Vacuum degassing serves as the definitive purification stage in the production of high-performance structural steel. By drastically reducing environmental pressure, this equipment forces dissolved gases and impurities out of the refined molten steel. This deep treatment is the prerequisite for achieving the strict chemical precision required in low-alloy fire-resistant steels.
Producing fire-resistant steel is not merely about adding alloys; it is about creating a pristine environment where those alloys can function. Vacuum degassing removes volatile contaminants to ensure the structural uniformity and purity essential for seismic and fire safety.

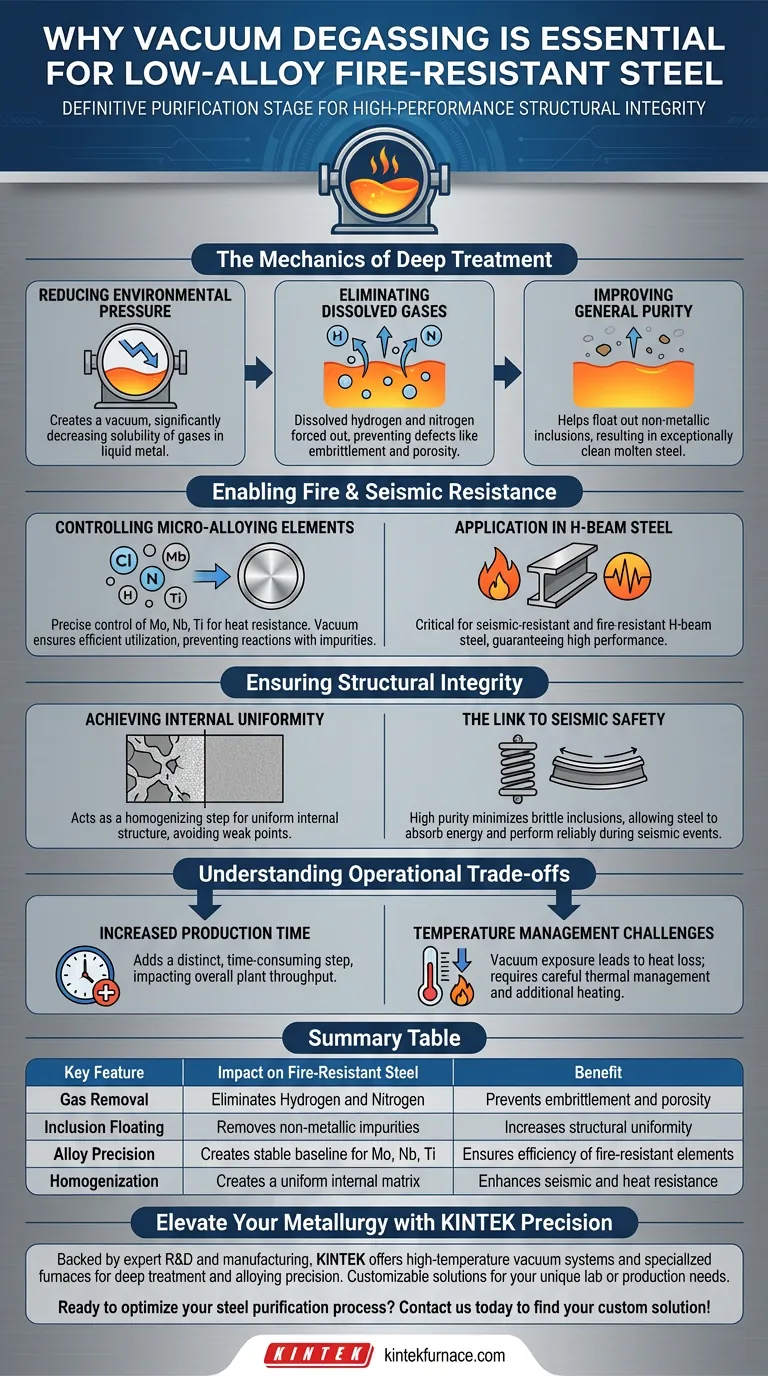
The Mechanics of Deep Treatment
Reducing Environmental Pressure
The primary function of vacuum degassing equipment is to lower the atmospheric pressure surrounding the molten steel.
By creating a vacuum, the solubility of gases within the liquid metal decreases significantly.
Eliminating Dissolved Gases
As the pressure drops, dissolved gases such as hydrogen and nitrogen are forced out of the solution.
Removing these gases is vital to prevent defects like embrittlement or porosity in the final solid steel.
Improving General Purity
Beyond gas removal, the process helps float out non-metallic inclusions.
This results in a "deep treatment" that leaves the molten steel exceptionally clean and ready for alloying.
Enabling Fire and Seismic Resistance
Controlling Micro-Alloying Elements
For fire-resistant steel, specific elements must be added in exact ratios.
Vacuum degassing creates the stable baseline needed to precisely control composition ratios of molybdenum (Mo), niobium (Nb), and titanium (Ti).
Why Precision Matters
If the steel retains high levels of oxygen or other gases, these expensive micro-alloys might react with the impurities rather than strengthening the steel matrix.
The vacuum process ensures these elements are utilized efficiently to provide heat resistance.
Application in H-Beam Steel
The primary reference highlights the specific application of this technology in seismic-resistant and fire-resistant H-beam steel.
These structural components require a guarantee of performance that only degassed, high-purity steel can provide.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
Achieving Internal Uniformity
Inconsistent steel composition leads to weak points that can fail under stress or heat.
Vacuum degassing acts as a homogenizing step, ensuring the internal structure of the steel is uniform throughout the beam.
The Link to Seismic Safety
For seismic resistance, the steel must be able to absorb energy without fracturing.
The high purity achieved through degassing minimizes brittle inclusions, allowing the steel to perform reliably during seismic events.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Increased Production Time
Vacuum degassing adds a distinct, time-consuming step to the secondary refining process.
It requires the steel to be held in the ladle longer, which can impact overall plant throughput.
Temperature Management Challenges
The process of exposing molten steel to a vacuum can lead to temperature losses.
Operators must carefully manage thermal energy, often requiring additional heating phases to maintain the metal in a liquid state for casting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
While vacuum degassing is a standard for high-performance materials, understanding its specific role helps in specifying the right steel grades.
- If your primary focus is Fire Resistance: Ensure the process guarantees precise ratios of Mo, Nb, and Ti to maintain strength at elevated temperatures.
- If your primary focus is Seismic Safety: Prioritize the removal of dissolved gases to maximize ductility and internal structural uniformity.
Vacuum degassing is not just a cleaning step; it is the fundamental process that transforms standard molten iron into engineering-grade, fire-resistant steel.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Impact on Fire-Resistant Steel | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Removal | Eliminates Hydrogen and Nitrogen | Prevents embrittlement and porosity |
| Inclusion Floating | Removes non-metallic impurities | Increases structural uniformity |
| Alloy Precision | Creates stable baseline for Mo, Nb, Ti | Ensures efficiency of fire-resistant elements |
| Homogenization | Creates a uniform internal matrix | Enhances seismic and heat resistance |
Elevate Your Metallurgy with KINTEK Precision
High-performance fire-resistant steel demands absolute purity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-temperature vacuum systems and specialized furnaces tailored for deep treatment and alloying precision. Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, or CVD systems, our equipment is fully customizable to meet your unique lab or production needs.
Ready to optimize your steel purification process? Contact us today to find your custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- J.D. Kim, Chansun Shin. Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization of Low-Alloy Fire- and Seismic-Resistant H-Section Steel. DOI: 10.3390/met14040374
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three Section Clamp
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the two-stage heat treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace optimize HA/Ti scaffolds? Master the Fabrication Process
- Why are vacuum ovens and argon gas protection necessary for MXene monoliths? Ensure Density and Chemical Integrity
- Why are multiple heat treatment cycles in a pyrolysis furnace necessary for dense SiC matrix formation in PIP?
- Why use a vacuum oven for composite fillers? Protect Material Integrity & Prevent Oxidation
- What are the technical advantages of using a high vacuum furnace for Si3N4/Al-Cu composites? Superior Sintering Quality
- What industries commonly use vacuum furnaces and for what purposes? Discover Key Applications in Aerospace, Medical, and More
- What environmental benefits do continuous vacuum furnaces provide? Achieve Zero Emissions and High Efficiency
- Why is short-term annealing followed by water quenching necessary for Ti-15Mo alloys? Lock in Peak Material Performance



















