Yes, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are highly customizable. Manufacturers can produce them in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and electrical configurations to meet the precise requirements of specific industrial furnaces and high-temperature applications. This flexibility allows for optimized thermal performance and integration into new or existing equipment designs.
The ability to customize SiC elements goes far beyond physical dimensions. A successful custom order requires a clear understanding of the necessary electrical properties, mounting hardware, and operational factors, most notably how the element's resistance will change over its service life.
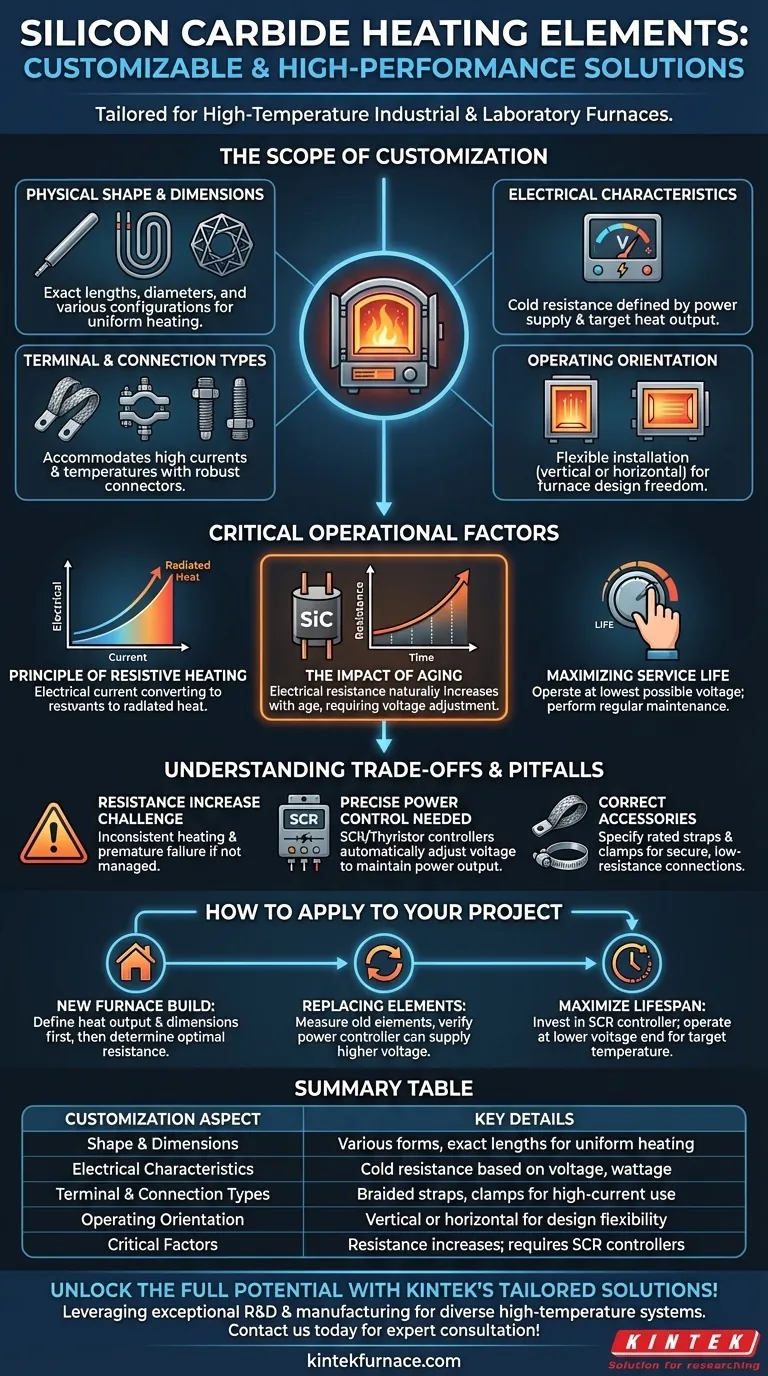
The Scope of Customization: What to Specify
When ordering custom SiC heating elements, you are defining the core components of your thermal system. Providing precise specifications is critical for performance and reliability.
Physical Shape and Dimensions
The most common customization is the element's physical form. While the standard "U" shape (a rod or spiral) is versatile, elements can be made to exact lengths, diameters, and in various configurations to fit your furnace geometry and ensure uniform heating.
Electrical Characteristics
You must specify the element's electrical resistance. This property is determined by your available power supply (voltage) and the desired heat output (wattage). Manufacturers will work with you to define a "cold resistance" value that delivers the target temperature in your specific environment.
Terminal and Connection Types
How the element connects to the power supply is a key detail. Custom elements can be configured with different terminal ends to accommodate various connection methods, including braided aluminum straps and specialized clamps. The connections must be able to handle high currents and temperatures.
Operating Orientation
A key advantage noted in furnace design is the flexibility of SiC elements. Most types, including the common U-shaped elements, can be specified for either vertical or horizontal installation, providing significant freedom in furnace chamber design.
Critical Operational Factors for Custom Elements
Specifying an element is only the first step. Understanding how it operates is essential for proper control and long-term performance.
The Principle of Resistive Heating
SiC elements function by passing an electrical current through the material, which has a high electrical resistance. This resistance converts electrical energy into heat, which then radiates into the furnace chamber. The temperature is controlled by precisely adjusting the voltage or current applied to the element.
The Impact of Aging on Performance
A critical characteristic of silicon carbide is that its electrical resistance increases as it ages. This is a natural, unavoidable process. As resistance goes up, the element will produce less heat at the same voltage, causing furnace temperatures to drop.
Maximizing Service Life
To prolong the life of your custom elements, it is best practice to operate the furnace at the lowest possible voltage that still achieves the required temperature. This reduces the rate of degradation. Careful handling and regular furnace maintenance also play a crucial role.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While highly effective, SiC elements have specific characteristics that must be managed to avoid common problems.
The Challenge of Resistance Increase
The primary pitfall is failing to account for the age-related increase in resistance. A system designed without this consideration will suffer from inconsistent heating and declining performance over time, requiring premature element replacement.
The Need for Precise Power Control
Because resistance changes, a simple on/off controller is inadequate. A robust system requires a thyristor or SCR (Silicon-Controlled Rectifier) power controller. These devices can automatically increase the voltage to the elements as their resistance rises, maintaining a constant power output and stable furnace temperature.
Specifying the Right Accessories
A custom element is only as good as its connection. When ordering, you must also specify the correct accessories, such as straps and clamps. These components must match the element's terminals and be rated for the electrical load to ensure a secure, low-resistance connection. A poor connection will overheat and fail quickly.
How to Apply This to Your Project
To ensure a successful custom order, align your specifications with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is a new furnace build: Define the required heat output (wattage) and physical dimensions first, then work with the supplier to determine the optimal element resistance for your power supply.
- If your primary focus is replacing existing elements: Carefully measure the old elements and note their cold resistance if possible, but also verify the specifications of your power controller to ensure it can supply the higher voltage that new elements will eventually require.
- If your primary focus is maximizing element lifespan: Invest in a high-quality SCR power controller and specify elements that allow you to operate at the lower end of their voltage range for your target temperature.
A well-specified custom element is the foundation of a reliable and efficient high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Customization Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Physical Shape & Dimensions | Various forms (e.g., U-shape), exact lengths, diameters for uniform heating |
| Electrical Characteristics | Cold resistance based on voltage, wattage for target temperature |
| Terminal & Connection Types | Options like braided straps, clamps for high-current, high-temperature use |
| Operating Orientation | Vertical or horizontal installation for flexible furnace design |
| Critical Factors | Resistance increases with age; requires SCR controllers for stable performance |
Unlock the full potential of your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's tailored solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures silicon carbide heating elements are precisely designed to meet your unique experimental and industrial needs—boosting efficiency, reliability, and lifespan. Ready to enhance your furnace performance? Contact us today for expert consultation and support!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















