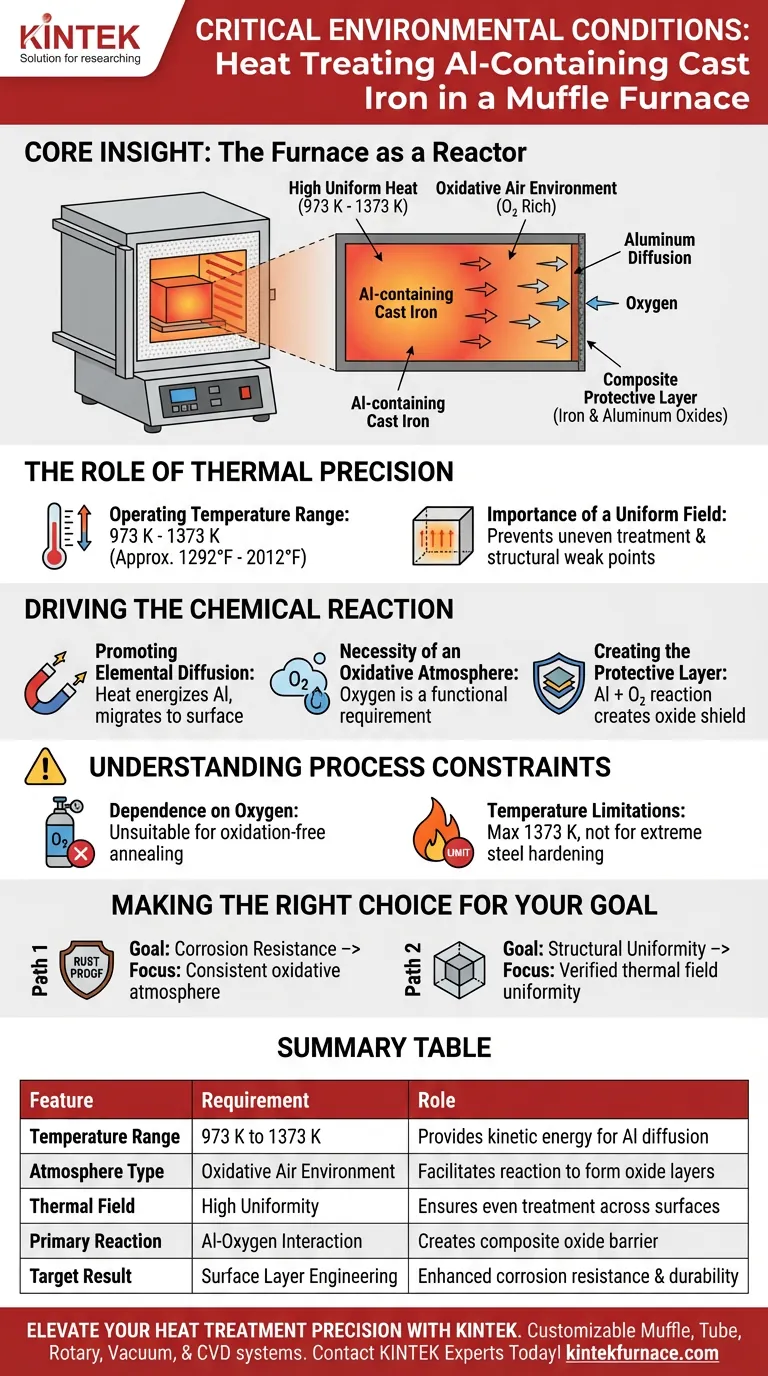
A box-type resistance furnace, often called a muffle furnace, establishes a stable oxidative air environment within a critical temperature range. Specifically, it maintains a precise and uniform thermal field between 973 K and 1373 K, which is required to facilitate necessary chemical changes on the surface of the metal.
Core Insight: The furnace does not simply heat the metal; it acts as a reactor. By combining high uniform heat with an oxygen-rich atmosphere, it drives the diffusion of aluminum to the surface to form a composite protective barrier of iron and aluminum oxides.
The Role of Thermal Precision
Operating Temperature Range
For effective treatment of aluminum-containing cast iron, specific thermal energy is required. The furnace must reliably operate between 973 K and 1373 K.
Importance of a Uniform Field
The "box-type" design is engineered to create a uniform temperature field throughout the chamber. This ensures that the entire workpiece receives the same thermal exposure, preventing uneven treatment or structural weak points.
Driving the Chemical Reaction
Promoting Elemental Diffusion
The high heat provided by the furnace serves a kinetic purpose. It energizes the aluminum elements within the cast iron, causing them to diffuse (migrate) from the interior of the material to the exterior surface.
The Necessity of an Oxidative Atmosphere
Unlike heat treatments that require a vacuum or inert gas to prevent oxidation, this process specifically requires an oxidative air environment. The presence of oxygen is a functional requirement, not a byproduct.
Creating the Protective Layer
When the diffusing aluminum reaches the surface, it reacts with the oxygen in the furnace chamber. This reaction results in the formation of a composite protective layer consisting of both iron oxides and aluminum oxides, which shields the underlying material.
Understanding Process Constraints
Dependence on Oxygen
This specific method relies entirely on the availability of oxygen to interact with the aluminum. Consequently, this equipment configuration is unsuitable for processes requiring oxidation-free annealing or bright finishes, as the formation of an oxide layer is the intended outcome here.
Temperature Limitations
While the furnace reaches 1373 K (approx. 2012°F), it is crucial to note that this falls within specific heat-treating and annealing ranges. It may not reach the extreme reheating temperatures (up to 2300°F) used for certain steel hardening processes, so equipment selection must align strictly with the 973 K – 1373 K requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the success of your heat treatment process, consider these specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance: Ensure the furnace maintains a consistent oxidative atmosphere to maximize the formation of the iron-aluminum oxide protective shell.
- If your primary focus is structural uniformity: Prioritize a furnace with verified thermal field uniformity to guarantee even aluminum diffusion across complex geometries.
By controlling both temperature and atmosphere, you transform a simple heating process into a precise surface engineering technique.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Requirement for Al-containing Cast Iron | Role in Heat Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 973 K to 1373 K | Provides kinetic energy for aluminum diffusion |
| Atmosphere Type | Oxidative Air Environment | Facilitates reaction to form protective oxide layers |
| Thermal Field | High Uniformity | Ensures even treatment across all workpiece surfaces |
| Primary Reaction | Aluminum-Oxygen Interaction | Creates a composite iron-aluminum oxide barrier |
| Target Result | Surface Layer Engineering | Enhanced corrosion resistance and material durability |
Elevate Your Heat Treatment Precision with KINTEK
Don't compromise on thermal uniformity or atmospheric control. KINTEK provides industry-leading Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of material science. Backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing, our high-temp lab furnaces are fully customizable to your specific temperature and atmosphere requirements.
Ready to optimize your aluminum cast iron treatment or lab processes?
Contact KINTEK Experts Today to find the perfect customizable solution for your unique needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Kazunori Asano, Seiji Sugimura. Erosion Resistance of Heat-Treated Aluminum Cast Iron to Aluminum Alloy Melt. DOI: 10.2320/matertrans.f-m2024804
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of the annealing process using a muffle furnace for ZnCo2O4? Boost Phase Purity and Conductivity
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature box resistance furnace for γ-Y1.5Yb0.5Si2O7 ceramics? Optimal Sintering & Densification
- What is the function of the muffle chamber in the furnace? Ensure Purity and Uniform Heating
- What is the significance of box type resistance furnaces in lithium battery material synthesis? Unlock Precision and Efficiency
- What factors should be considered when selecting materials for a Muffle furnace? Optimize Your Thermal Processing Today
- What is the recommended operating temperature to extend the lifespan of the furnace wire? Maximize Longevity with a 50°C Buffer
- What role does a high-temperature box-type resistance furnace play in solar cell electrode processing? Master Sintering
- Why is a double-chamber device preferred over a standard electric furnace for sintering? Achieve Oxidation-Free Results



















