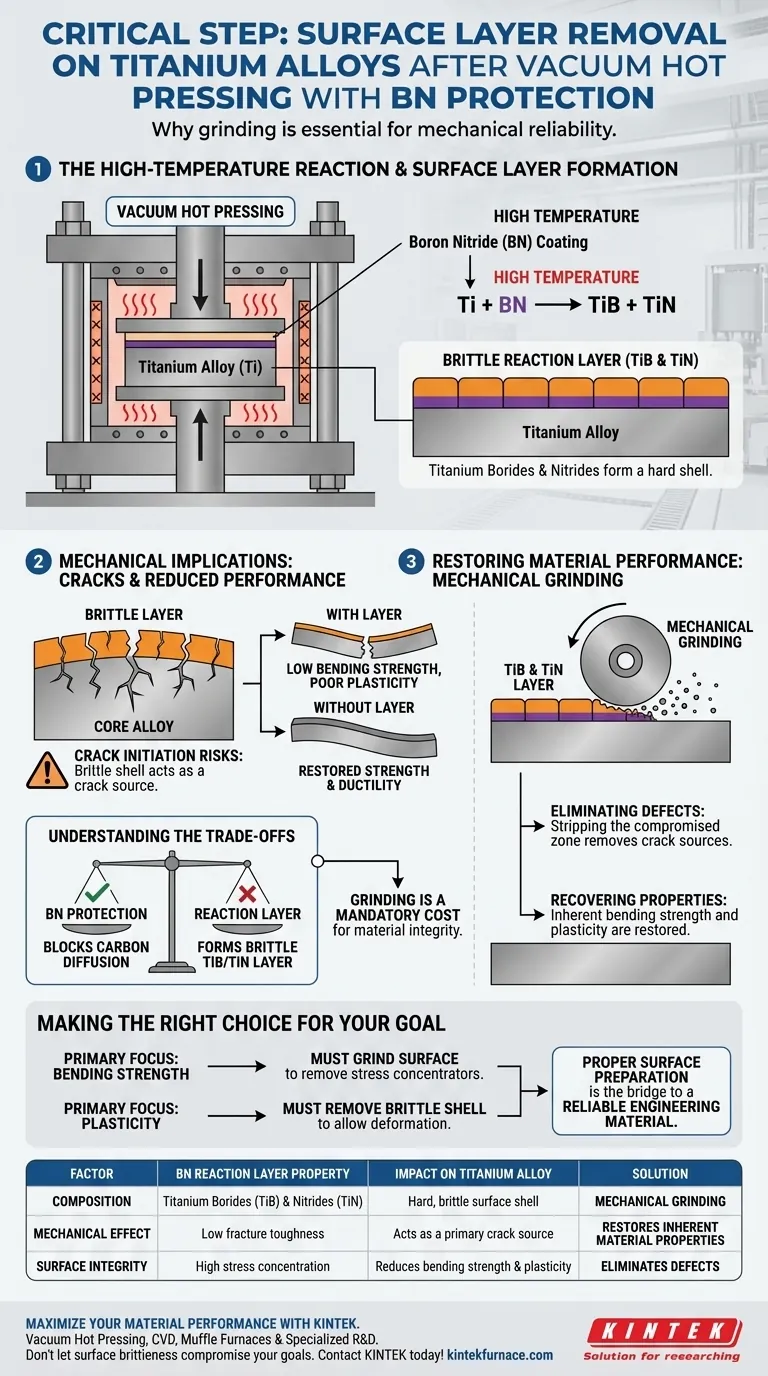
The removal of the surface layer is a critical step for mechanical reliability. Even with Boron Nitride (BN) protection, high-temperature processing induces a chemical reaction between the coating and the titanium alloy. This results in a compromised surface that must be ground away to prevent premature failure.
While Boron Nitride serves as a barrier against carbon, it reacts with titanium to create a hard, brittle interface of titanium borides and nitrides. Removing this layer eliminates crack sources, directly restoring the material's bending strength and ductility.

The Chemistry of the Interface
The High-Temperature Reaction
During vacuum hot pressing, the protective environment is not entirely inert. Titanium reacts with the Boron Nitride (BN) coating when subjected to high temperatures.
Composition of the Surface Layer
This reaction creates a specific chemical profile on the surface of the sample. The resulting layer is composed of titanium borides (TiB) and titanium nitrides (TiN).
Mechanical Implications
Hardness and Brittleness
The reaction layer possesses physical properties vastly different from the core alloy. The TiB and TiN compounds form a hard and brittle shell around the sample.
Crack Initiation Risks
Because this surface layer is brittle, it cannot accommodate stress as well as the base metal. It acts as a potential crack source, creating weak points where fractures can easily begin under load.
Restoring Material Performance
Eliminating Defects
Using grinding equipment allows for the thorough removal of this compromised zone. By stripping away the TiB and TiN layer, you effectively eliminate the sources of surface cracks.
Recovering Mechanical Properties
Once the brittle layer is removed, the inherent properties of the titanium alloy are regained. This process significantly restores the material's bending strength and its capacity for plastic deformation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Protection vs. Reaction
The primary purpose of the BN coating is to block carbon diffusion, which it does effectively. However, the trade-off is the formation of the brittle TiB/TiN reaction layer.
The Cost of Integrity
You cannot simply coat the material and consider it finished. You must accept the additional processing step of grinding as a mandatory "cost" to ensure the material performs as intended without surface-induced brittleness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your titanium alloy performs correctly after vacuum hot pressing, apply the following principles:
- If your primary focus is Bending Strength: You must grind the surface to remove stress concentrators that lead to early fracture.
- If your primary focus is Plasticity: You must remove the brittle TiB/TiN shell to allow the material to deform without cracking.
Proper surface preparation is the bridge between a raw processed sample and a reliable engineering material.
Summary Table:
| Factor | BN Reaction Layer Property | Impact on Titanium Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Titanium Borides (TiB) & Nitrides (TiN) | Hard, brittle surface shell |
| Mechanical Effect | Low fracture toughness | Acts as a primary crack source |
| Surface Integrity | High stress concentration | Reduces bending strength & plasticity |
| Solution | Mechanical Grinding | Restores inherent material properties |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Precise thermal processing requires more than just high temperatures—it demands expert control over material integrity. KINTEK provides industry-leading Vacuum Hot Pressing systems, CVD systems, and Muffle Furnaces, backed by specialized R&D to help you navigate complex chemical reactions like BN-titanium interactions.
Whether you are processing advanced alloys or ceramics, our customizable lab high-temperature furnaces ensure uniform heating and superior results. Don't let surface brittleness compromise your engineering goals.
Contact KINTEK today for expert solutions and customized equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What control features does a vacuum hot press furnace offer? Precision Control for Advanced Materials Processing
- What is the core role of a Vacuum Hot Pressing (VHP) furnace? Achieve Peak Infrared Transmittance in ZnS Ceramics
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- What factors should be considered when choosing between hot pressing and cold compacting and sintering? Optimize Your Material Manufacturing
- What are the advantages of using Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) for Mo-Cr-Y composites? High-Performance Fabrication
- What factors should be considered when selecting vacuum press equipment? Key Insights for Optimal Performance
- What alternative mold materials are used in Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)? Avoid Carbon Contamination Effectively
- What is a vacuum press used for? Achieve Flawless Bonding and Material Transformation









