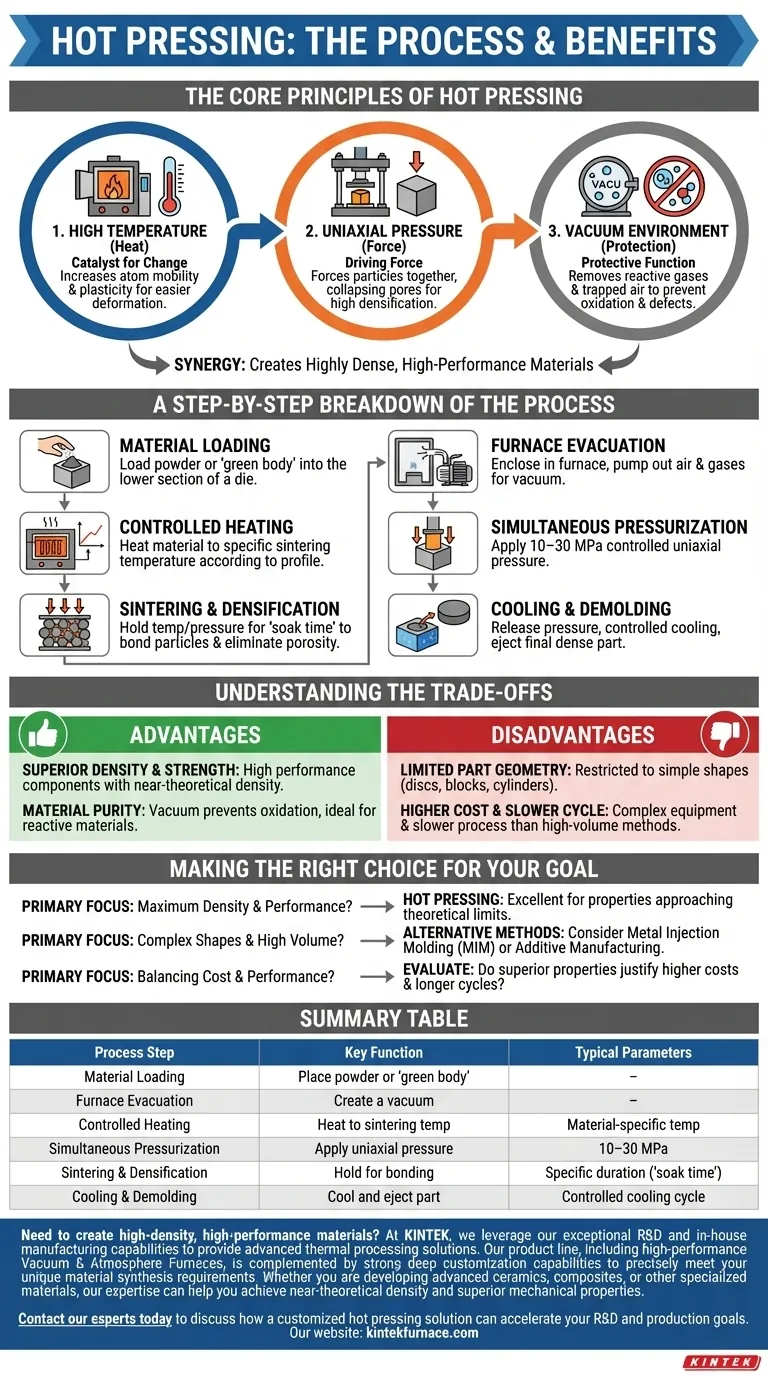
At its core, hot pressing is a materials manufacturing process that consolidates powders or pre-formed parts by simultaneously applying high temperature and uniaxial pressure within a controlled atmosphere. The typical process involves loading the material into a die, evacuating the surrounding chamber to create a vacuum, heating the material to its sintering temperature, applying a pressure of 10–30 MPa, and holding it there until the desired density is achieved before cooling.
The fundamental purpose of hot pressing is to leverage the combined effects of heat, pressure, and a vacuum environment. This synergy enables the creation of highly dense, high-performance materials with superior mechanical properties that are often impossible to achieve through pressure or heat alone.

The Core Principles of Hot Pressing
To understand the process, you must first understand the three critical factors at play and how they interact to transform loose material into a solid, dense part.
The Role of High Temperature
Heat is the catalyst for change. By raising the material to its sintering temperature, its atoms become more mobile and its structure becomes more plastic, or easier to deform.
This elevated temperature significantly lowers the material's resistance to densification, allowing particles to bond and diffuse into one another more readily.
The Function of Uniaxial Pressure
While heat makes the material receptive to change, pressure is the driving force. A uniaxial pressure is applied through a simple die, physically forcing the material's particles together.
This external force dramatically accelerates the rate of densification by collapsing pores and eliminating voids between particles. This is the key to achieving a final part that is close to its near-theoretical density.
The Importance of a Vacuum Environment
The vacuum serves a critical protective function. By evacuating the chamber, reactive gases like oxygen are removed, preventing oxidation and contamination that could compromise the material's final properties.
Furthermore, the vacuum helps remove any gases that might otherwise become trapped within the material's structure, which would inhibit full densification and create internal defects.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
Modern hot pressing is a highly automated and precise operation, but it follows a consistent sequence of fundamental steps.
Step 1: Material Loading
The process begins by loading the starting material, typically a powder or a pre-compacted part (a "green body"), into the lower section of a die.
Step 2: Furnace Evacuation
The die is enclosed within a furnace chamber. Air and other gases are then pumped out to create the low-pressure vacuum environment essential for the process.
Step 3: Controlled Heating
The furnace then heats the die and the material inside it according to a precise temperature profile, bringing it up to the target sintering temperature for that specific material.
Step 4: Simultaneous Pressurization
As the material reaches the correct temperature, a hydraulic or mechanical press applies a controlled, uniaxial pressure through a punch or ram onto the material.
Step 5: Sintering and Densification
The material is held at the target temperature and pressure for a specific duration. During this "soak time," the particles bond and consolidate, eliminating porosity and transforming the loose powder into a dense, solid component.
Step 6: Cooling and Demolding
After the soak time is complete, the pressure is released, and the furnace begins a controlled cooling cycle. Once cooled, the newly formed, dense part is ejected or demolded from the die.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, hot pressing is a specialized technique with specific limitations that must be considered. Understanding these trade-offs is key to determining if it is the right solution for your application.
Advantage: Superior Density and Strength
The primary benefit is the ability to produce components with exceptionally high density and, consequently, superior mechanical strength, hardness, and performance.
Disadvantage: Limited Part Geometry
Because pressure is applied along a single axis (uniaxially), hot pressing is generally restricted to producing parts with simple shapes, such as discs, blocks, or cylinders. Complex geometries are not feasible.
Advantage: Material Purity
Operating in a vacuum prevents oxidation, making the process ideal for reactive materials or applications where ultimate purity is a requirement.
Disadvantage: Higher Cost and Slower Cycle Times
Hot press machines are complex and expensive. The process of heating, soaking, and cooling is also inherently slower than other high-volume manufacturing methods like conventional sintering or powder metallurgy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use hot pressing depends entirely on your project's specific performance requirements and constraints.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and mechanical performance: Hot pressing is an excellent choice for creating parts with properties that approach the theoretical limits of the material.
- If your primary focus is producing complex shapes in high volumes: You should investigate alternative methods like metal injection molding (MIM) or additive manufacturing (3D printing).
- If your primary focus is balancing cost and performance: You must evaluate if the superior properties justify the higher equipment costs and longer cycle times compared to less complex methods.
Choosing the right manufacturing process begins with a clear understanding of your end goal.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Function | Typical Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Material Loading | Place powder or 'green body' into die. | - |
| Furnace Evacuation | Create a vacuum to prevent oxidation. | - |
| Controlled Heating | Heat material to sintering temperature. | Material-specific sintering temperature |
| Simultaneous Pressurization | Apply uniaxial pressure to densify material. | 10-30 MPa |
| Sintering & Densification | Hold temperature/pressure for particle bonding. | Specific duration ('soak time') |
| Cooling & Demolding | Cool and eject the final, dense part. | Controlled cooling cycle |
Need to create high-density, high-performance materials?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities to provide advanced thermal processing solutions. Our product line, including high-performance Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique material synthesis requirements.
Whether you are developing advanced ceramics, composites, or other specialized materials, our expertise can help you achieve near-theoretical density and superior mechanical properties.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a customized hot pressing solution can accelerate your R&D and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum or protective atmosphere reduce oxidation in molten metals? Prevent Oxide Inclusions for Stronger Metals
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- What materials can be densified using a vacuum press and what are their applications? Unlock High-Performance Material Densification
- How does precise temperature control affect Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Master Titanium Hot Pressing Accuracy



















