At its core, vacuum hot pressing sintering furnaces are primarily classified into three main temperature ranges. These common groupings are low-temperature (up to approximately 800-1200°C), medium-temperature (up to 1600-1700°C), and high-temperature (up to 2400°C and beyond). While the exact temperature boundaries can vary slightly between manufacturers, this three-tier system is the industry standard for categorization.
The temperature classification of a furnace is not an arbitrary label; it is a direct reflection of the materials used in its construction, particularly the heating elements and insulation. This fundamentally determines the types of materials the furnace can process and dictates its operational cost and complexity.
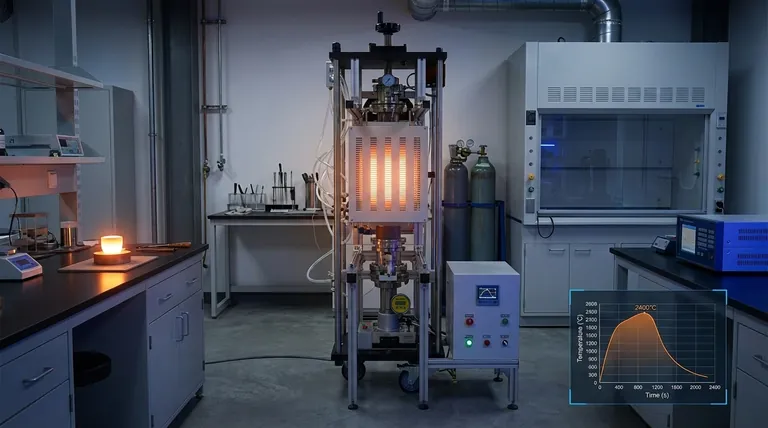
The Primary Temperature Classifications
Understanding these tiers is the first step in selecting the correct equipment for a specific material science or manufacturing goal. Each class is engineered for a distinct set of applications.
Low-Temperature Range (Up to ~1200°C)
Furnaces in this category are typically used for processes like brazing, annealing, and sintering of metals with lower melting points. They are also suitable for processing certain types of polymers and glass-ceramics.
The design of these furnaces is relatively straightforward, often employing robust and cost-effective heating elements like nickel-chromium (NiCr) or Kanthal (FeCrAl) alloys.
Medium-Temperature Range (~1200°C to 1700°C)
This is a very common range for sintering a wide variety of materials, including many technical ceramics like alumina (Al₂O₃) and zirconia (ZrO₂), as well as for powder metallurgy applications.
These furnaces require more advanced heating elements capable of withstanding higher temperatures, such as silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi₂).
High-Temperature Range (Above 1700°C)
This category is reserved for processing the most advanced and demanding materials. Applications include sintering non-oxide ceramics like silicon carbide (SiC) and silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), as well as processing refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum.
Operating at these extreme temperatures necessitates specialized heating elements made from graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten, which must be protected from oxidation by a high-vacuum or pure inert gas environment.
Why Temperature Dictates Furnace Design
The maximum operating temperature is the single most critical factor in a furnace's design. It creates a cascade of engineering decisions that affect every component.
The Role of Heating Elements
The material of the heating element must be able to withstand the target temperature without degrading. A low-temperature NiCr element would simply melt or rapidly oxidize if used in a high-temperature application.
Conversely, using an expensive graphite or tungsten element for a low-temperature process is economically inefficient and unnecessary.
The Importance of Insulation
The insulation package must also be rated for the maximum temperature. Low-temperature furnaces might use ceramic fiber boards, while high-temperature systems often rely on layers of graphite felt or reflective metallic heat shields.
Poor insulation leads to heat loss, inefficiency, and potential damage to the furnace chamber and external components.
The Impact on Operating Environment
High-temperature heating elements like graphite and tungsten will rapidly burn away in the presence of oxygen. This is a primary reason these furnaces must operate in a vacuum or be backfilled with an inert gas like argon.
This requirement adds significant complexity, demanding robust vacuum pumps, seals, and control systems that are less critical in lower-temperature furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace is a matter of balancing capability with practical constraints. Higher temperatures come with significant trade-offs.
Cost vs. Capability
There is an exponential increase in cost with temperature capability. The exotic materials required for high-temperature elements (graphite, tungsten) and insulation are far more expensive than the materials used in low or medium-temperature furnaces.
Operational Complexity
High-temperature systems demand more rigorous operational procedures. Managing the vacuum levels, gas purity, and precise heating and cooling ramps is critical to protect the furnace and ensure process repeatability.
Maintenance and Consumables
Components in high-temperature furnaces, especially the heating elements and some types of insulation, are considered consumables with a finite lifespan. Their replacement contributes to the overall cost of ownership.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific material and process goals will directly determine the necessary furnace class.
- If your primary focus is metal annealing, brazing, or basic powder metallurgy: A low-temperature furnace (up to 1200°C) offers the most reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is sintering common technical ceramics or advanced metal alloys: A medium-temperature furnace (up to 1700°C) provides the versatile performance needed for a broad range of materials.
- If your primary focus is developing non-oxide ceramics, refractory metals, or novel composites: A high-temperature furnace (above 1700°C) is essential, requiring investment in both the equipment and its operational expertise.
Ultimately, aligning the furnace's temperature capability with your material's processing requirements is the key to achieving successful and economical results.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Typical Applications | Common Heating Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Temp (Up to ~1200°C) | Metal brazing, annealing, low-melting-point sintering | Nickel-Chromium (NiCr), Kanthal (FeCrAl) alloys |
| Medium-Temp (~1200°C to 1700°C) | Technical ceramics (Al₂O₃, ZrO₂), powder metallurgy | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) |
| High-Temp (Above 1700°C) | Non-oxide ceramics (SiC, Si₃N₄), refractory metals | Graphite, Molybdenum, Tungsten |
Need a Vacuum Hot Pressing Sintering Furnace Tailored to Your Temperature Requirements?
At KINTEK, we understand that selecting the right furnace is critical to your material science or manufacturing success. Our expertise in high-temperature furnace design, backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, ensures you get a solution that precisely matches your needs—whether for low-temperature brazing, medium-temperature ceramic sintering, or high-temperature processing of advanced composites.
We offer a comprehensive range of high-temperature furnaces, including advanced Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, with deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our experts today to find the optimal furnace solution for your lab.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does precise temperature control affect Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Master Titanium Hot Pressing Accuracy
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density



















