At its core, the price of a muffle furnace is determined by three main technical factors: its maximum achievable temperature, the size of its internal chamber, and the sophistication of its temperature controller. While buyer expectations and specific brand features play a role, these core engineering specifications are the primary drivers of cost.
The price of a muffle furnace is a direct reflection of its technical capabilities. Understanding this relationship allows you to move beyond simply comparing prices and instead focus on acquiring the right tool for your specific application, ensuring you don't overpay for features you don't need.
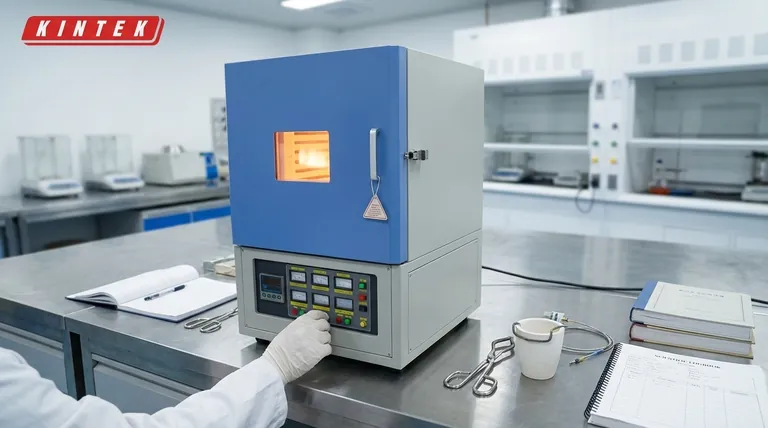

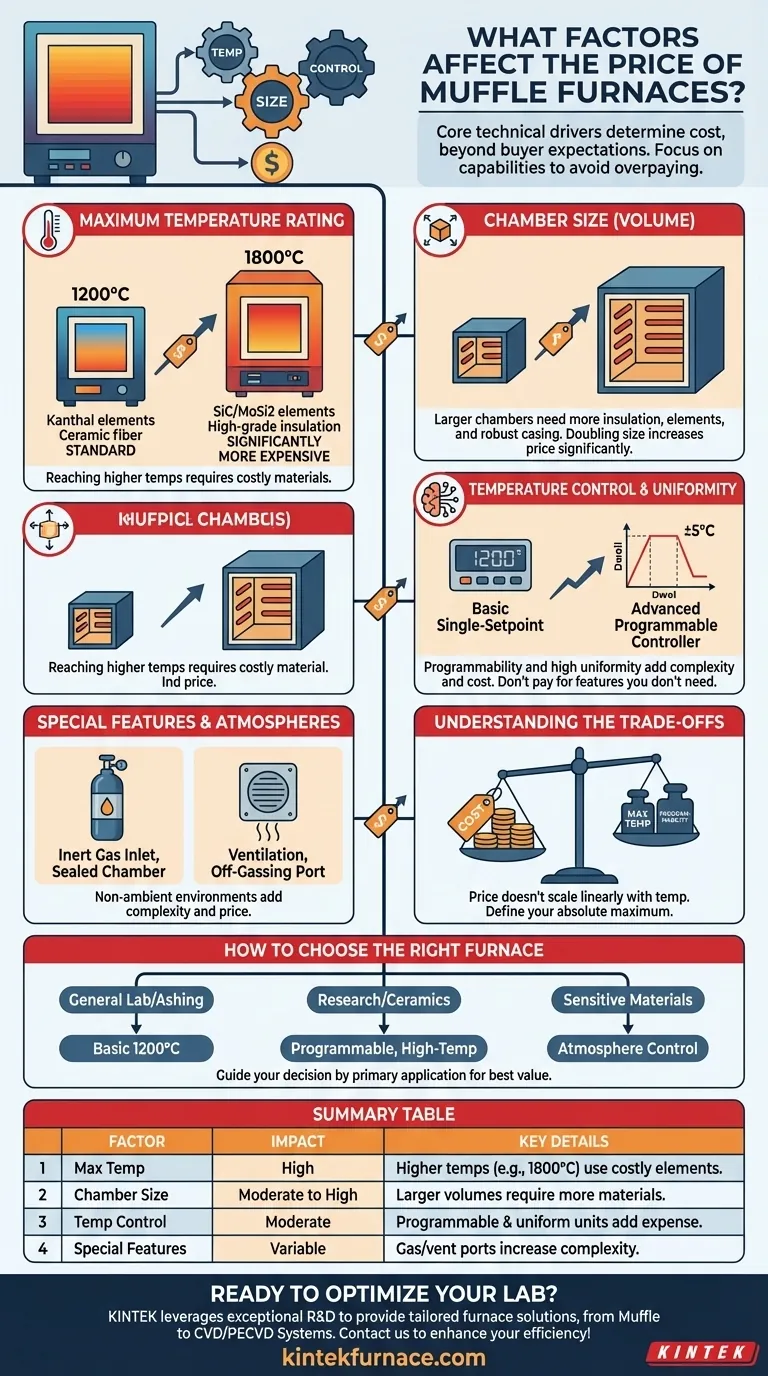
Core Technical Drivers of Muffle Furnace Cost
The final price tag on a furnace is not arbitrary; it is the sum of its engineered components. Higher-performance components required for more demanding tasks are inherently more expensive.
Maximum Temperature Rating
This is often the single most significant factor in furnace cost. Reaching and maintaining higher temperatures requires more advanced and expensive materials.
A furnace rated for 1100-1200°C typically uses durable Kanthal (iron-chromium-aluminum) heating elements and ceramic fiber insulation. This is the standard for many general-purpose applications.
To achieve temperatures of 1500-1800°C, furnaces must use silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements. These elements, along with the required higher-grade insulation, are substantially more expensive.
Chamber Size (Volume)
The internal volume of the furnace chamber directly impacts material cost. A larger chamber requires more insulation, more powerful (and more numerous) heating elements, and a larger, more robust external casing.
This relationship means that doubling the chamber volume will result in a significant, though not necessarily double, price increase.
Temperature Control and Uniformity
The "brains" of the furnace are a key cost driver. A basic controller that simply holds a single setpoint temperature is the most affordable option.
More advanced, programmable controllers that allow for multiple heating and cooling ramp rates and dwell times add to the cost. These are essential for complex material processing or ceramics firing cycles.
Furthermore, achieving high temperature uniformity (e.g., ±5°C) across the entire chamber requires more sophisticated engineering, better insulation design, and sometimes multiple heating zones, all of which increase the price.
Special Features and Atmospheres
Standard muffle furnaces operate in ambient air. If your process requires a specific environment, the cost will increase accordingly.
Features like an inert gas inlet for running processes under argon or nitrogen require sealed chambers and gas handling hardware. A port for ventilation or off-gassing adds complexity and cost to the design.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance against budget. Paying for capabilities you will never use is the most common purchasing mistake.
Cost vs. Maximum Temperature
The price of a furnace does not scale linearly with temperature. The jump from a 1200°C furnace to a 1700°C furnace can be dramatic.
Carefully define your absolute maximum required temperature. Purchasing a furnace with a significant temperature buffer "just in case" is an expensive strategy if that need never materializes.
Simplicity vs. Programmability
For applications like ashing, simple drying, or basic heat-treating, a single-setpoint controller is perfectly adequate and highly cost-effective.
Only invest in a multi-stage programmable controller if your process explicitly demands controlled ramp rates and multiple temperature holds.
A Note on Terminology
Historically, a "muffle" was a ceramic insert that protected the workpiece from the soot and fumes of fuel-fired heating. With the advent of clean electric heating elements, this physical barrier is no longer necessary.
Today, the terms muffle furnace and chamber furnace are used interchangeably to describe a front-loading box furnace with electric heating elements.
How to Choose the Right Furnace for Your Budget
Your decision should be guided by your primary application. Define your needs first, then find the furnace that meets them at the best value.
- If your primary focus is general lab work, ashing, or basic metal heat treating: A standard 1100-1200°C furnace with a basic single-setpoint controller offers the best combination of performance and value.
- If your primary focus is materials research, ceramics, or complex processing: Invest in a furnace with the necessary maximum temperature and a multi-stage programmable controller to ensure process accuracy and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is working with sensitive materials: Consider the added cost of a furnace with atmosphere control (e.g., an inert gas port) to protect your work from oxidation.
Ultimately, the most affordable furnace is the one that reliably accomplishes your technical goals for the lowest total cost of ownership.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Price | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | High | Higher temps (e.g., 1500-1800°C) use costly materials like SiC or MoSi2 elements, increasing price significantly. |
| Chamber Size | Moderate to High | Larger volumes require more insulation, elements, and casing, leading to higher costs. |
| Temperature Control | Moderate | Basic controllers are affordable; programmable ones with ramp rates and uniformity (±5°C) add expense. |
| Special Features | Variable | Inert gas inlets or ventilation ports increase complexity and price due to sealed designs. |
Ready to optimize your lab with the perfect muffle furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and achieve reliable results with the right furnace for your budget and application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















