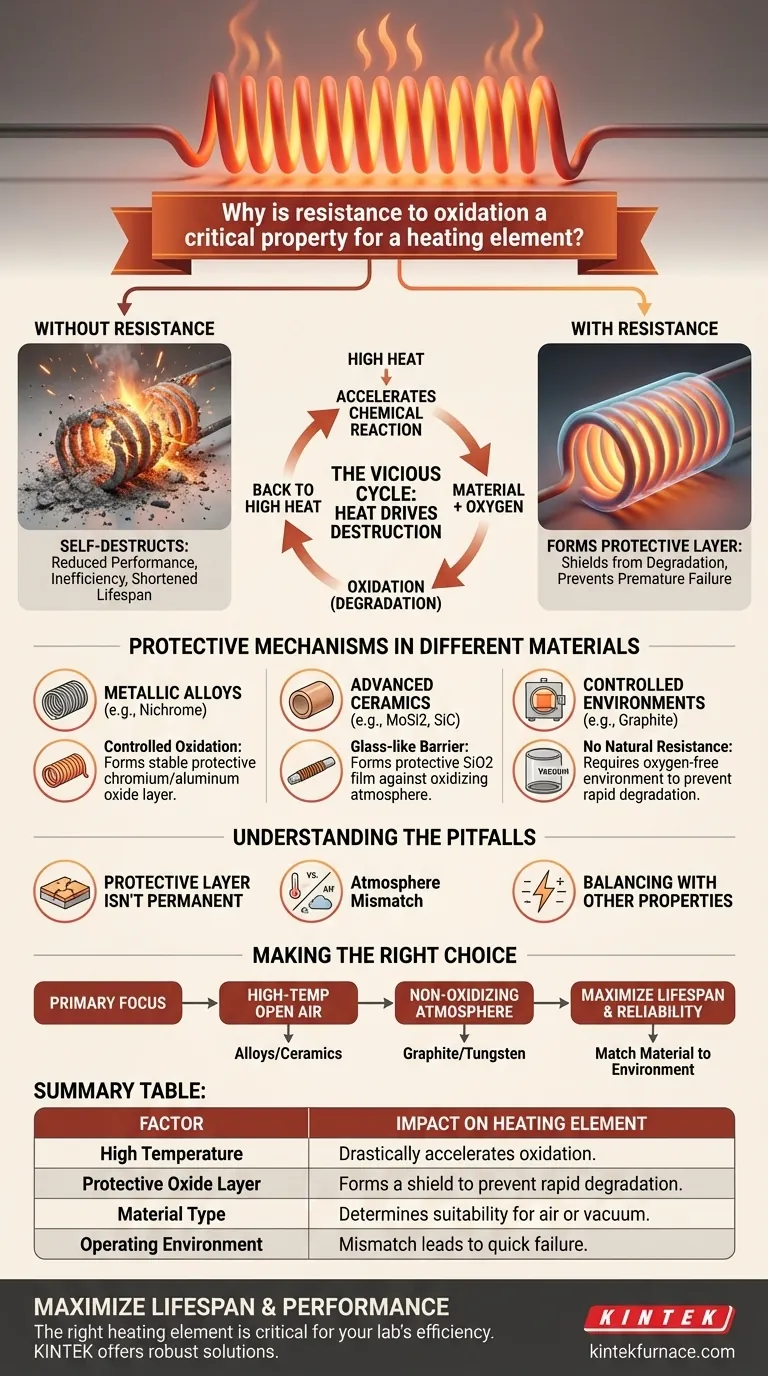
Resistance to oxidation is a critical property for a heating element because the very act of generating intense heat dramatically accelerates this destructive chemical process. Without this resistance, the element essentially self-destructs, leading to reduced performance, inefficiency, and a drastically shortened operational lifespan.
At the high temperatures required for heating, oxygen in the air aggressively attacks the element's material. A heating element's survival depends on its ability to form a stable, protective oxide layer that shields it from this constant assault, preventing rapid degradation and premature failure.

The Vicious Cycle: How Heat Drives Destruction
To understand why oxidation resistance is so vital, you must first understand the fundamental process. It is a chemical reaction that is supercharged by the element's own function.
What is Oxidation?
At its core, oxidation is the reaction of a material with oxygen. Think of it as an aggressive, high-speed version of common rust. When the material of a heating element oxidizes, it is literally being consumed and converted into a different, often weaker, substance.
The Role of High Temperature
While oxidation can occur at room temperature, heat acts as a powerful catalyst. The intense heat generated by the element provides the energy needed to speed up this chemical reaction exponentially, causing the material to degrade far more quickly than it would otherwise.
The Consequences of Degradation
This continuous oxidation has direct, negative consequences. It physically destroys the heating material, reduces its ability to convert electricity into heat efficiently, and ultimately leads to complete failure of the element.
Protective Mechanisms in Different Materials
The most effective heating elements don't just resist oxidation; they use it to their advantage by forming a protective "skin" or scale. However, this strategy varies significantly between material types.
Self-Protecting Metallic Alloys
Common metallic heating elements are made from alloys like nickel-chromium (Nichrome). These materials are designed to oxidize, but in a controlled way. The chromium and aluminum in the alloy react with oxygen to form a thin, stable, and non-conductive layer of chromium or aluminum oxide on the surface, which then protects the metal underneath from further attack.
Advanced Ceramics
Ceramic elements, such as molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) and silicon carbide (SiC), employ a similar strategy. When heated, they form a protective, glass-like film of silicon dioxide (SiO2) on their surface. This layer acts as a durable barrier against the oxidizing atmosphere.
The Need for Controlled Environments
Some materials, like graphite, have excellent heating properties but possess no natural resistance to oxidation. When heated in the presence of air, they degrade very rapidly. For this reason, they can only be used in controlled environments, such as vacuum furnaces, where oxygen is removed.
Understanding the Pitfalls
Selecting a material is not just about finding one with good oxidation resistance; it's about matching its specific properties to the application's environment.
A Protective Layer Isn't Permanent
Even the best protective oxide layers have a lifespan. Over many heating and cooling cycles, thermal expansion and contraction can cause this layer to crack or flake off, exposing fresh material to attack. This is a primary driver of eventual element failure.
Atmosphere is Everything
A material that thrives in an oxidizing atmosphere may fail in a different one. The protective oxide layer that forms in air cannot be created in a vacuum or an inert gas environment. This mismatch can lead to unexpected and rapid degradation.
Balancing with Other Properties
Oxidation resistance is just one piece of the puzzle. A material must also have the correct electrical resistivity. High resistivity allows a practical length and thickness to be used for the element design, ensuring efficient and safe conversion of electricity to heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The defining factor in material selection is the environment in which the element will operate. Understanding this relationship is the key to a successful design.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature operation in open air: Select an alloy or ceramic specifically designed to form a stable, protective oxide layer, such as Nichrome or silicon carbide.
- If your primary focus is operating in a non-oxidizing atmosphere (like a vacuum): Materials without inherent oxidation resistance, such as graphite or tungsten, become viable and highly effective options.
- If your primary focus is maximizing lifespan and reliability: Ensure your chosen material's protective mechanism is well-suited to your specific operating temperature range and atmospheric chemistry.
Ultimately, matching the material's defense mechanism to its operating environment is the key to designing a durable and reliable heating system.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Heating Element |
|---|---|
| High Temperature | Drastically accelerates the oxidation process. |
| Protective Oxide Layer | Forms a shield (e.g., chromium oxide on Nichrome) to prevent rapid degradation. |
| Material Type | Determines suitability for air (e.g., SiC) or vacuum (e.g., graphite) environments. |
| Operating Environment | Mismatch between material and atmosphere leads to quick failure. |
Maximize the lifespan and performance of your heating systems. The right heating element is critical for your lab's efficiency and success. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all featuring robust, high-temperature heating elements designed for your specific application. Let our experts help you select the perfect solution for your unique needs.
Contact us today for a consultation to ensure your furnace operates reliably, batch after batch.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















