In simple terms, vacuum hot pressing is a high-performance manufacturing process that uses a combination of intense heat, mechanical pressure, and a vacuum to bond, densify, or shape materials. By removing air and other contaminants, the process creates materials with superior strength, density, and purity that would be impossible to achieve in a normal atmosphere.
The core purpose of vacuum hot pressing is not just to heat and squeeze materials together, but to do so in a perfectly controlled, contaminant-free environment. This vacuum is the key that unlocks exceptional material properties by preventing oxidation and promoting stronger, cleaner bonds.
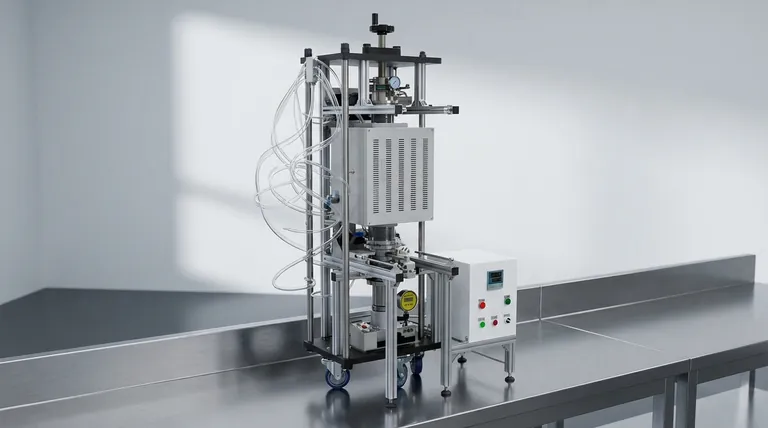

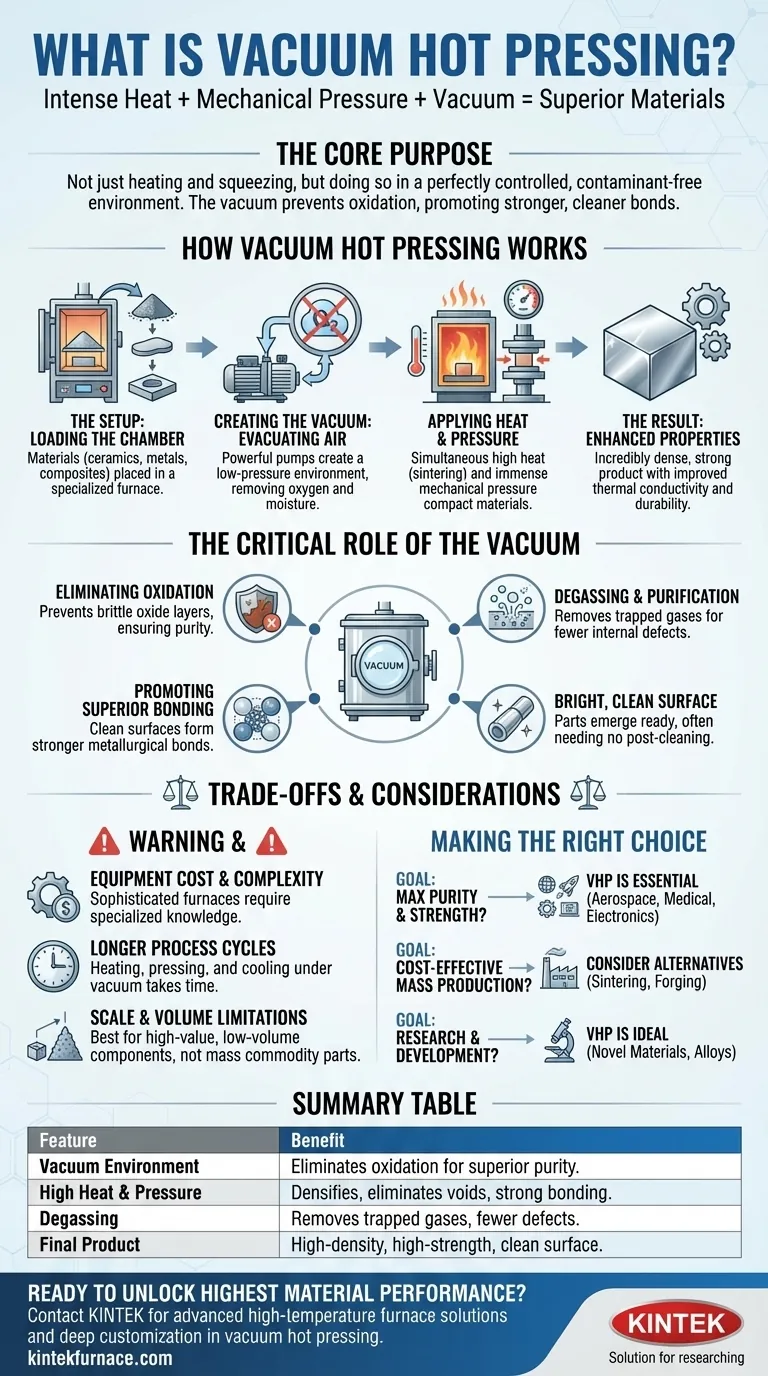
How Vacuum Hot Pressing Works
The process is a precise, multi-stage operation designed for maximum control over the final material properties. It combines the principles of metallurgy, material science, and vacuum technology.
The Setup: Loading the Chamber
Materials, often in powder or pre-formed shapes, are placed inside a specialized furnace chamber. This can include ceramics, metals, carbon composites, or layers of different materials intended for bonding.
Creating the Vacuum: Evacuating the Air
The chamber is sealed, and powerful pumps remove the air, creating a low-pressure vacuum environment. This step is critical for removing oxygen, moisture, and other reactive gases that could compromise the material's integrity at high temperatures.
Applying Heat and Pressure
Once the vacuum is established, the materials are heated to a specific temperature, often high enough to soften them or initiate sintering reactions. Simultaneously, a mechanical press exerts immense pressure, compacting the material, eliminating voids, and forcing the particles or layers into intimate contact.
The Result: Enhanced Material Properties
This unique combination of a clean environment, high temperature, and direct pressure results in a final product that is incredibly dense and strong. The process enhances properties like mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and overall durability.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
While "hot pressing" describes the heat and pressure, the "vacuum" is what makes this a truly advanced manufacturing technique. It solves several fundamental problems that occur during high-temperature processing.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
The primary benefit is the prevention of oxidation. At high temperatures, most metals and many other materials react with oxygen, forming brittle, weak oxide layers. The vacuum removes the oxygen, ensuring the material remains pure.
Degassing and Purification
The vacuum actively pulls trapped gases and other volatile impurities out of the raw materials. This degassing step leads to a final product with higher purity and fewer internal defects.
Promoting Superior Bonding
Because the surfaces of the material particles or layers are perfectly clean and free of oxide films, they can form much stronger, more complete metallurgical or chemical bonds. This is the foundation of the process's ability to create high-strength components.
Producing a Bright, Clean Surface
Parts emerge from a vacuum hot press with a clean, bright surface, often requiring no further cleaning or post-processing to remove scale or discoloration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum hot pressing is a specialized process with specific considerations. It is not the right solution for every application.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Vacuum hot press furnaces are sophisticated and expensive pieces of equipment that require specialized knowledge to operate and maintain.
Longer Process Cycles
Achieving a deep vacuum, heating to temperature, pressing, and cooling down in a controlled manner can be a time-consuming process. This generally makes it slower than atmospheric pressing methods.
Scale and Volume Limitations
The process is best suited for producing high-value, high-performance components rather than high-volume, low-cost commodity parts. The size of the components is limited by the chamber dimensions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use vacuum hot pressing depends entirely on your material requirements and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity and strength: This process is essential, as it eliminates the oxidation and contamination that inherently weaken materials processed in air.
- If your primary focus is creating lightweight, high-performance parts for critical applications: VHP is a leading choice for aerospace, medical, and advanced electronics where material integrity is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of simple parts: You should investigate alternative methods like conventional sintering or forging, as the cost and cycle time of VHP may be prohibitive.
- If your primary focus is research and material development: VHP provides the ideal controlled environment for experimenting with and creating novel materials like advanced ceramics, composites, and metal alloys.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum hot pressing is a commitment to achieving the highest possible material quality when performance cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Eliminates oxidation and contamination for superior purity. |
| High Heat & Pressure | Densifies materials, eliminates voids, and promotes strong bonding. |
| Degassing | Removes trapped gases and impurities for fewer internal defects. |
| Final Product | High-density, high-strength components with a bright, clean surface. |
Ready to unlock the highest material performance for your critical applications?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our expertise in vacuum hot pressing technology, including our range of Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique material requirements—whether you're in aerospace, medical, electronics, or advanced materials research.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum hot pressing solutions can bring superior strength and purity to your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-pressure press play in the preparation of zinc sample pellets? Optimize Carbothermic Reduction
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory hot press for F-MWCNT films? Boost Power Factor by 400%
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What considerations guide the selection of heating elements and pressurization methods for a vacuum hot press furnace?
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity



















