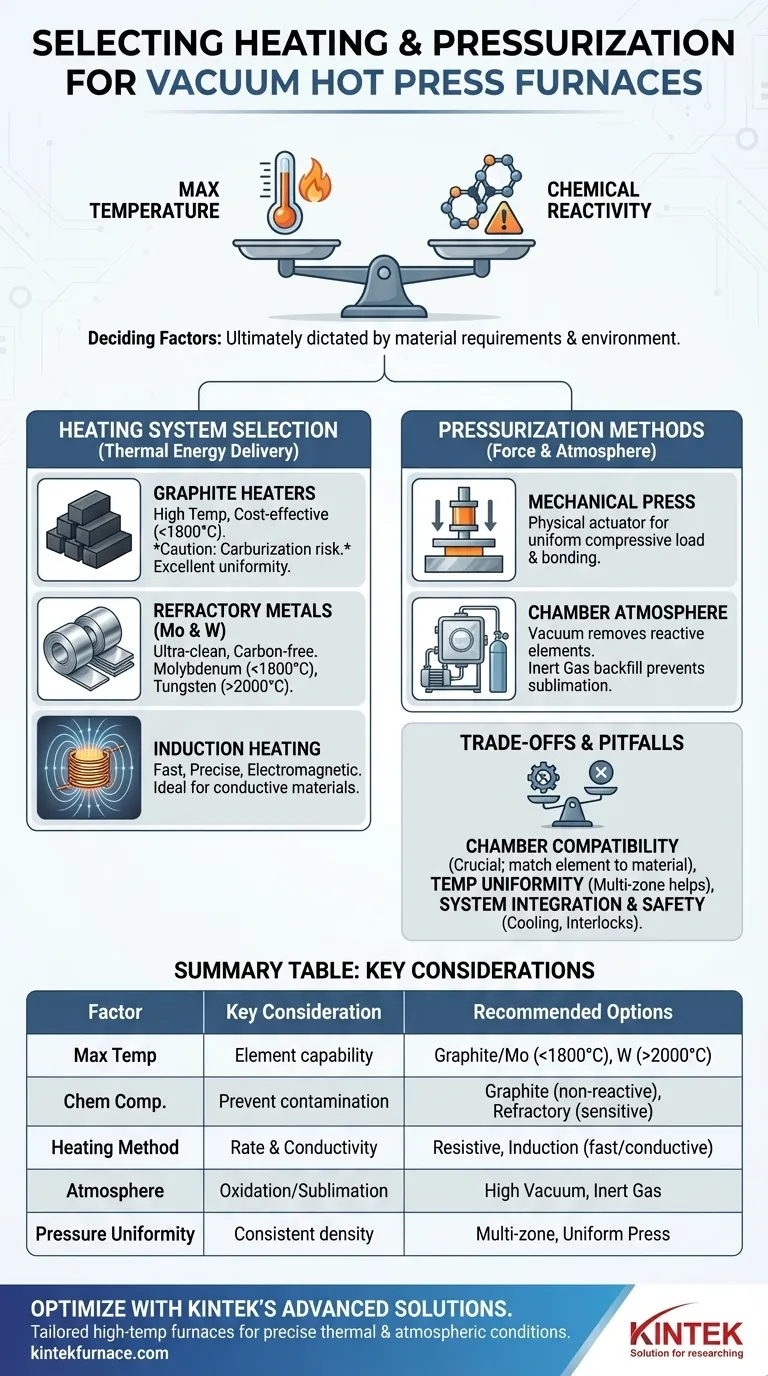
Ultimately, your choice is dictated by two factors: the maximum temperature your material requires and its chemical reactivity within the furnace environment. The heating element must be able to reach the target temperature without contaminating your sample, while the pressurization method must apply the necessary force in a controlled, non-reactive atmosphere.
The selection process for a vacuum hot press is a balancing act. You must choose a heating element that can achieve the target process temperature without chemically interfering with your material, and a pressurization system that delivers uniform force within a carefully controlled vacuum or inert gas atmosphere.
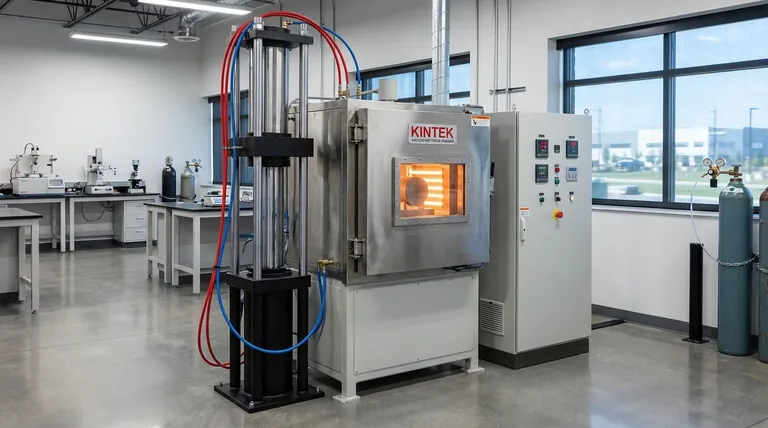

Deconstructing the Core Systems: Heat and Pressure
A vacuum hot press furnace integrates two distinct yet interdependent systems to achieve its function. Understanding them separately is the first step to making an informed choice.
The Heating System's Role
This system is responsible for delivering thermal energy. Its design and material composition directly influence the furnace's maximum temperature, heating rate, and the cleanliness of the processing environment.
The Pressurization System's Role
This system has two components: the mechanical press that applies physical force for compaction and bonding, and the vacuum system that controls the gaseous atmosphere, removing reactive elements like oxygen.
Selecting the Right Heating Element
The heating element is the heart of the furnace. Your decision here is primarily driven by the temperature requirements of your process and the chemical compatibility with the materials you are heating.
Temperature as the Primary Driver
The first question you must answer is: what is my maximum processing temperature? This will immediately narrow your options, as each element type has a distinct operational range.
Graphite Heaters
Graphite is a common, cost-effective choice for high-temperature applications. It offers excellent thermal uniformity and is robust.
However, its primary limitation is reactivity. At high temperatures, it can introduce carbon into your sample, a process known as carburization, which is undesirable for many metals and ceramics.
Refractory Metal Heaters (Molybdenum & Tungsten)
For applications requiring an ultra-clean, carbon-free environment, refractory metals are the superior choice.
Molybdenum is often used for temperatures up to approximately 1800°C. Tungsten is reserved for the most extreme applications, capable of reaching temperatures well above 2000°C.
Induction Heating
Induction is a different method of heating. Instead of relying on resistive elements, it uses an electromagnetic field to directly heat an electrically conductive susceptor or the workpiece itself.
This method provides exceptionally fast heating rates and precise control, making it ideal for applications like vacuum casting or processing specific conductive materials.
Understanding Pressurization Methods
The term "pressure" in a hot press refers to both the mechanical force applied to the sample and the gaseous pressure within the chamber.
The Mechanical Press System
This is the physical actuator (typically hydraulic) that applies a controlled, compressive load onto your material. The key consideration here is ensuring the system can deliver the required force uniformly across the entire part to achieve consistent density and bonding.
The Chamber Atmosphere Control
The vacuum system, composed of pumps, valves, and gauges, is critical for removing air and preventing oxidation. For many processes, a high vacuum is all that is needed.
In some cases, the chamber is backfilled with a low pressure of an inert gas, such as Argon. This can prevent the sublimation of certain elements from the sample at high temperatures and improve thermal uniformity through convection.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Selecting the right components involves navigating a series of critical trade-offs that can impact process success and equipment longevity.
The Challenge of Chemical Compatibility
This is the most common failure point. Using a graphite heater to process a carbon-sensitive alloy, for example, will contaminate the material and compromise its properties. Always cross-reference your workpiece material with the heating element's composition.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
Applying high mechanical pressure makes uniform heating difficult. Modern systems often use three or four independently controlled heating zones to ensure the entire workpiece reaches the target temperature evenly, preventing internal stresses or incomplete sintering.
System Integration and Safety
A hot press is a complex system where every component must work in concert. A robust water-cooling system is essential to protect the chamber and vacuum pumps. Likewise, safety interlocks on doors, valves, and pressure systems are non-negotiable for preventing accidents during operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be based on a clear understanding of your process goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective sintering of carbides or other non-reactive materials: Graphite heating elements provide an excellent balance of high-temperature performance and economic value.
- If your primary focus is processing contamination-sensitive metals or ceramics: Refractory metal heaters, like molybdenum or tungsten, are essential for maintaining a clean, carbon-free environment.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating of conductive materials for casting or brazing: An induction heating system offers unmatched speed and precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation and material sublimation: A high-performance vacuum system is critical, with the option for inert gas backfilling providing an additional layer of process control.
By carefully matching your system's capabilities to your material's specific needs, you ensure a precise, repeatable, and successful manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Selection Factor | Key Considerations | Recommended Options |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | Determines heating element material capability | Graphite (<1800°C), Molybdenum (<1800°C), Tungsten (>2000°C) |
| Chemical Compatibility | Prevents sample contamination and carburization | Graphite (non-reactive materials), Refractory Metals (carbon-sensitive materials) |
| Heating Method | Balances heating rate and material conductivity | Resistive Heating (general use), Induction Heating (fast heating for conductive materials) |
| Atmosphere Control | Prevents oxidation and material sublimation | High Vacuum (standard), Inert Gas Backfilling (enhanced control) |
| Pressure Uniformity | Ensures consistent density and bonding | Multi-zone heating systems, Hydraulic press with uniform force distribution |
Optimize Your Vacuum Hot Press Process with KINTEK's Advanced Solutions
Struggling to balance temperature requirements, material compatibility, and pressure uniformity in your vacuum hot press applications? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities to deliver precisely tailored high-temperature furnace solutions. Our expertise in Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems ensures your materials receive the perfect thermal and atmospheric conditions for successful processing.
Whether you're working with carbon-sensitive alloys requiring refractory metal heaters or need rapid induction heating for conductive materials, our strong deep customization capability addresses your unique experimental requirements. Contact our engineering team today to discuss how we can enhance your manufacturing process with reliable, contamination-free hot press solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory hot press for F-MWCNT films? Boost Power Factor by 400%
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure



















