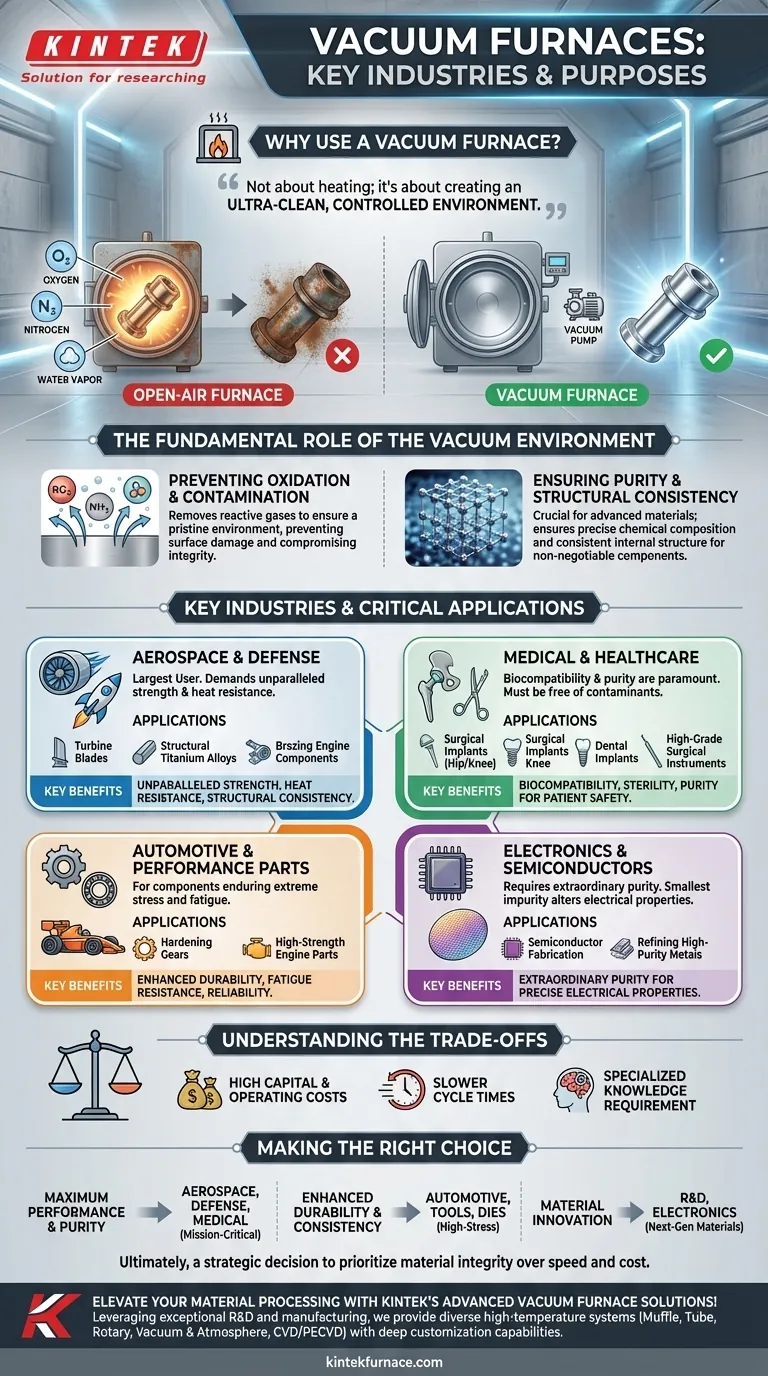
In short, vacuum furnaces are most commonly used by the aerospace, medical, automotive, and electronics industries. They are essential for processes like heat treating, brazing, and sintering where preventing oxidation and contamination is critical to producing high-performance, mission-critical components.
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is not about heating a material; it is about creating an ultra-clean, controlled environment. This allows for the production of components with metallurgical properties and a level of purity that are simply impossible to achieve in an open-air furnace.
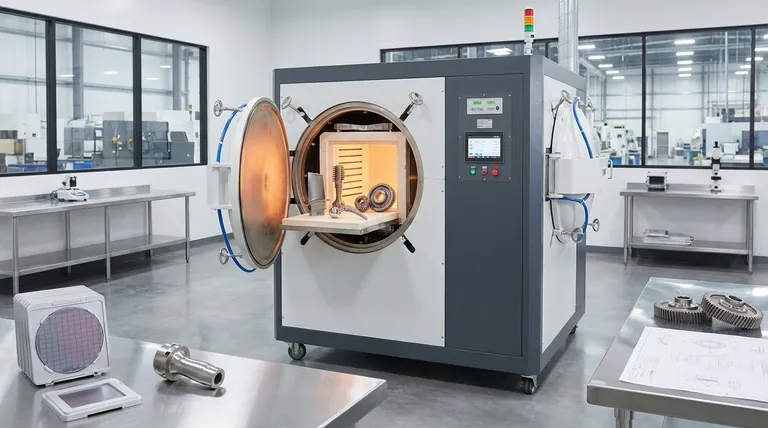

The Fundamental Role of the Vacuum Environment
Before examining specific industries, it is crucial to understand why a vacuum is necessary. At high temperatures, reactive metals and alloys are highly susceptible to damage from atmospheric gases.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Heating a metal in the presence of oxygen, even in trace amounts, causes rapid oxidation. This can compromise the material's surface finish, structural integrity, and mechanical properties.
A vacuum furnace removes these reactive gases—primarily oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor—from the heating chamber. This creates a pristine environment, ensuring the material remains uncontaminated throughout the thermal cycle.
Ensuring Purity and Structural Consistency
For advanced materials like superalloys or titanium, even microscopic impurities can create weak points in the final product.
The vacuum environment ensures that the alloy's chemical composition remains precise and its internal structure is perfectly consistent. This is non-negotiable for components where failure is not an option.
Key Industries and Their Critical Applications
The need for this level of control drives adoption in several high-stakes industries. Each uses vacuum technology to solve specific, demanding challenges.
Aerospace and Defense
This sector is the largest user of vacuum furnaces. The extreme operating conditions of jet engines and structural airframe components demand materials with unparalleled strength and heat resistance.
Applications include heat-treating turbine blades, aging structural titanium alloys, and brazing complex engine components.
Medical and Healthcare
In the medical field, biocompatibility and purity are paramount. Any material implanted in the human body must be free of contaminants that could cause an adverse reaction.
Vacuum furnaces are used to manufacture surgical implants (like hip and knee joints), dental implants, and high-grade surgical instruments, ensuring they are sterile, strong, and inert.
Automotive and Performance Parts
While the entire automotive industry uses heat treating, the high-performance segment relies on vacuum furnaces for components that endure extreme stress and fatigue.
This includes hardening gears, treating bearings, and processing high-strength parts for racing and performance engines where durability and reliability are critical.
Electronics and Semiconductors
The manufacturing of semiconductors and advanced electronics requires materials of extraordinary purity. Even the smallest impurity can alter the electrical properties of a component.
Vacuum furnaces are used for processes like semiconductor fabrication and refining the high-purity metals used in advanced electronic devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Their benefits come with significant considerations.
High Capital and Operating Costs
Vacuum furnaces are complex machines that are significantly more expensive to purchase, install, and maintain than their atmospheric counterparts. The energy required to create and hold a vacuum adds to the operating cost.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of pumping down the chamber to the required vacuum level adds considerable time to each production cycle. This makes vacuum furnaces less suitable for high-volume, low-margin manufacturing where speed is the primary driver.
Specialized Knowledge Requirement
Operating and maintaining a vacuum furnace requires highly skilled technicians. Proper programming, leak detection, and maintenance are critical to achieving consistent and reliable results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to invest in or specify a vacuum process depends entirely on the required properties of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and purity: A vacuum furnace is essential for mission-critical parts in aerospace, defense, and medical applications where failure has catastrophic consequences.
- If your primary focus is enhanced durability and consistency: Vacuum processing is the superior choice for high-stress automotive parts, tools, and dies where fatigue resistance and a long service life are key.
- If your primary focus is material innovation: The controlled environment of a vacuum furnace is indispensable for R&D and electronics, enabling the development of next-generation alloys and materials.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum furnace technology is a strategic decision to prioritize material integrity over production speed and cost.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Common Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Heat-treating turbine blades, aging titanium alloys, brazing engine components | Unparalleled strength, heat resistance, and structural consistency |
| Medical & Healthcare | Manufacturing surgical implants, dental implants, surgical instruments | Biocompatibility, sterility, and purity for patient safety |
| Automotive & Performance Parts | Hardening gears, treating bearings, processing high-strength engine parts | Enhanced durability, fatigue resistance, and reliability |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Semiconductor fabrication, refining high-purity metals | Extraordinary purity to ensure precise electrical properties |
Elevate your material processing with KINTEK's advanced vacuum furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in aerospace, medical, automotive, or electronics, our solutions ensure ultra-clean environments for superior purity and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and deliver reliable, high-quality results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today



















