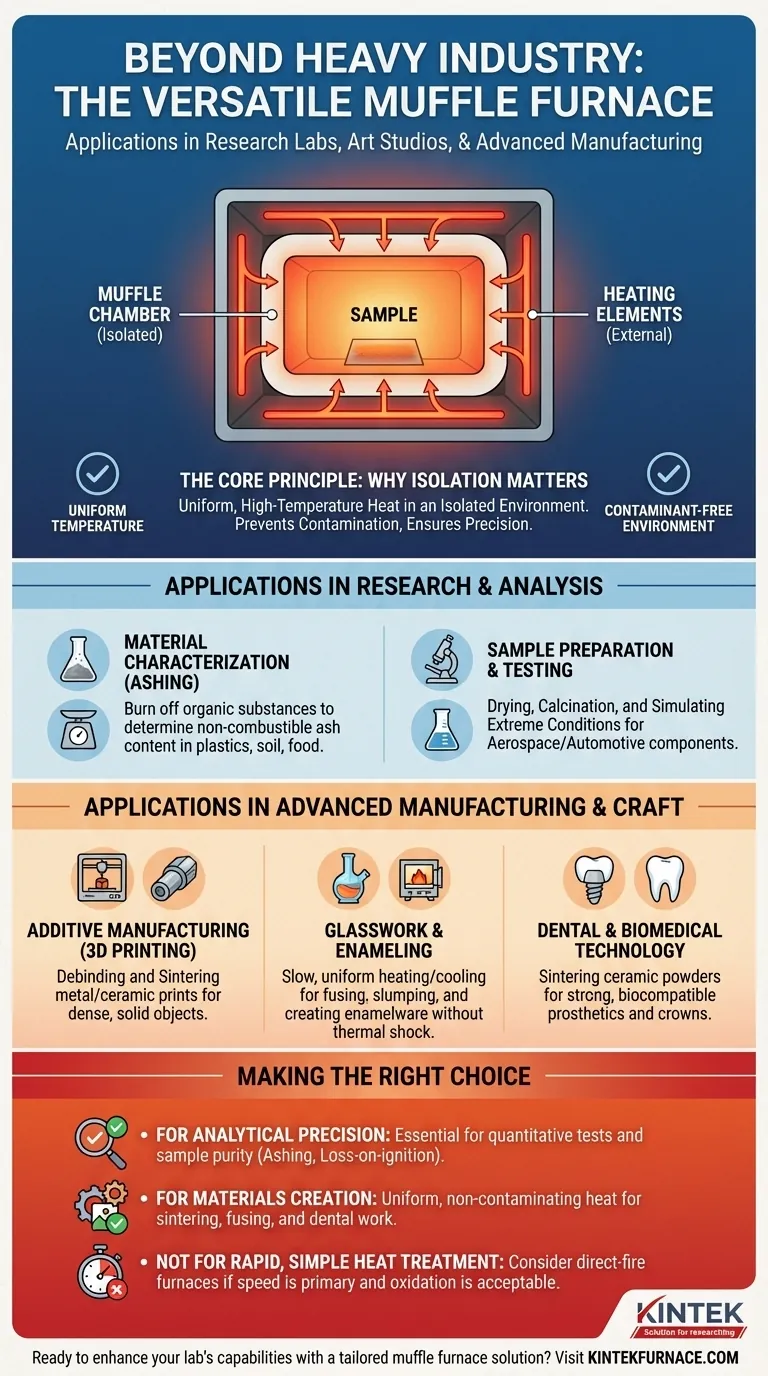
Beyond heavy industry, the muffle furnace is a surprisingly versatile tool found in research labs, art studios, and advanced manufacturing facilities. Its applications extend far beyond simple metal treatment, encompassing everything from creating dental crowns and testing aerospace components to post-processing 3D-printed parts and analyzing the ash content of plastics.
The core value of a muffle furnace is its ability to deliver uniform, high-temperature heat within a chamber that is isolated from the heating elements. This prevents contamination and provides precise thermal control, making it an indispensable tool for any process where material purity and structural integrity are paramount.

The Core Principle: Why Isolation Matters
A standard furnace heats a chamber directly, exposing the material to the heating elements and potential byproducts of combustion. A muffle furnace works differently.
The "Muffle" Design
The term "muffle" refers to the inner chamber that contains the material being heated. This chamber is a separate, sealed box made from a high-temperature ceramic.
The heating elements are located outside this muffle, heating it from all sides. This design ensures the sample is never directly exposed to the heat source, providing two critical advantages: uniform temperature and a contaminant-free environment.
Applications in Research and Analysis
The precision of a muffle furnace makes it a cornerstone of the modern laboratory for quantitative analysis and material testing.
Material Characterization (Ashing)
Many quality control and research processes rely on ashing. The furnace heats a sample to a high temperature to burn off all organic and volatile substances.
What remains is the non-combustible ash content. This is critical for determining the filler content in plastics, analyzing soil or sludge composition, and ensuring food products meet standards.
Sample Preparation for Analysis
In biomedical and materials science, samples must often be prepared for further analysis. A muffle furnace can be used to dry samples, induce specific chemical changes (calcination), or prepare materials for microscopic examination.
Simulating Extreme Conditions
Engineers in fields like aerospace or automotive use muffle furnaces to test a material's resistance to extreme heat or fire. By subjecting a component to a controlled temperature profile, they can verify its performance and safety under harsh operating conditions.
Applications in Advanced Manufacturing and Craft
The ability to create without contaminating is essential for producing high-value, detailed objects.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
For metal and ceramic 3D printing, a printed object is often in a "green" state, where material particles are held together by a binding agent. The object is then placed in a muffle furnace for two key steps.
First is debinding, where the furnace gently heats the part to burn away the binder. Second is sintering, where the temperature is increased to just below the material's melting point, causing the particles to fuse into a dense, solid object.
Glasswork and Enameling
Artists and craftspeople use muffle furnaces for glass fusing, slumping, and creating enamelware. The slow, uniform heating and cooling cycles prevent thermal shock, which would otherwise cause the glass or enamel to crack.
Dental and Biomedical Technology
The creation of ceramic crowns, bridges, and other dental prosthetics relies on sintering ceramic powders in a highly controlled muffle furnace. This process creates strong, biocompatible, and aesthetically pleasing results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the muffle furnace is not the right tool for every heating task. Understanding its limitations is key.
Atmosphere Control is a Specialty
A standard muffle furnace operates with a normal air atmosphere. If your process requires an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation, you need a more specialized and expensive controlled-atmosphere furnace.
Heating and Cooling Rates
The ceramic muffle has significant thermal mass. This means muffle furnaces generally heat up and cool down more slowly than direct-fire furnaces or kilns. This is an advantage for preventing thermal shock but a disadvantage if speed is the primary concern.
Not for All Heat Treatment
For simple heat treatments like hardening or tempering a steel tool where some surface discoloration (oxidation) is acceptable, a simpler, faster furnace or even a forge may be more practical. The muffle furnace is best reserved for when purity and uniformity are non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a muffle furnace is the correct tool, consider your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical precision: A muffle furnace is essential for quantitative tests like ashing or loss-on-ignition where sample purity cannot be compromised.
- If your primary focus is materials creation: It provides the uniform, non-contaminating heat needed for sintering 3D prints, fusing glass, or creating dental ceramics without introducing defects.
- If your primary focus is rapid, simple heat treatment: For tasks where surface oxidation is not a concern, a less complex and faster-heating direct-fire furnace may be a more efficient choice.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is the definitive tool when a process demands precise temperature control in a chemically isolated environment.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Research & Analysis | Ashing, sample preparation, material testing | Precise temperature control, contaminant-free environment |
| Advanced Manufacturing | Sintering 3D-printed parts, glass fusing, enameling | Uniform heating, prevents thermal shock |
| Dental & Biomedical | Creating ceramic crowns, prosthetics | Biocompatible results, high structural integrity |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Testing material heat resistance | Simulates extreme conditions, ensures safety |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a tailored muffle furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior purity, precision, and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and drive your projects forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















