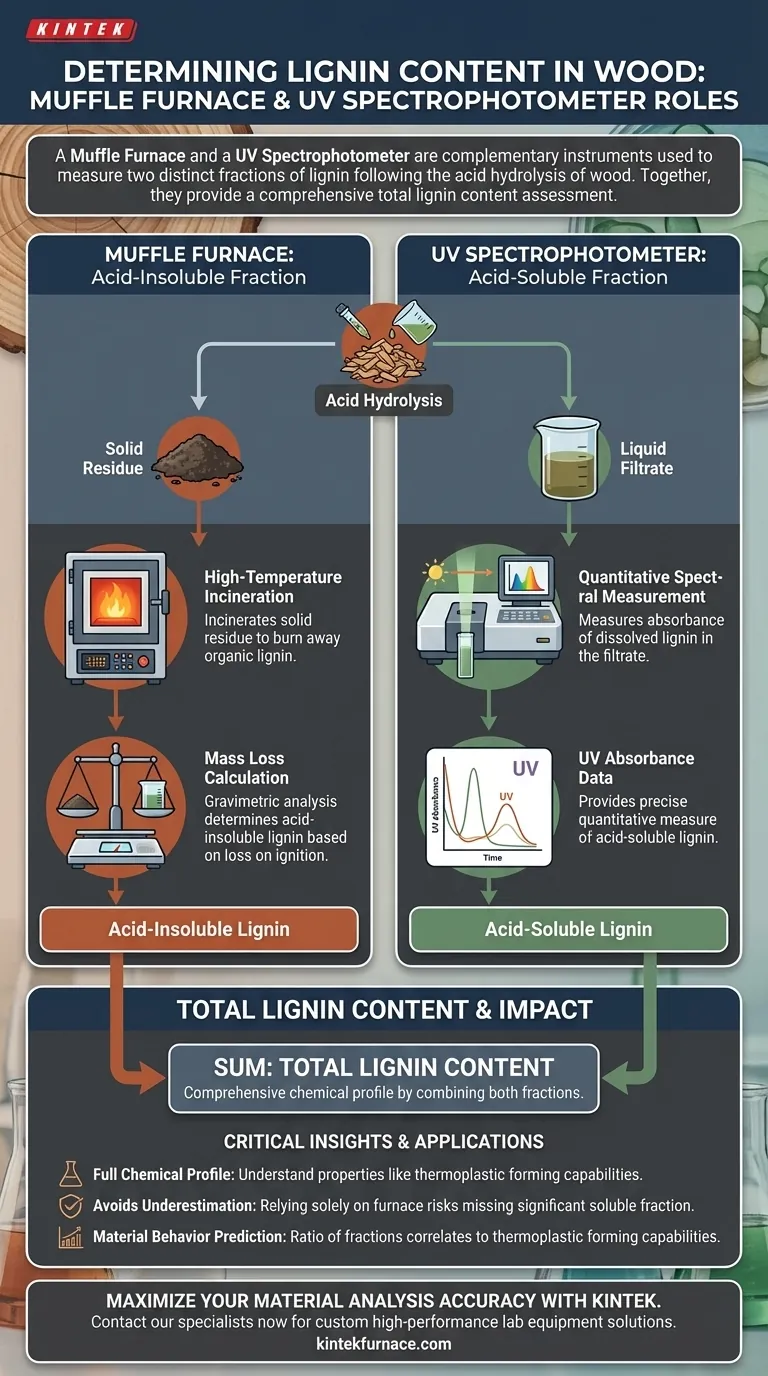
A Muffle furnace and a UV spectrophotometer are complementary instruments used to measure two distinct fractions of lignin following the acid hydrolysis of wood. The Muffle furnace determines the acid-insoluble lignin by incinerating the solid residue, while the UV spectrophotometer measures the acid-soluble lignin present in the liquid filtrate.
To achieve a comprehensive assessment of total lignin content, researchers must analyze both the solid residue and the liquid filtrate. These two instruments work in tandem to quantify the acid-insoluble and acid-soluble fractions, providing the full chemical profile necessary to understand properties like the thermoplastic forming capabilities of wood.

Quantifying the Acid-Insoluble Fraction
The Muffle furnace is the primary tool used to analyze the solid material left behind after the wood has been treated with acid.
High-Temperature Incineration
After acid hydrolysis, a solid residue remains. This residue contains the acid-insoluble lignin. The Muffle furnace is used to subject this residue to extremely high temperatures.
Determining Mass Loss
The core principle used here is loss on ignition. By incinerating the residue, the organic lignin content is burned away.
By measuring the mass loss during this combustion process, researchers can gravimetrically calculate the exact proportion of acid-insoluble lignin in the original wood sample.
Quantifying the Acid-Soluble Fraction
While the furnace handles the solids, the UV spectrophotometer is essential for analyzing the liquid component of the sample.
Analyzing the Filtrate
During acid hydrolysis, a small portion of the lignin dissolves into the acid solution. This liquid is separated from the solids and collected as filtrate.
Ignoring this fraction would lead to an underestimation of the total lignin content.
Quantitative Spectral Measurement
The UV spectrophotometer analyzes this filtrate. Lignin absorbs ultraviolet light at specific wavelengths.
By measuring the absorbance of the liquid, the instrument provides a precise quantitative measure of the acid-soluble lignin that was not captured in the solid residue.
Critical Trade-offs and Methodology
Understanding the limitations of using only one instrument is vital for accurate chemical profiling.
The Risk of Partial Data
A common pitfall in wood chemistry is relying solely on gravimetric analysis (the Muffle furnace) and assuming it represents the total lignin.
While acid-insoluble lignin often makes up the majority of the lignin content, the acid-soluble fraction can be significant depending on the wood species and treatment method.
The Impact on Material Insight
Excluding the data from the UV spectrophotometer results in an incomplete chemical profile.
According to the primary reference, a comprehensive assessment—using both tools—is required to fully understand how chemical composition influences the thermoplastic forming capabilities of the wood.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your analysis supports your broader research objectives, apply the following guidelines:
- If your primary focus is Total Lignin Quantification: You must utilize both instruments to sum the acid-insoluble (furnace) and acid-soluble (UV spec) fractions for an accurate total.
- If your primary focus is Material Behavior Prediction: You should analyze the ratio of these fractions, as the complete composition directly correlates to the wood's thermoplastic forming capabilities.
Accurate lignin determination is not about choosing between these tools, but understanding how they complete each other to reveal the full picture.
Summary Table:
| Instrument | Lignin Fraction Analyzed | Method of Measurement | Role in Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | Acid-Insoluble Lignin | Gravimetric (Loss on Ignition) | Incinerates solid residue to calculate mass loss. |
| UV Spectrophotometer | Acid-Soluble Lignin | Ultraviolet Absorbance | Measures concentration in filtrate to prevent underestimation. |
| Combined Result | Total Lignin Content | Data Summation | Provides full profile for thermoplastic forming capabilities. |
Maximize Your Material Analysis Accuracy with KINTEK
Achieving precise lignin determination requires reliable thermal processing and analytical precision. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle furnaces, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as other lab high-temp equipment, all customizable for your unique research needs.
Whether you are quantifying wood fractions or developing advanced thermoplastic materials, our equipment provides the uniform heating and durability essential for consistent results. Empower your laboratory with KINTEK’s industry-leading technology today.
Contact our specialists now to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Yujie Wang, Zhongyuan Zhao. Research on the Factors Influencing the Thermoplastic Rheological Properties of Wood. DOI: 10.3390/f16010118
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of ashing in a muffle furnace? Unlock Material Purity and Quality Insights
- How does a microwave heating system compare to traditional muffle furnaces? Fast & Safe Solid Electrolyte Regeneration
- What role does an electric muffle furnace play in the siliconization of 10Kh23N18 steel welds? Expert Thermal Insight
- Why is atmosphere control important in a Muffle furnace, and what types of atmospheres can be used?
- How is an industrial muffle furnace used to assess the ash content of biomass fibers? Master High-Temp Calcination
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace necessary for SiO2@CuO/g-C3N4 synthesis? Achieve Precision Phase Transformation
- How does a high-precision muffle furnace contribute to the evaluation of coatings? 1100°C Oxidation Test Insights
- What necessary process conditions does a muffle furnace provide for fruit powder ash analysis? Mastering 550°C Oxidation



















