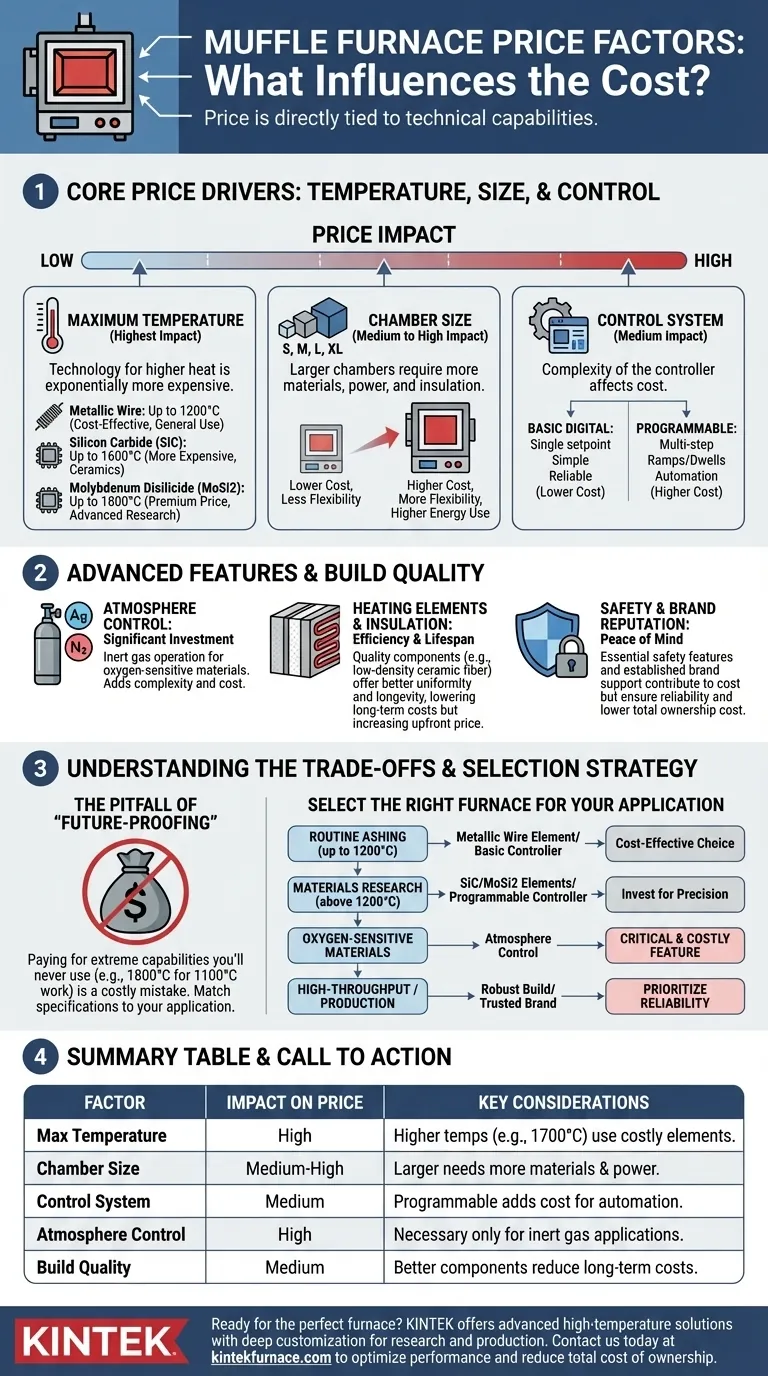
The price of a muffle furnace is directly tied to its technical capabilities. A basic, small-chamber furnace for low-temperature work can cost a few hundred dollars, while a large, high-temperature research furnace with atmosphere control can exceed $20,000. The most significant cost drivers are the maximum achievable temperature, the internal chamber size, and the sophistication of the control system.
The core principle is to match the furnace's specifications precisely to your application. The largest source of unnecessary cost is paying for capabilities—like extreme temperatures or complex programming—that your process will never require.

Core Price Drivers: Temperature, Size, and Control
The fundamental features of a furnace establish its base price. Getting these three elements right is the most critical step in managing your budget.
Maximum Temperature: The Primary Cost Factor
A furnace’s maximum temperature is its single most significant price driver. The technology required to safely generate and contain higher heat is exponentially more expensive.
Furnaces are generally categorized by the heating elements they use:
- Metallic Wire Elements: These are standard for furnaces operating up to 1000°C-1200°C. They are cost-effective and suitable for general-purpose applications like ashing and basic heat treating.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements: To reach temperatures up to 1600°C, furnaces require SiC elements. These are more expensive and are used for applications involving ceramics and some metal alloys.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Elements: For the highest range of 1700°C-1800°C, MoSi2 elements are necessary. These are found in advanced research and materials science furnaces and carry a premium price.
Chamber Size: Paying for Volume
The internal volume of the furnace chamber directly impacts the price. A larger chamber requires more raw materials, more powerful heating elements, and more extensive insulation to maintain temperature uniformity.
When selecting a size, consider your typical sample or batch size. A slightly larger chamber offers flexibility, but a significantly oversized one increases both the initial purchase price and ongoing energy consumption.
Control System: From Simple to Sophisticated
The controller is the brain of the furnace, and its complexity affects the cost.
- Basic Digital Controllers: These allow you to set a single target temperature (setpoint). They are simple, reliable, and ideal for straightforward, non-critical processes.
- Programmable Controllers: These allow you to create multi-step programs with different ramp rates, temperatures, and dwell times. This automation and precision are essential for complex material treatments but represent a significant cost increase over basic controllers.
Advanced Features and Build Quality
Beyond the core specifications, build quality and specialized features add layers of cost. These are often what separate a general-purpose unit from a specialized piece of laboratory equipment.
Atmosphere Control: A Significant Investment
A standard muffle furnace operates in an air atmosphere. If your process requires an inert atmosphere (e.g., using argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation), you need a furnace with sealed chambers and gas inlet/outlet ports.
This feature for atmosphere control dramatically increases complexity and cost and should only be specified if your application absolutely requires it.
Heating Elements and Insulation: The Engine of the Furnace
The quality of the core components determines efficiency and lifespan. Higher-quality insulation, like low-density ceramic fiber, provides better temperature uniformity and reduces heat loss, lowering long-term operating costs.
Likewise, superior heating elements may cost more upfront but offer a longer service life and better resistance to thermal shock, reducing downtime and replacement costs.
Safety and Brand Reputation
Essential safety features, such as automatic shutoff for overheating and door interlocks that cut power when opened, are standard on reputable models and contribute to the cost.
Finally, brand reputation reflects a history of reliability, customer support, and adherence to certifications. An established brand may cost more, but it often provides greater peace of mind and a lower total cost of ownership.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Making an informed decision requires weighing features against their true necessity. Miscalculating your needs is the most common and costly mistake.
The Pitfall of "Future-Proofing"
It is tempting to buy a furnace with a much higher temperature rating than you currently need "just in case." This is rarely a good investment.
An 1800°C furnace is a highly specialized tool. If your work is consistently at 1100°C, you have paid a massive premium for capability you will never use. Buy for your 95% use case, not the 5% outlier.
Programmability vs. Practicality
A fully programmable touchscreen controller offers immense power, but it can be a hindrance if your processes are simple. For routine quality control tests, a basic, robust digital controller is often faster to operate and less prone to user error.
Price vs. Total Cost of Ownership
A cheaper furnace may seem like a victory, but it can lead to higher long-term expenses. Poor insulation increases electricity bills, and low-quality heating elements require frequent and costly replacement. Consider the initial price as only one part of the furnace's total cost over its lifetime.
How to Select the Right Furnace for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your decision and filter out unnecessary features and costs.
- If your primary focus is routine ashing or basic heat treating (up to 1200°C): A standard furnace with metallic wire elements and a simple digital controller is your most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is materials research or specialized processes (above 1200°C): You must invest in a high-temperature model with SiC or MoSi2 elements and a programmable controller for precision.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive materials: Budget for a furnace with atmosphere control, as this is a critical and costly feature.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput work or production: Prioritize robust build quality and a trusted brand to ensure reliability and minimize downtime, even if the initial investment is higher.
Defining your exact technical requirements is the most effective way to control costs and secure the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Price | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | High | Higher temps (e.g., 1700°C) use costly elements like MoSi2, increasing price significantly. |
| Chamber Size | Medium to High | Larger chambers need more materials and power, raising initial and operating costs. |
| Control System | Medium | Basic controllers are cheaper; programmable ones add cost for automation and precision. |
| Atmosphere Control | High | Adds complexity and expense; only necessary for inert gas applications. |
| Build Quality | Medium | Better insulation and elements reduce long-term costs but increase upfront price. |
Ready to find the perfect muffle furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials research, quality control, or production, we can help you optimize performance and reduce total cost of ownership. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















