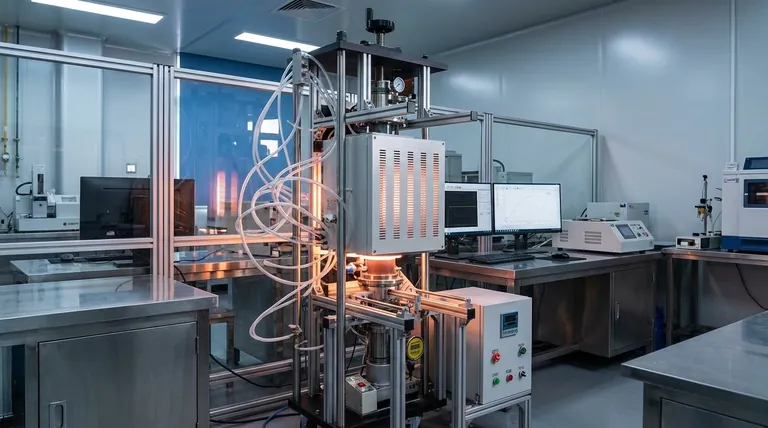
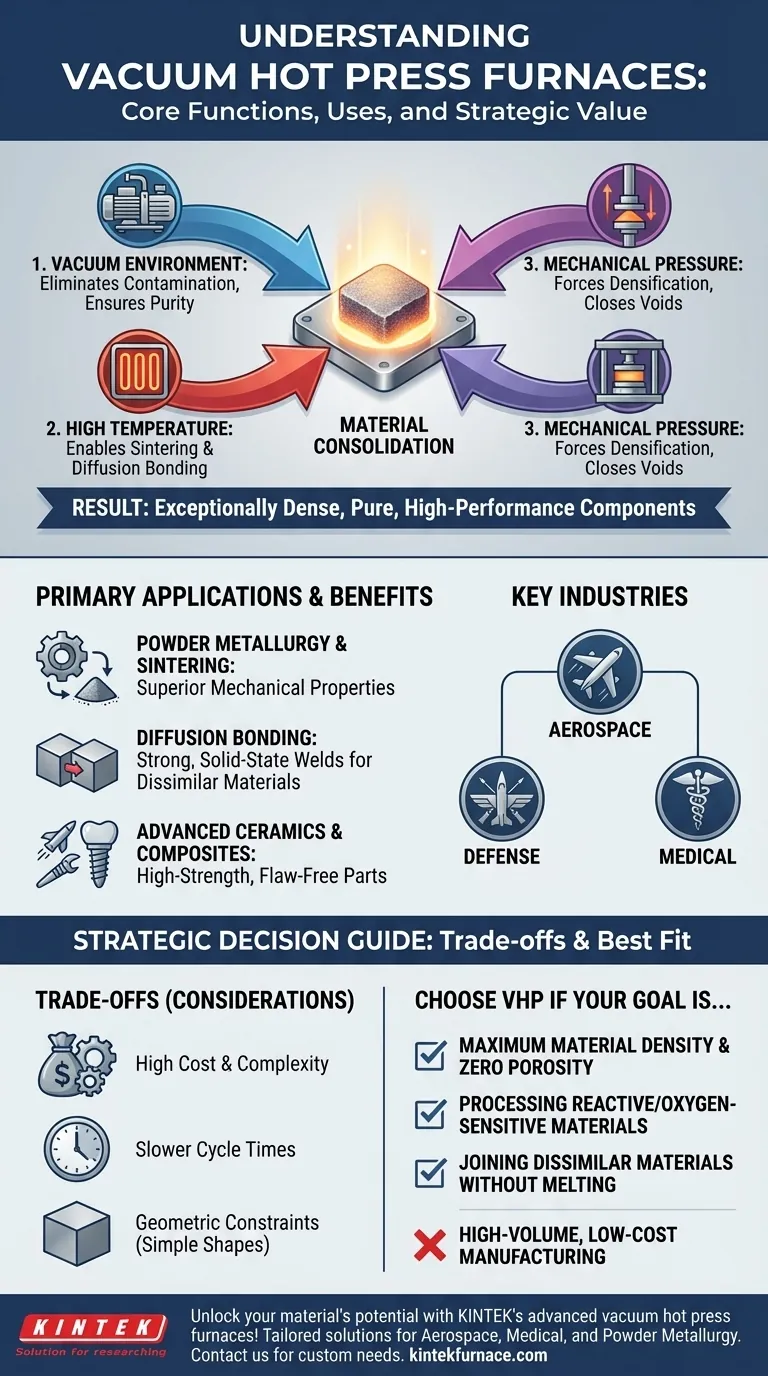
At its core, a vacuum hot press furnace is a highly specialized piece of equipment that simultaneously applies high temperature, mechanical pressure, and a vacuum environment to process materials. This unique combination is used for advanced applications like sintering, diffusion bonding, and hot forming, where the goal is to create exceptionally dense, pure, and high-performance components from materials like metals, ceramics, and composites.
The defining advantage of a vacuum hot press is its ability to eliminate atmospheric contamination while physically consolidating a material. This allows for the creation of parts with superior density, minimal porosity, and enhanced mechanical properties that are often unattainable through heat or pressure alone.
The Three Pillars of a Vacuum Hot Press
A vacuum hot press furnace integrates three critical functions to achieve its results. Understanding how these functions work together is key to understanding the technology's value.
The Vacuum Environment: Ensuring Material Purity
The process begins by creating a vacuum inside the furnace chamber. This removes atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen.
By eliminating these reactive gases, the furnace prevents oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions, which is critical when working with sensitive materials like titanium, refractory metals, or high-purity ceramics.
The Heating System: Enabling Material Transformation
Once under vacuum, precision-controlled heating elements (often made of graphite or molybdenum) raise the material's temperature.
This controlled heating is essential for processes like sintering, where heat encourages powder particles to bond together, or diffusion bonding, where it allows atoms from two different surfaces to intermingle and form a solid-state weld.
The Pressure System: Forcing Densification
While the material is at a high, malleable temperature, a hydraulic or pneumatic system applies significant mechanical force.
This pressure physically compacts the material, closing internal voids and pores. This step is what drives the densification process, resulting in a final product with near-theoretical density and dramatically improved strength.
Common Applications and Industries
The unique capabilities of vacuum hot pressing make it indispensable in fields that demand the highest material performance.
Powder Metallurgy and Sintering
This is a primary application where fine metal or ceramic powders are transformed into a solid, dense part. The pressure dramatically accelerates the sintering process and produces a component with superior mechanical properties compared to conventional sintering.
Diffusion Bonding
Vacuum hot presses are ideal for joining dissimilar materials without melting them. The combination of clean vacuum, heat, and pressure encourages atoms to diffuse across the joint interface, creating a bond that can be as strong as the parent materials themselves.
Advanced Ceramics and Composites
For industries like aerospace, defense, and medical, this technology is used to create high-strength, lightweight, and heat-resistant components. The process ensures that there are no internal flaws that could lead to catastrophic failure under stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum hot press is a specialized tool with specific considerations.
High Cost and Complexity
These are sophisticated, expensive machines that require significant capital investment and skilled operators. Maintenance of the vacuum, hydraulic, and control systems is also more demanding than with simpler furnaces.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of pumping down to a vacuum, controlled heating, pressing, and cooling is inherently slower than many atmospheric furnace processes. This makes it less suitable for high-volume, low-cost manufacturing.
Geometric Constraints
The direct-pressure nature of the hot press means it is best suited for producing components with relatively simple geometries, such as discs, blocks, or plates. Complex, net-shape parts are often better produced via other methods like hot isostatic pressing (HIP).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting this technology depends entirely on your end-goal for the material.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material density and eliminating porosity: A vacuum hot press is the definitive choice, as the combination of pressure and heat directly compacts the material structure.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive or oxygen-sensitive materials: The vacuum environment is non-negotiable for preventing oxidation and ensuring the final part's chemical purity.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials without a weak melted layer: Diffusion bonding within a vacuum hot press provides the ideal environment for creating strong, solid-state welds.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production where ultimate density is not critical: Simpler and faster methods, such as conventional sintering in a controlled atmosphere, may be more cost-effective.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum hot press is a strategic decision to prioritize final material quality and performance above all else.

Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Removes atmospheric gases | Prevents oxidation, ensures material purity |
| Heating System | Applies controlled high temperatures | Enables sintering and diffusion bonding |
| Pressure System | Applies mechanical force | Compacts material, reduces porosity, increases density |
| Primary Uses | Industries Served | |
| Sintering | Transforms powders into solid parts | Powder metallurgy, ceramics |
| Diffusion Bonding | Joins materials without melting | Aerospace, defense, medical |
| Hot Forming | Shapes materials under heat and pressure | Composites, advanced materials |
Unlock the potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced vacuum hot press furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide tailored solutions for industries like aerospace, medical, and powder metallurgy. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and material performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does Vacuum Hot Press equipment contribute to the energy and power generation sector? Boost Efficiency and Durability
- What materials can be densified using a vacuum press and what are their applications? Unlock High-Performance Material Densification
- How does precise temperature control affect Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Master Titanium Hot Pressing Accuracy
- How does a vacuum or protective atmosphere reduce oxidation in molten metals? Prevent Oxide Inclusions for Stronger Metals
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure



















