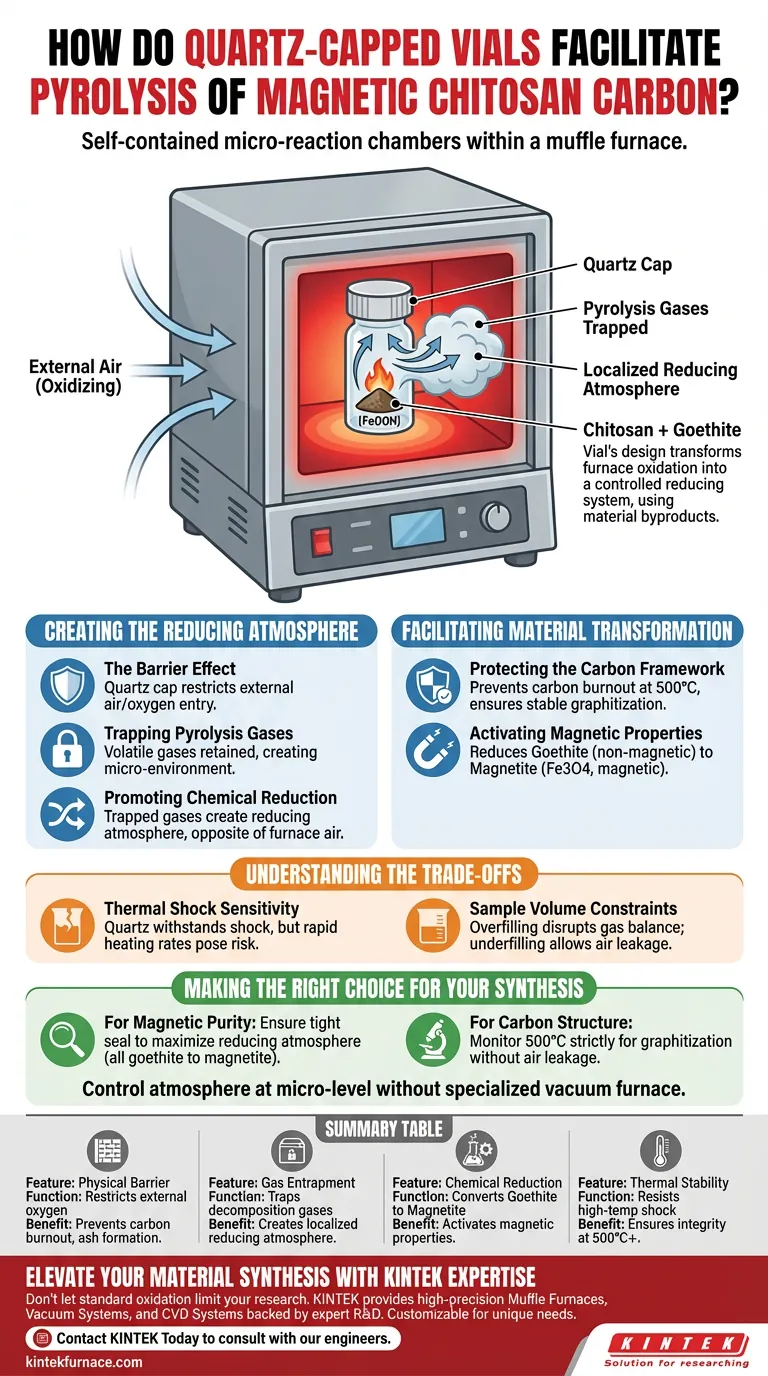
Quartz-capped vials function as self-contained micro-reaction chambers. By physically restricting the entry of external air within the muffle furnace, they trap gases generated during decomposition to create a localized reducing atmosphere. This specific environment is critical for preventing carbon burnout and facilitating the chemical reduction required for magnetization.
The vial’s design transforms the standard oxidation environment of a muffle furnace into a controlled reducing system, utilizing the material's own byproducts to drive the synthesis of magnetic carbon.
Creating the Reducing Atmosphere
The Barrier Effect
The quartz cap acts as a critical physical gatekeeper during the heating process.
It significantly restricts the entry of external air and oxygen from the muffle furnace into the sample area.
This isolation is necessary because standard muffle furnaces generally facilitate oxidation, which would be detrimental to this specific synthesis.
Trapping Pyrolysis Gases
As the chitosan undergoes pyrolysis, it releases volatile gases.
The nearly closed setup of the vial retains these gases, forcing them to interact with the sample rather than escaping immediately.
This accumulation converts the interior of the vial into a localized micro-environment.
Promoting Chemical Reduction
The trapped gases create a reducing atmosphere, which is chemically opposite to the oxidizing air outside the vial.
This environment enables specific chemical changes that cannot occur in open-air calcination.
It ensures the reaction is driven by the internal chemistry of the decomposing material, not the external furnace atmosphere.
Facilitating Material Transformation
Protecting the Carbon Framework
At the calcination temperature of 500°C, unprotected carbon is highly susceptible to burning away.
The vial prevents excessive oxidation, ensuring the chitosan successfully decomposes into a stable, graphitized carbon layer.
Without the cap, the carbon backbone would likely degrade into ash or gas.
Activating Magnetic Properties
The reducing micro-environment is essential for transforming the iron components.
It drives the chemical reduction of goethite (gamma-FeOOH) found in the sludge.
This process successfully converts the non-magnetic iron into magnetic magnetite (Fe3O4), integrating magnetic properties directly into the carbon structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Shock Sensitivity
Quartz is selected specifically for its engineering to withstand thermal shocks.
However, the rapid heating rates common in pyrolysis can still pose a risk to the structural integrity of the containment if the material quality is low.
Sample Volume Constraints
The efficacy of this method relies on the "micro" nature of the reaction chamber.
Overfilling the vial may disrupt the balance of generated gases required to maintain the reducing environment.
Conversely, underfilling might allow too much residual air to remain inside, potentially affecting the purity of the magnetic phase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Synthesis
To ensure consistent production of magnetic chitosan carbon, apply the following guidelines:
- If your primary focus is Magnetic Purity: Ensure the vial cap creates a tight seal to maximize the reducing atmosphere, converting all goethite to magnetite.
- If your primary focus is Carbon Structure: Monitor the temperature strictly at 500°C to allow for graphitization without burning off the material due to air leakage.
By controlling the atmosphere at the micro-level, you enable complex chemical synthesis without requiring a specialized vacuum furnace.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Pyrolysis | Benefit to Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Barrier | Restricts external oxygen entry | Prevents carbon burnout and ash formation |
| Gas Entrapment | Traps volatile decomposition gases | Creates a localized reducing atmosphere |
| Chemical Reduction | Converts Goethite to Magnetite | Activates magnetic properties in carbon |
| Thermal Stability | Resists high-temp thermal shock | Ensures containment integrity at 500°C+ |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Expertise
Don't let standard oxidation limit your research. KINTEK provides high-precision laboratory solutions designed to solve complex thermal processing challenges. Whether you require standard Muffle Furnaces, Vacuum Systems, or CVD Systems, our equipment is backed by expert R&D and is fully customizable for your unique material needs.
Ready to achieve superior magnetic purity and carbon structure? Contact KINTEK today to consult with our engineers on the perfect high-temperature setup for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Huiping Zeng, Dong Li. Facile Preparation of Magnetic Chitosan Carbon Based on Recycling of Iron Sludge for Sb(III) Removal. DOI: 10.3390/su16072788
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is high-precision constant temperature heating equipment required when preparing 17-4 PH stainless steel composite?
- What is the importance of using a vacuum drying oven for MoS2/rGO battery electrodes? Maximize Battery Performance
- What is the function of a high-temperature heat treatment furnace? Optimize AlCuCrFe2NiTi0.25 Alloy Properties
- Why Use a Vacuum Oven for Cu-Cu2O/g-C3N4 Catalysts? Preserve Purity and Structural Integrity
- What role does a laboratory precision ventilated oven play in the post-processing of dispersed carbon nanotubes?
- Why is a drying oven with precise temperature control necessary for NiO-CGO anode supports? Ensure Cell Integrity
- Why is a pre-melting process required in phase equilibrium studies? Reset Your Sample for Precise Results
- Why is the use of high-temperature furnace systems critical for delta-MnO2 development? Master Atomic Engineering



















