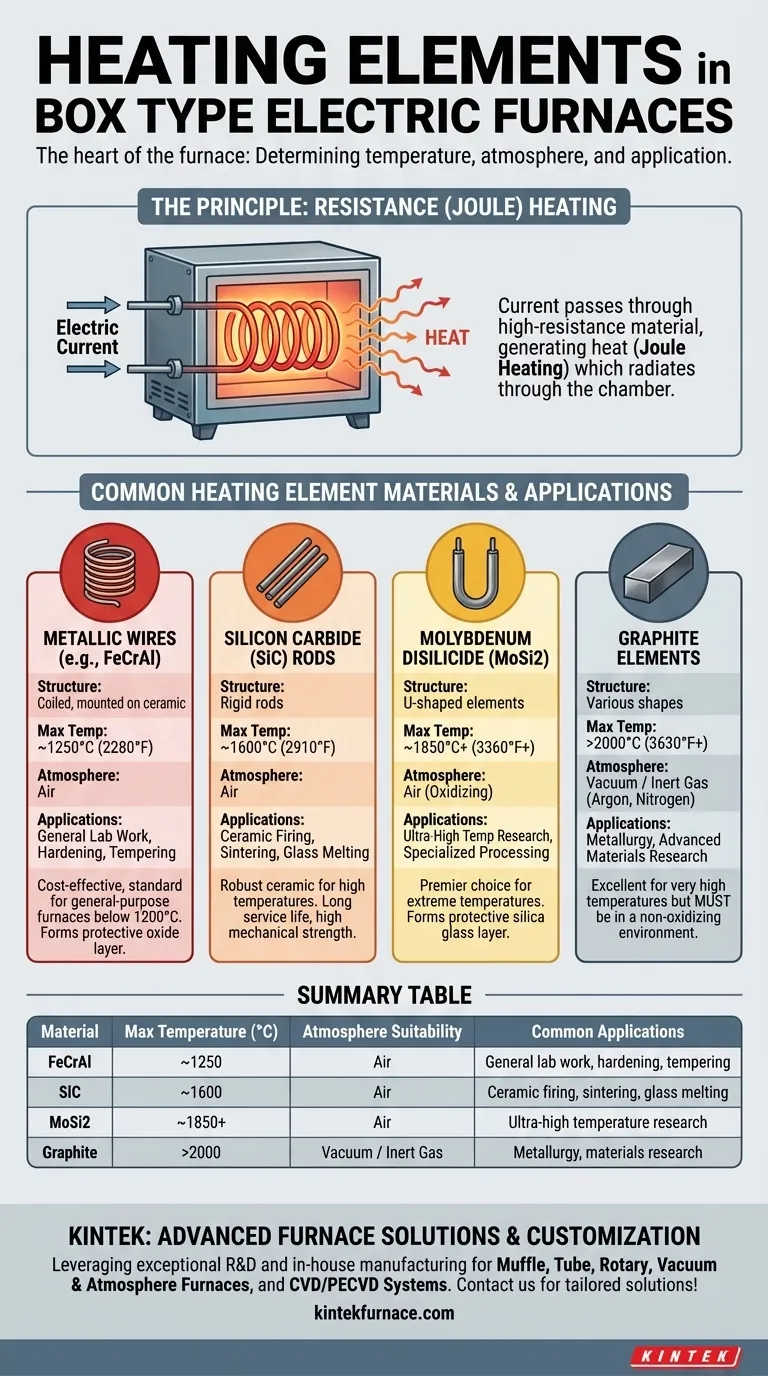
Box type electric furnaces primarily utilize resistance heating elements, which generate heat when an electric current passes through them. The most common materials for these elements are metallic alloys like iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl), ceramics such as silicon carbide (SiC) and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), and in specialized cases, graphite.
The specific heating element used in a box furnace is not an arbitrary detail; it is the single most important factor determining the furnace's maximum operating temperature and its suitability for different chemical atmospheres and processes.
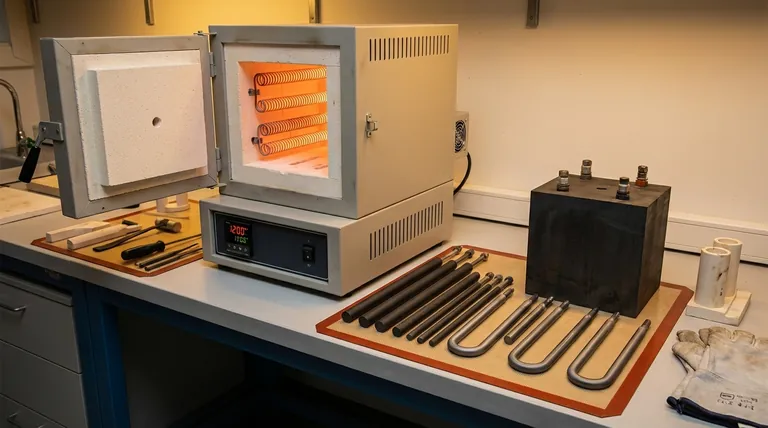

The Principle: Resistance (Joule) Heating
How Heat is Generated
At its core, every electric box furnace operates on the principle of resistance heating, also known as Joule heating.
An electrical current is passed through a specially designed material—the heating element. This material has high electrical resistance, causing it to heat up intensely as it impedes the flow of electricity.
This generated heat then radiates throughout the furnace chamber, heating the contents to the desired temperature. The choice of element material dictates how hot the furnace can get and how long the element will last.
A Breakdown of Common Heating Element Materials
The material of the heating element is chosen based on the required temperature and the process being performed. Each has distinct properties.
Metallic Resistance Wires (e.g., FeCrAl)
These are the most common and cost-effective elements for general-purpose furnaces. They are typically wound into coils and mounted on ceramic supports.
Iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys are a standard choice for air atmospheres, forming a protective aluminum oxide layer that prevents burnout.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Rods
For temperatures beyond the limits of metallic wires, silicon carbide (SiC) is a robust ceramic alternative.
These rigid rods can operate at high temperatures in air and are known for their long service life and mechanical strength, making them a workhorse for many industrial and lab processes like sintering and melting.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Elements
When extremely high temperatures are required, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements are the premier choice. They are often U-shaped and can operate at temperatures well above those achievable with SiC.
These elements form a protective silica glass layer at high temperatures, allowing them to function in oxidizing atmospheres without degrading.
Graphite Elements
Graphite is an excellent high-temperature heating element, but with one critical limitation: it cannot be used in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures.
For this reason, graphite elements are exclusively used in furnaces that operate with a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen). They are common in metallurgy and advanced materials research.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing temperature capability, atmospheric requirements, and cost. The heating element is at the center of this decision.
The Critical Role of Temperature
The maximum operating temperature is the most significant differentiator. Each element type has a clear operational ceiling.
- Metallic Wires (FeCrAl): Typically up to ~1250°C (2280°F).
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Typically up to ~1600°C (2910°F).
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2): Up to ~1850°C (3360°F) or higher.
- Graphite: Can exceed 2000°C (3630°F) in a non-oxidizing environment.
The Impact of Furnace Atmosphere
The chemical environment inside the furnace is just as important as the temperature. Using the wrong element in a given atmosphere will lead to rapid failure.
Elements like MoSi2 and SiC are designed to operate in air by forming a protective oxide layer. In contrast, materials like graphite and pure molybdenum will rapidly burn away (oxidize) in air at high temperatures, mandating a vacuum or inert gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your intended use case directly maps to a specific type of heating element.
- If your primary focus is general lab work, hardening, or tempering below 1200°C: A furnace with standard FeCrAl metallic wire elements is the most practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature ceramic firing, sintering, or glass melting (up to 1600°C): A furnace equipped with Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements provides the necessary performance and durability.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperature research or processing (above 1600°C in air): You will require a furnace with Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing in a vacuum or inert gas: A furnace with graphite heating elements is specifically designed for this purpose.
By understanding the heating element, you are empowered to select the precise tool required to achieve your thermal processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature (°C) | Atmosphere Suitability | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| FeCrAl | ~1250 | Air | General lab work, hardening, tempering |
| SiC | ~1600 | Air | Ceramic firing, sintering, glass melting |
| MoSi2 | ~1850+ | Air | Ultra-high temperature research |
| Graphite | >2000 | Vacuum/Inert gas | Metallurgy, materials research |
Need the perfect box furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your thermal processing efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















