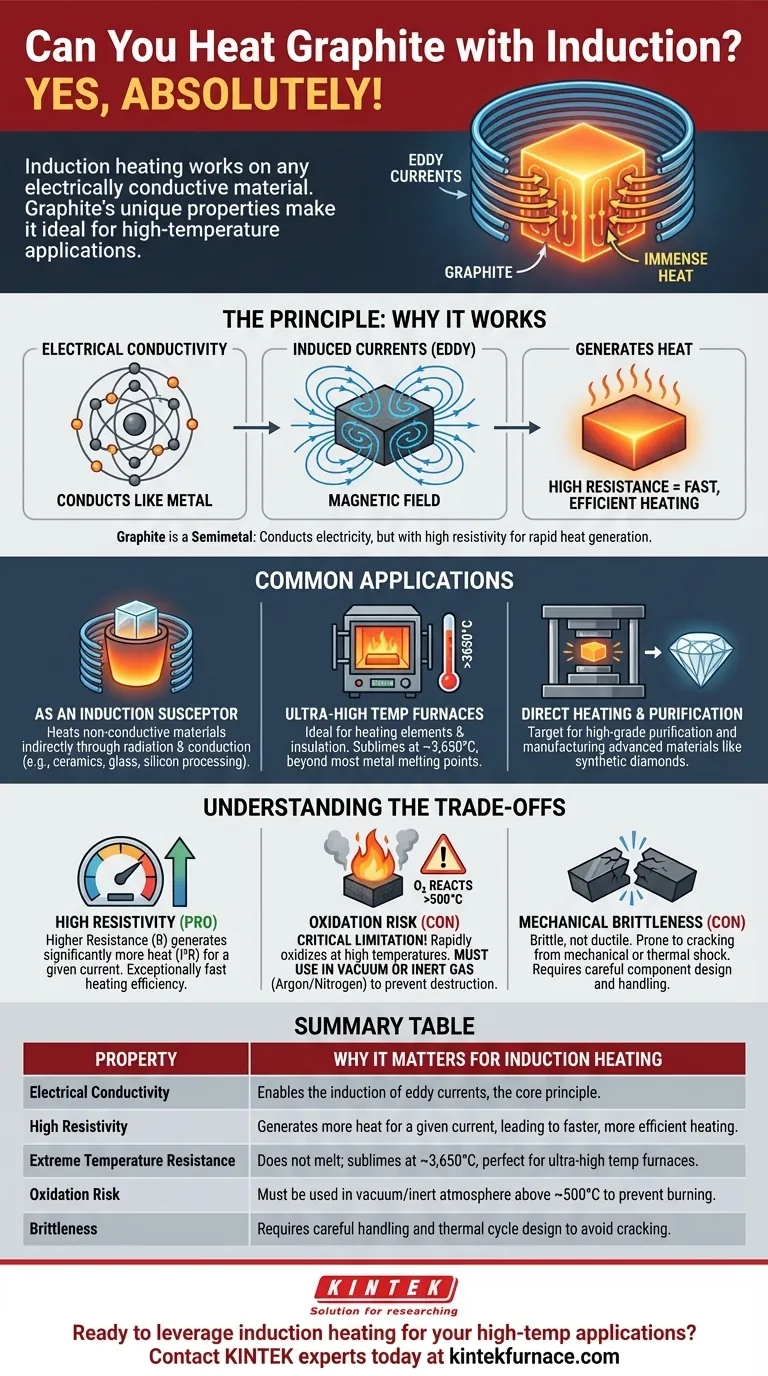
Yes, absolutely. Graphite can be heated very effectively using an induction system. Because induction heating works on any electrically conductive material, graphite's ability to conduct electricity makes it a prime candidate for this process, often with unique advantages over traditional metals.
While we typically associate induction with heating metals, graphite's distinct combination of electrical conductivity, high thermal resistance, and high resistivity makes it an exceptionally useful—and sometimes superior—material for specialized high-temperature induction applications.

The Principle: Why Induction Works on Graphite
Induction heating is fundamentally about inducing electrical currents within a material. If a material can conduct electricity, it can be heated by induction.
Electrical Conductivity is Key
The alternating magnetic field generated by an induction coil causes electrons within a conductive material to move, creating powerful internal electrical currents called eddy currents. The material's natural resistance to the flow of these currents generates immense heat very quickly.
Graphite's Conductive Structure
Graphite is an allotrope (a specific form) of carbon. Its atoms are arranged in a layered, sheet-like structure. Electrons can move freely along these layers, allowing graphite to conduct electricity, similar to a metal.
A Semimetal, Not a Typical Metal
While not a metal in the traditional sense, graphite is classified as a semimetal or semiconductor. Its electrical conductivity is lower than that of copper but more than sufficient for the induction process to work efficiently. In fact, its higher electrical resistance can often lead to faster and more efficient heating.
Common Applications for Induction-Heated Graphite
Graphite is not just a material that can be heated by induction; it is often the preferred material for several critical industrial and scientific processes.
As an Induction Susceptor
This is the most common application. A graphite susceptor (typically a crucible or chamber) is heated by the induction coil. It then transfers this heat to a non-conductive material placed inside it through radiation and conduction. This is how materials like ceramics, glass, or silicon are processed in induction furnaces.
For Ultra-High Temperature Furnaces
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure; it sublimes (turns from a solid directly to a gas) at around 3,650°C (6,602°F). This incredible temperature resistance makes it the ideal material for constructing the heating elements and insulation in vacuum or inert-gas induction furnaces that operate at temperatures far beyond the melting point of most metals.
For Direct Heating and Purification
In some processes, the graphite part itself is the target. This can be used for purifying graphite to extremely high grades or for manufacturing advanced materials like synthetic diamonds, where graphite is heated under immense pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Using graphite is not without its specific considerations. Its properties are very different from metals, which creates both advantages and challenges.
High Resistivity and Heating Efficiency
Graphite has a significantly higher electrical resistivity than metals like steel or copper. This higher resistance (R) means that for a given induced current (I), the heat generated (I²R) is much greater. This can make graphite heat exceptionally fast, but it may require different power supply frequencies for optimal performance.
Oxidation Risk
This is the most critical limitation. At high temperatures (typically above 500°C or 932°F), graphite reacts with oxygen in the air and will rapidly oxidize, essentially burning away. For any high-temperature application, graphite must be used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent its destruction.
Mechanical Brittleness
Unlike metals, which are typically ductile and can bend, graphite is brittle. It can crack or shatter if subjected to mechanical shock or thermal stress from uneven heating. Components must be designed carefully to account for this.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To decide if graphite is the correct material, consider your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is heating a non-conductive material: Use a graphite crucible as an induction susceptor for reliable and efficient indirect heating.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (>2000°C): Graphite is one of the best choices available, but you must operate within a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
- If your primary focus is rapidly heating a complex shape: Graphite's high resistivity allows for very fast heating, but ensure your part design and heating cycle account for its mechanical brittleness to avoid fractures.
By understanding its unique properties and limitations, you can leverage graphite as a powerful and efficient tool in advanced induction heating systems.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Induction Heating |
|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Enables the induction of eddy currents, the core principle of the process. |
| High Resistivity | Generates more heat (I²R) for a given current, leading to faster, more efficient heating. |
| Extreme Temperature Resistance | Does not melt; sublimes at ~3,650°C, making it perfect for ultra-high temperature furnaces. |
| Oxidation Risk | Must be used in a vacuum or inert atmosphere (e.g., argon) above ~500°C to prevent burning. |
| Brittleness | Requires careful handling and thermal cycle design to avoid cracking from mechanical or thermal shock. |
Ready to leverage the power of induction heating for your most demanding high-temperature applications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced thermal solutions. Our expertise in high-temperature furnace design, including Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong in-house R&D and manufacturing capabilities. Whether you need a standard system or a deeply customized solution for processing graphite or other advanced materials, we can deliver the precise performance and reliability your lab requires.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results with your high-temperature processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















