce the active surface area.
Achieving the Dual Chemical State
The ultimate goal of this calcination process is to create a hybrid structure.
The furnace's stable atmosphere allows metallic and oxidized ruthenium species to exist simultaneously within the same cluster. This balance is the defining characteristic that enables the catalyst to function effectively in its intended applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Sensitivity
While 200°C is the target for Ru-2, deviations can be detrimental.
Excessive temperatures (e.g., nearing 800°C, as seen in other material syntheses) can lead to severe sintering. This causes pore structures to collapse and reduces the surface oxygen vacancies required for activity.
Atmosphere Stability
The furnace relies on a consistent air supply to maintain the oxidation rate.
If the air atmosphere fluctuates, the ratio of metallic to oxidized ruthenium may shift. This imbalance can lead to inconsistent catalytic behaviors or incomplete formation of the active sites.
Ensuring Optimal Catalyst Formation
To replicate high-performance Ru-2 clusters, focus on the following operational parameters:
- If your primary focus is Phase Composition: Ensure the furnace maintains a strict 200°C setpoint to balance metallic and oxidized species.
- If your primary focus is Substrate Interaction: Verify that the oxidative atmosphere is stable to maximize the bonding between Ru edge sites and the alumina support.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Avoid temperature overshoots, as higher heat will degrade the micro-structure and reduce specific surface area.
Precision in thermal regulation and atmosphere control is the single most important factor in synthesizing effective ruthenium-2 catalysts.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Optimal Condition | Role in Catalyst Formation |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 200°C (Precise) | Prevents sintering; balances metallic & oxidized species |
| Atmosphere | Oxidative Air | Facilitates gradual, uniform oxidation of Ru edge sites |
| Substrate | Alumina (Al2O3) | Provides anchor points to prevent cluster agglomeration |
| Core Result | Dual Chemical State | Enables coexistence of metallic and oxidized ruthenium |
| Risk Factor | >550°C - 800°C | Causes structural collapse and pore sintering |
Unlock Precision in Your Catalyst Synthesis
High-performance ruthenium catalysts demand absolute thermal accuracy and atmosphere stability. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum furnaces specifically engineered to maintain the strict tolerances required for advanced material R&D.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique low-temperature calcination or high-temp sintering needs. Whether you are optimizing Ru-2 cluster formation or developing next-generation CVD processes, KINTEK ensures your research is supported by the highest standards of structural integrity and chemical consistency.
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities? Contact our technical specialists today to find the perfect thermal solution for your application.
Visual Guide
References
- DeSheng Su, Liang Chen. Efficient amine-assisted CO2 hydrogenation to methanol co-catalyzed by metallic and oxidized sites within ruthenium clusters. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-55837-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What factors influence the price range of muffle furnaces? Key Drivers and Cost-Saving Tips
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the curing process of GaN and TiO2? Optimize Your Photoanode Sintering
- What insulation materials are used in muffle furnaces? Choose the Best for Heat Efficiency and Durability
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace facilitate the sintering of Sr4Al6O12SO4 ceramics at 1400°C? Expert Guide
- What are the design features of Box Furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment with Advanced Engineering
- What are the roles of a Muffle furnace and a UV spectrophotometer in determining the lignin content of wood?
- What other applications do muffle furnaces have? Unlock Versatile Uses in Labs and Manufacturing
- What factors affect the price of muffle furnaces? Key Drivers for Smart Lab Investment



















