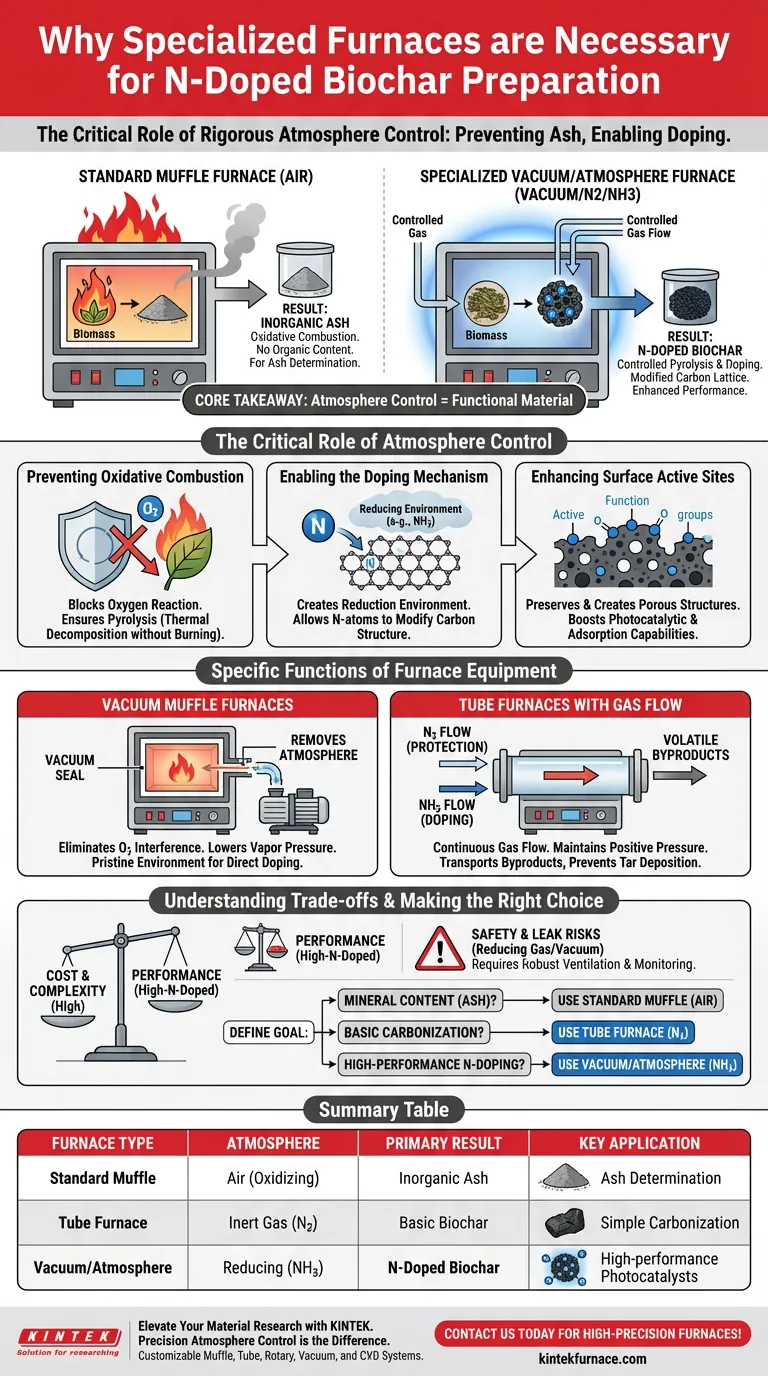
The rigorous exclusion of oxygen is the single most critical requirement when preparing nitrogen-doped (N-doped) biochar. Vacuum muffle furnaces or atmosphere-controlled equipment are necessary to create a specific reduction environment that prevents the biomass from simply burning into ash. This controlled setting enables nitrogen elements to successfully penetrate the carbon lattice or attach to surface active sites, which is the primary mechanism for enhancing the material's photocatalytic performance.
Core Takeaway Standard heating in air results in combustion, leaving behind only inorganic ash. To create functional N-doped biochar, specialized furnaces must be used to maintain a vacuum or reducing atmosphere (such as Ammonia); this forces nitrogen atoms into the carbon structure rather than oxidizing the material.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
Preventing Oxidative Combustion
In a standard environment, high temperatures cause biomass to react with oxygen, resulting in complete combustion. This process removes all organic components and leaves only mineral residue (ash), as seen in ash content determination protocols. Specialized furnaces utilize vacuum seals or inert gas flows (like Nitrogen) to strictly exclude oxygen, ensuring the biomass undergoes pyrolysis—thermal decomposition without burning—rather than combustion.
Enabling the Doping Mechanism
Creating N-doped biochar requires more than just carbonization; it requires a chemical modification of the carbon structure. A vacuum or controlled atmosphere (often containing Ammonia/NH3) creates a "reduction environment." This environment is thermodynamically necessary for doping elements to effectively enter the biochar lattice and modify its electronic properties.
Enhancing Surface Active Sites
The exclusion of oxygen allows for the preservation and creation of specific porous structures and surface functional groups. By controlling the atmosphere, you ensure that nitrogen atoms attach to specific active sites on the surface. This atomic-level engineering is what significantly boosts the material’s photocatalytic response and adsorption capabilities.
Specific Functions of Furnace Equipment
Vacuum Muffle Furnaces
These units operate by physically removing the atmosphere from the chamber. By creating a vacuum, they eliminate oxygen interference and lower the vapor pressure, which can facilitate the desorption of impurities. This creates a pristine environment where doping agents can interact directly with the carbon matrix without competition from atmospheric gases.
Tube Furnaces with Gas Flow
Tube furnaces allow for the continuous flow of specific gases, such as Nitrogen (N2) for protection or Ammonia (NH3) for doping. This flow system serves a dual purpose: it maintains positive pressure to keep oxygen out, and it actively transports volatile byproducts away from the sample. This transport is crucial for preventing the re-deposition of tars, ensuring the final biochar maintains its intended porosity and carbon content.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Sensitivity vs. Equipment Cost
While standard muffle furnaces are cost-effective and simple, they are fundamentally incapable of producing N-doped materials. Vacuum and atmosphere-controlled furnaces are significantly more expensive and complex to operate. However, this complexity is the non-negotiable cost of producing high-performance functional materials rather than simple charcoal or ash.
Safety and Leak Risks
The use of reducing atmospheres (like Ammonia) or vacuum conditions introduces safety challenges not present in air-calcination. A minor leak in a vacuum furnace allows oxygen ingress, which will immediately degrade the doping quality and yield. Furthermore, handling reactive gases for doping requires robust ventilation and safety monitoring systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct thermal treatment method, you must clearly define the intended application of your biochar.
- If your primary focus is determining mineral content (Ash): Use a standard muffle furnace in an air atmosphere to completely combust organic matter.
- If your primary focus is basic carbonization: Use a tube furnace with a Nitrogen (N2) flow to prevent combustion and develop basic porosity.
- If your primary focus is high-performance N-Doping: Use a vacuum or atmosphere-controlled furnace with a doping gas (like NH3) to modify the carbon lattice and enhance catalytic activity.
The difference between a pile of ash and a sophisticated photocatalyst lies entirely in the precision of your atmosphere control.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Atmosphere Environment | Primary Result | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Muffle | Air (Oxidizing) | Inorganic Ash | Ash content determination |
| Tube Furnace | Inert Gas (e.g., N2) | Basic Biochar | Simple carbonization & porosity |
| Vacuum/Atmosphere | Reducing (e.g., NH3) | N-Doped Biochar | High-performance photocatalysts |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision atmosphere control is the difference between simple ash and high-performance photocatalysts. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific nitrogen-doping and pyrolysis requirements.
Ready to achieve superior doping results? Contact us today to find the perfect high-temp furnace for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Yunfang Liu, Yibo Ma. Recent progress in TiO<sub>2</sub>–biochar-based photocatalysts for water contaminants treatment: strategies to improve photocatalytic performance. DOI: 10.1039/d3ra06910a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the overall dimensions and shipping weight of the muffle furnace? Plan Your Lab Space Efficiently
- What are the typical uses of muffle furnaces in laboratory settings? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment for Your Lab
- What types of heating elements are used in box type electric furnaces? Choose the Right Element for Your Lab
- What safety measures should be observed regarding the surroundings of a muffle furnace? Ensure a Secure Lab Setup
- What are the advantages of muffle furnaces in terms of energy efficiency and heating speed? Achieve Fast, Efficient Heat Processing
- What critical environmental conditions does a muffle furnace provide for aluminum cast iron? Optimize Your Heat Treatment
- What are the recommended heating and cooling protocols for a muffle furnace? Ensure Longevity and Safety in Your Lab
- What options are available for temperature uniformity in Box Furnaces? Achieve Precise Heat for Your Critical Processes



















