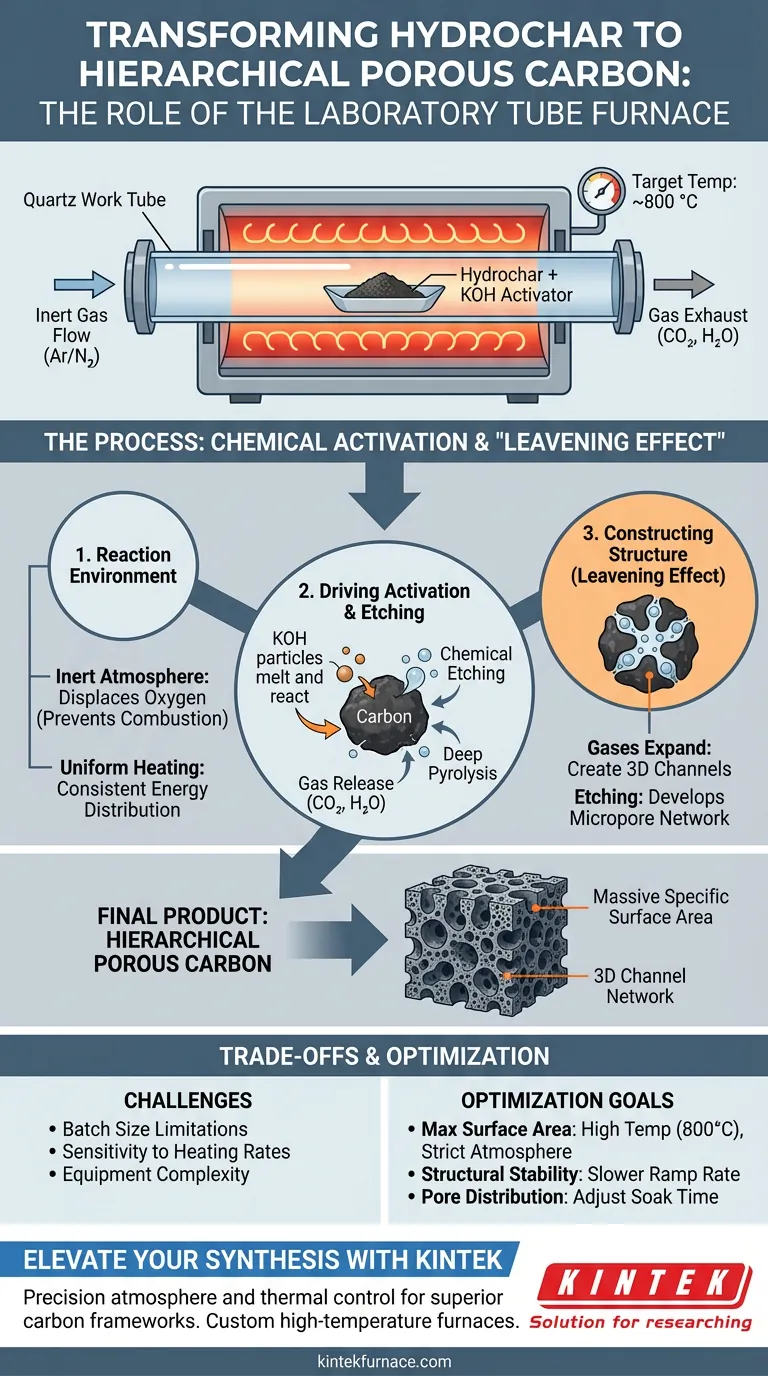
A laboratory tube furnace facilitates the transformation of hydrochar into hierarchical porous carbon by creating a strictly controlled thermal and atmospheric environment essential for chemical etching. It heats hydrochar mixed with an activator, such as potassium hydroxide (KOH), to high temperatures (typically 800 °C) under an inert gas flow, triggering reactions that sculpt the carbon's internal structure.
The tube furnace enables a "leavening effect" by maintaining an oxygen-free zone where chemical decomposition releases gases; these gases expand to construct a vast network of 3D channels and micropores without burning away the carbon framework.
Establishing the Reaction Environment
The Role of Inert Atmosphere
For hierarchical porous carbon to form, oxidation must be prevented. The tube furnace utilizes a continuous flow of inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen, to displace oxygen within the work tube.
Preventing Combustion
Without this inert environment, the high temperatures required for activation would simply cause the hydrochar to burn into ash. The furnace ensures the material undergoes thermochemical decomposition rather than combustion.
Uniform Heating Profile
Heating elements surround the cylindrical tube, providing consistent thermal energy along the sample's length. This uniformity is critical for ensuring that the chemical activator (KOH) reacts evenly across the entire hydrochar sample.
Driving the Chemical Activation
Triggering Chemical Etching
As the furnace ramps up to target temperatures (e.g., 800 °C), the KOH melts and begins to react chemically with the hydrochar. This process is known as chemical etching, where the activator "eats away" specific parts of the carbon skeleton.
Thermal Decomposition
Simultaneously, the precise heat facilitates deep pyrolysis. This removes volatile components from the hydrochar, leaving behind a stable, rigid carbon framework ready to be restructured.
Release of Activation Gases
The reaction between the carbon and the KOH at these temperatures generates gases, specifically carbon dioxide ($CO_2$) and water vapor ($H_2O$). The controlled release of these gases is the engine of pore formation.
Constructing the Hierarchical Structure
The Leavening Effect
The gases generated during activation cannot escape instantly; instead, they expand within the material. This creates a leavening effect, similar to how yeast makes bread rise.
Formation of 3D Channels
As these gases force their way out, they create three-dimensional hierarchical channels. These macro-channels allow fluids or electrolytes to easily access the deeper internal structure of the material.
Developing the Micropore Network
Within the walls of these larger channels, the etching process creates a vast network of micropores. This results in a material with a massive specific surface area and a highly amorphous structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Batch Size Limitations
Tube furnaces are ideal for research and small-scale synthesis but are limited in volume. The geometry of the tube restricts the amount of hydrochar that can be processed uniformly in a single run.
Sensitivity to Heating Rates
The quality of the final carbon is highly sensitive to the heating ramp rate. If the furnace heats too quickly, the "leavening" gases may release too violently, collapsing the pore structure rather than building it.
Equipment Complexity
Achieving the correct hierarchy requires precise synchronization of gas flow, temperature ramping, and hold times. Miscalibrating the furnace controller can lead to incomplete activation or excessive burn-off of the carbon yield.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a tube furnace for carbon activation, align your parameters with your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is maximizing specific surface area: Prioritize higher activation temperatures (around 800 °C) and ensure the inert atmosphere is strictly maintained to allow aggressive micropore etching.
- If your primary focus is structural stability: Use a slower heating ramp rate to allow volatile gases to escape gradually, preserving the integrity of the carbon walls.
- If your primary focus is pore size distribution: Adjust the "soak time" (the duration the furnace holds the peak temperature) to control the depth of the chemical etching process.
Success in creating hierarchical porous carbon relies not just on high heat, but on the precise orchestration of atmosphere and time.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Carbon Activation | Impact on Material |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Displaces oxygen using Argon/Nitrogen | Prevents combustion; ensures thermochemical decomposition |
| Uniform Heating | Consistent thermal energy distribution | Ensures even KOH reaction across the hydrochar skeleton |
| Temperature Control | Precise ramping to ~800 °C | Triggers chemical etching and deep pyrolysis |
| Gas Management | Controlled release of CO2 and H2O | Creates a "leavening effect" to build 3D porous channels |
Elevate Your Materials Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between carbon ash and a high-performance hierarchical framework. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Tube, Vacuum, CVD, and Muffle systems designed to give you total control over atmosphere and thermal profiles.
Whether you are optimizing micropore networks or scaling up small-batch research, our customizable high-temperature furnaces provide the stability your lab requires.
Ready to refine your activation process? Contact KINTEK today for a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Marija Ercegović, Jugoslav Krstić. Efficient Adsorption of Pollutants from Aqueous Solutions by Hydrochar-Based Hierarchical Porous Carbons. DOI: 10.3390/w16152177
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a vertical tube resistance furnace in WEEE and copper co-smelting? Precision Smelting Solutions
- How do tube furnaces contribute to energy efficiency? Boost Your Lab's Performance with Advanced Thermal Solutions
- Why is it necessary to precisely control the oxygen flow rate in a tube furnace? Optimize Li-Deficient Composites
- Why are three-zone tube furnaces in high demand? Unlock Precision for Advanced Materials
- What is the technical significance of phased high-temperature annealing in a tube furnace for 3D Porous Graphene?
- How is a vertical alumina tube resistance furnace applied in the hydrogen reduction of bauxite residue particles?
- What critical environmental conditions does a high-temperature tube furnace provide? Optimize CPOF-4/5 Cross-Linking
- What are the key features of high temperature tube furnaces? Unlock Precision for Material Science



















