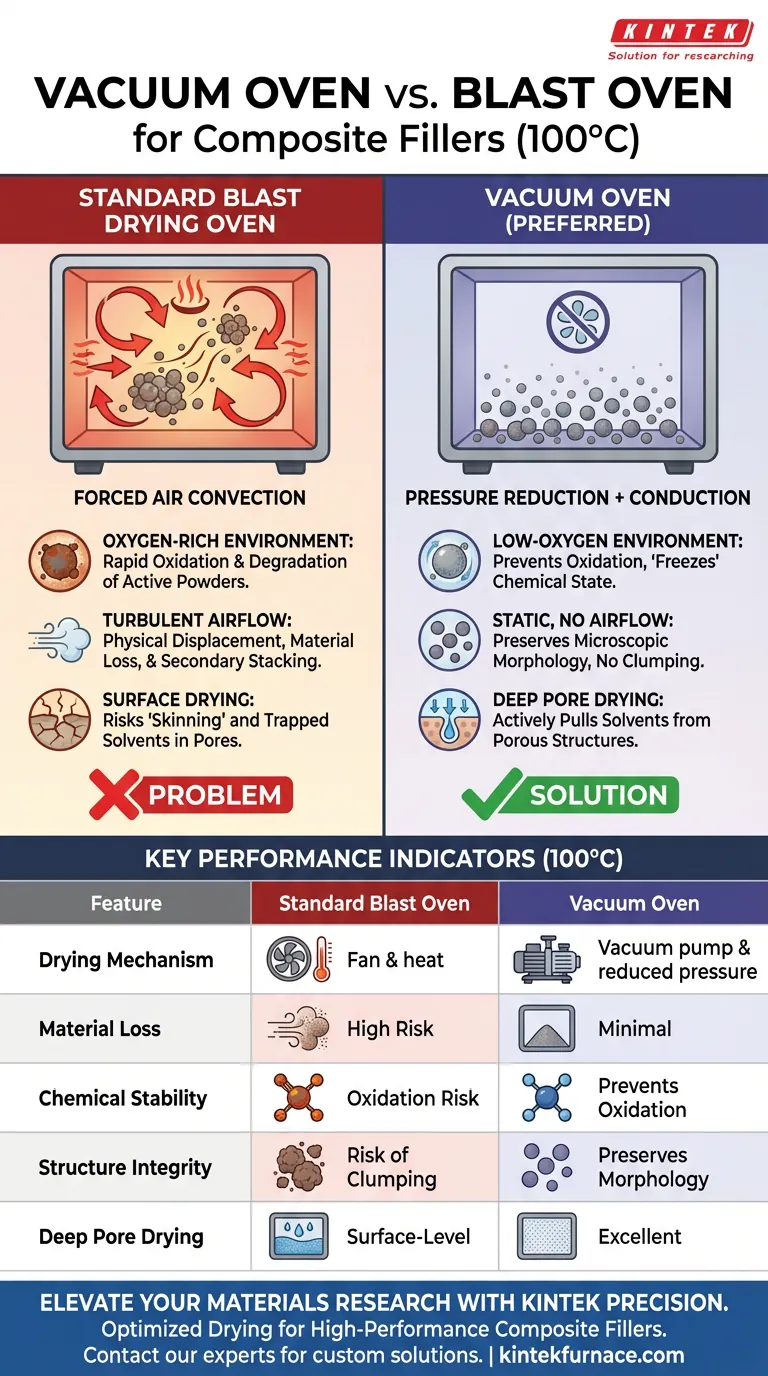
Choosing a vacuum oven over a blast drying oven is a decision to prioritize material integrity and structural preservation. At 100°C, a vacuum environment fundamentally alters the drying process by reducing pressure, which allows solvents like ethanol to evaporate rapidly without requiring excessive thermal exposure. This method is specifically preferred for composite fillers because it prevents the oxidation of highly active powders and eliminates the physical displacement of ultra-light particles caused by forced air.
Core Takeaway Standard blast ovens utilize hot air currents that can degrade sensitive chemical properties and physically disturb nanomaterials. In contrast, vacuum drying lowers the boiling point of solvents to ensure deep drying while maintaining a static, oxygen-deprived environment that preserves the filler's original microscopic morphology.

The Critical Role of Atmospheric Control
Preventing Oxidation and Degradation
Standard blast ovens operate by circulating heated air, which introduces a constant supply of oxygen to the material. For highly active mixed powders or reduced graphene, this exposure at 100°C can lead to rapid oxidation and chemical degradation.
A vacuum oven removes the air from the chamber. This creates a low-oxygen environment that effectively "freezes" the chemical state of the material during the drying process. This preservation is essential for maintaining the performance characteristics of the filler in the final composite.
Accelerating Evaporation via Pressure Reduction
The vacuum environment significantly reduces the boiling point of solvents such as ethanol, NMP, or water. This allows these liquids to volatilize rapidly even if the temperature is kept moderate.
By relying on pressure reduction rather than just thermal energy, you ensure that solvents are removed efficiently without subjecting the material to the thermal stress that might otherwise occur if you attempted to force evaporation using heat alone.
Preserving Microscopic Structure
Eliminating Airflow Interference
Blast drying ovens rely on fans to circulate air, creating turbulence within the chamber. For ultra-light materials like Graphene Nanoplatelets, this airflow is destructive; it can blow the powder away, resulting in material loss.
A vacuum oven operates without internal airflow interference. This static environment ensures that light powders remain in their containment vessels, preventing loss and ensuring consistent yield.
Avoiding Secondary Stacking
Beyond simple material loss, airflow turbulence can force nanoparticles to clump together. This phenomenon, known as secondary stacking, compromises the dispersion of the filler.
Vacuum drying allows the material to settle naturally. This preserves the original microscopic morphology of the filler, ensuring that the particles remain distinct and retain their intended surface area for interaction within the composite matrix.
Deep Pore Solvent Removal
Composite materials often contain internal pores where moisture or solvents can become trapped. Standard thermal drying may dry the surface quickly, potentially trapping liquid inside (skinning).
The negative pressure of a vacuum oven actively pulls gases and vapors from within these porous agglomerates. This ensures the thorough removal of residual moisture and prevents the formation of internal voids or defects in the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat Transfer Limitations
Vacuum ovens lack air, which is the primary medium for convection heat transfer in blast ovens. Consequently, heat transfer in a vacuum relies mostly on conduction (from the shelves) and radiation.
This means that while the drying (evaporation) is faster due to pressure changes, the initial heating of the material mass may take longer compared to a forced-air system.
Batch Processing Constraints
Vacuum drying is inherently a batch process—you must seal the chamber, pump it down, dry, and then repressurize.
This contrasts with blast drying, which can sometimes be adapted for continuous conveyor systems. Therefore, vacuum drying generally requires more manual intervention and allows for lower throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
The decision between vacuum and blast drying depends entirely on the sensitivity of your material.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Use a vacuum oven to prevent oxidation of active powders and ensure chemical stability.
- If your primary focus is Structural Morphology: Use a vacuum oven to prevent ultra-light nanoparticles (like Graphene) from blowing away or re-stacking.
- If your primary focus is Deep Drying: Use a vacuum oven to extract solvents from complex, porous structures that forced air cannot reach.
By selecting the vacuum oven, you are ensuring that the physical structure and chemical potential of your composite fillers remain intact for maximum performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Oven (100°C) | Standard Blast Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Mechanism | Pressure reduction + Conduction | Forced air convection |
| Material Loss | Minimal (No airflow interference) | High risk for ultra-light powders |
| Chemical Stability | Prevents oxidation (Oxygen-free) | High oxidation risk due to airflow |
| Structure Integrity | Preserves microscopic morphology | Risk of secondary stacking/clumping |
| Deep Pore Drying | Excellent (Pulls vapor from pores) | Surface-level drying (Potential skinning) |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let oxidation or airflow turbulence compromise your high-performance composite fillers. KINTEK provides industry-leading drying solutions designed for the most sensitive lab and industrial applications. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your precise thermal requirements.
Whether you are processing Graphene Nanoplatelets or highly active mixed powders, our customizable vacuum ovens ensure deep solvent removal while maintaining structural morphology.
Ready to optimize your drying process? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temperature furnace for your unique needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhengjia Ji, Chao Xu. Potassium Titanate Whisker/Graphene Multi-Dimensional Fillers to Improve the Wear Resistance of Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Composite. DOI: 10.3390/lubricants13050211
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What types of heat treatment processes can a vacuum furnace support? Achieve Purity and Precision in Material Processing
- What key technologies are used in the development of multi-chamber continuous vacuum furnaces? Boost Throughput with Advanced Automation
- Why are vacuum furnaces important for stainless steel processing? Ensure Corrosion Resistance and Pristine Finishes
- What innovations are being made in graphite for vacuum furnaces? Boost Efficiency with Advanced Coatings & Custom Parts
- What commercial options are mentioned for vacuum or high-temperature furnaces? Find Your Ideal Industrial Furnace Solution
- What are some common troubleshooting considerations for vacuum furnaces? Master System Diagnostics for Reliable Performance
- How does temperature control precision of industrial melting furnaces affect intermetallic phase selection?
- What is the purpose of using industrial vacuum furnaces for 3003mod aluminum? Optimize H14 Temper & Material Stress



















