In short, a vacuum press is a device used to bond, shape, or process materials by removing air from a sealed chamber or bag. This allows uniform atmospheric pressure to clamp down on the workpiece, ensuring a perfect bond or form. It is a cornerstone technology in industries ranging from woodworking and composites to the manufacturing of advanced aerospace components and medical implants.
A vacuum press is not simply a clamp; it is a controlled environment. By creating a vacuum, it eliminates air pockets and enables the application of perfectly even pressure across an entire surface, a feat impossible with mechanical methods. This unlocks the ability to create complex, high-strength, and flawless materials.
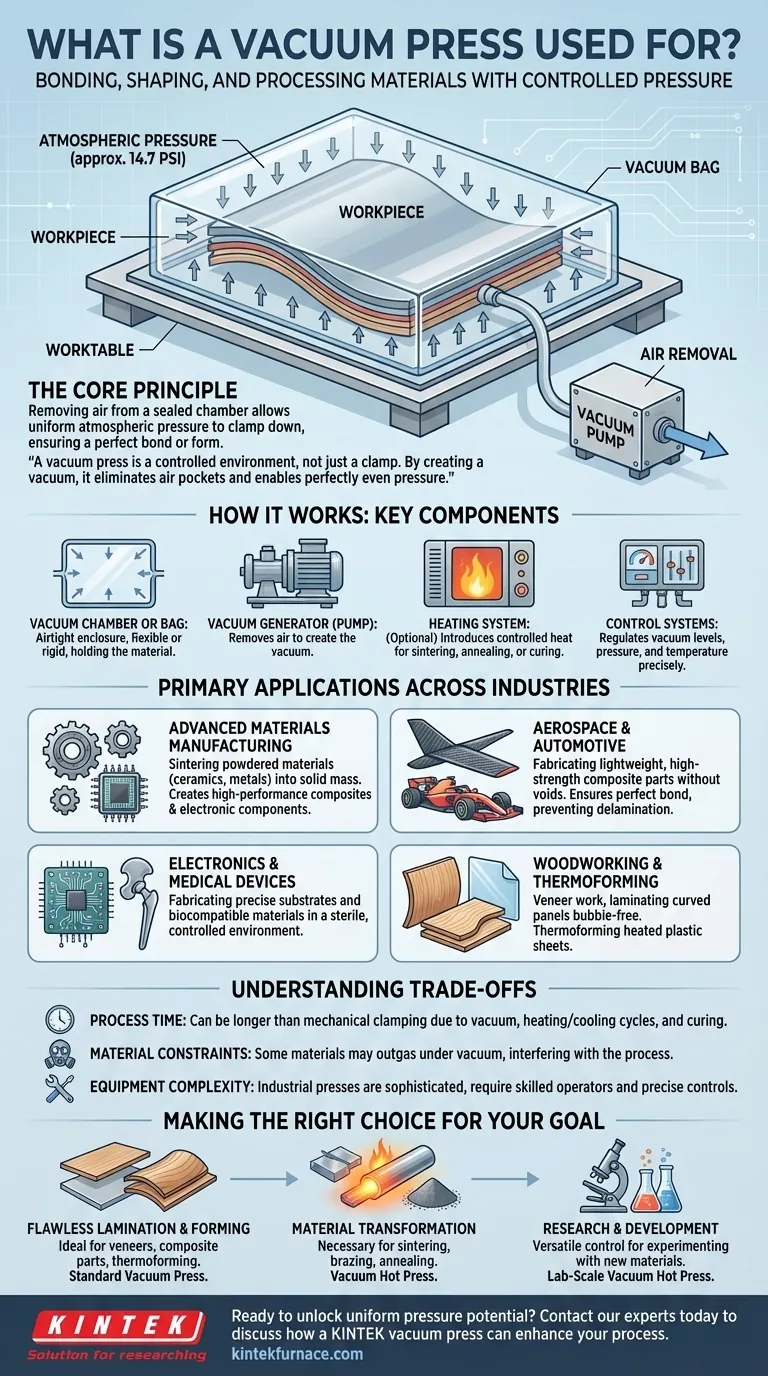
How a Vacuum Press Works: The Core Principle
A vacuum press operates on a simple but powerful principle: removing the air from a sealed space allows the external atmospheric pressure to exert a significant and perfectly uniform force.
The Role of the Vacuum
The vacuum itself does not "suck" or "pull." Instead, a vacuum pump removes air and other gases from inside a sealed bag or chamber containing the workpiece.
This creates a pressure differential. The external air pressure (approximately 14.7 pounds per square inch at sea level) then pushes down evenly on every part of the object's surface inside the bag.
Key Components
A typical system consists of a few critical parts:
- Vacuum Chamber or Bag: An airtight enclosure that holds the material. Bags are flexible for forming curved parts, while rigid chambers are used for processes like sintering.
- Vacuum Generator (Pump): The engine of the system that removes air to create the vacuum.
- Heating System: In a vacuum hot press, this element introduces controlled heat, which is essential for processes like sintering, annealing, or curing certain adhesives.
- Control Systems: Modern presses use sophisticated controls to precisely regulate vacuum levels, pressure, and temperature throughout the process.
Primary Applications Across Industries
The ability to apply flawless pressure in a controlled atmosphere makes the vacuum press invaluable for producing high-performance goods.
Advanced Materials Manufacturing
This is where vacuum presses truly excel. They are used for sintering, a process that bonds powdered materials (like ceramics or metals) into a solid mass using heat and pressure without melting them.
This enables the creation of ceramic/metal composites, high-performance cutting tools, and electronic components with specific thermal properties.
Aerospace and Automotive
In these industries, every gram matters. Vacuum pressing is essential for fabricating lightweight, high-strength composite parts, such as carbon fiber panels.
The process ensures a perfect bond between layers of material, eliminating voids or delamination that could lead to catastrophic failure.
Electronics and Medical Devices
Vacuum presses are used to fabricate precise electronic substrates and to produce biocompatible materials for medical implants and surgical tools. The sterile, controlled environment is a significant advantage.
Woodworking and Thermoforming
On a more accessible scale, vacuum presses are used by woodworkers for veneer work and laminating curved panels. The uniform pressure ensures a bubble-free bond between a thin veneer and a complex substrate. It's also used to shape heated plastic sheets in a process called thermoforming.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum pressing is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Process Time
Vacuum processes can be time-consuming. Achieving a full vacuum, running a heating and cooling cycle (in a hot press), and allowing adhesives to cure can take significantly longer than mechanical clamping.
Material Constraints
Not all materials are suitable. Some materials can release gases under vacuum (a process called outgassing), which can interfere with the process or contaminate the material.
Equipment Complexity
Industrial vacuum hot presses are sophisticated and expensive machines. They require skilled operators to manage the precise control systems for temperature, pressure, and vacuum levels to achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a vacuum press depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is flawless lamination and forming: A standard vacuum press is ideal for bonding veneers, creating composite parts, or thermoforming plastics.
- If your primary focus is material transformation: A vacuum hot press is necessary for sintering powders, brazing metals, or annealing materials to alter their fundamental properties.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A versatile lab-scale vacuum hot press provides the control needed to experiment with new materials and manufacturing processes.
Ultimately, mastering the use of a vacuum press is about controlling an environment to achieve material properties and forms that would otherwise be unattainable.

Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Composite Fabrication | Bonds layers (e.g., carbon fiber) without voids | Aerospace, Automotive |
| Sintering & Brazing | Fuses powdered materials with heat & pressure | Advanced Materials, Electronics |
| Veneer Lamination | Creates bubble-free bonds on curved surfaces | Woodworking, Furniture |
| Thermoforming | Shapes heated plastic sheets with uniform pressure | Packaging, Consumer Goods |
| Medical Device Manufacturing | Produces biocompatible materials in a controlled environment | Medical, Electronics |
Ready to unlock the potential of uniform pressure and controlled environments for your projects?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced vacuum press solutions tailored to your unique requirements. Whether you are working with advanced composites in aerospace, sintering new materials in R&D, or perfecting veneer work in woodworking, our expertise ensures you get the precise performance you need.
Our product line includes versatile Vacuum Hot Presses and standard vacuum pressing systems, complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your specific process challenges.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum press can enhance your manufacturing process and deliver flawless, high-strength results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What role do a laboratory pressure machine and a steel die-set play in the preparation of Mn2AlB2 compacts?
- What considerations guide the selection of heating elements and pressurization methods for a vacuum hot press furnace?
- What role does a high-performance laboratory hot press machine play in curing? Unlock Superior Composite Strength



















