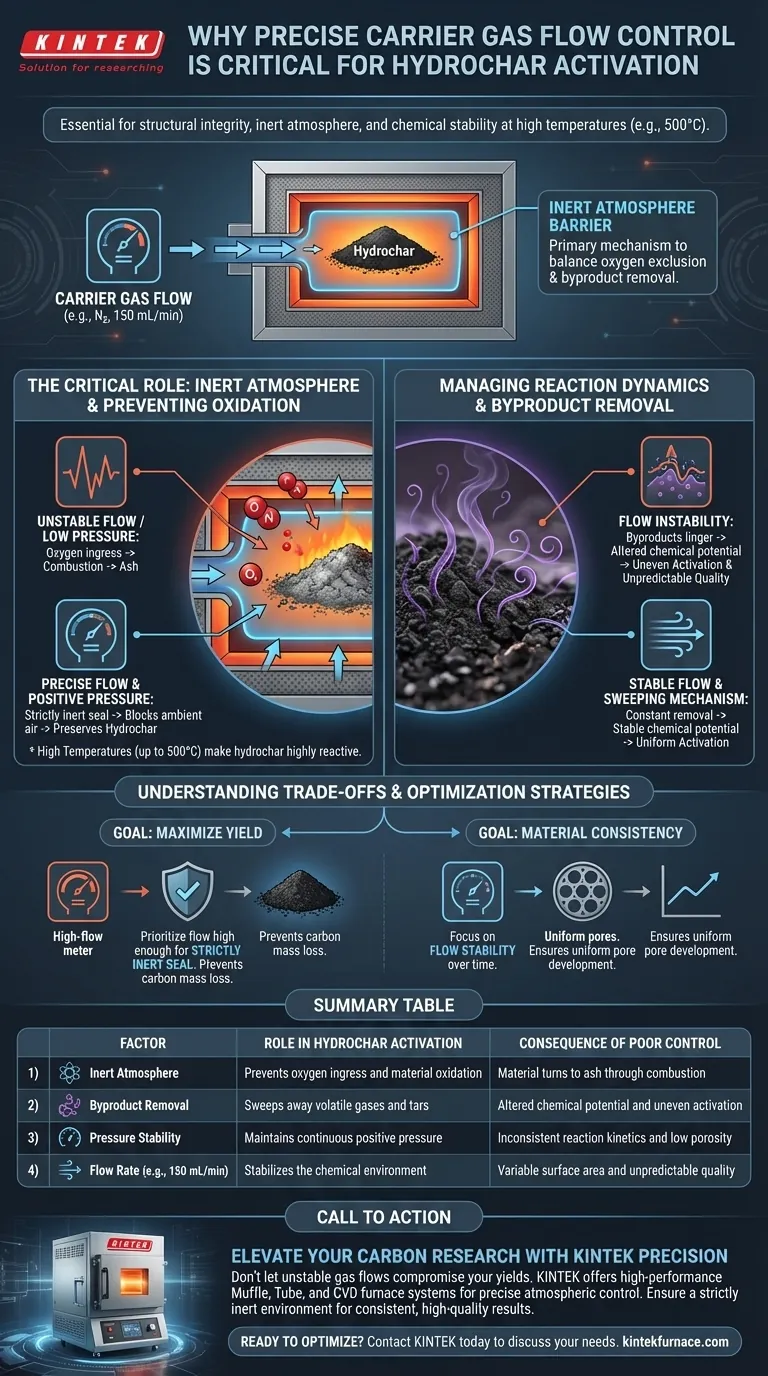
Precise control of carrier gas flow rates is essential for preserving the structural integrity of hydrochar during high-temperature activation. A specific, steady flow—such as 150 mL/min—is required to create and maintain a strictly inert atmosphere that prevents the material from burning while simultaneously stabilizing the chemical environment.
The regulation of carrier gas is the primary mechanism for controlling the reaction conditions. It balances the absolute exclusion of oxygen to prevent combustion with the necessary removal of volatile byproducts to ensure consistent activation.

The Critical Role of the Inert Atmosphere
Preventing Catastrophic Oxidation
At activation temperatures reaching 500 °C, hydrochar is highly reactive. Without a precisely controlled barrier of inert gas (like nitrogen), the carbon material is susceptible to excessive oxidation.
avoiding Combustion
If the flow rate fluctuates or drops too low, oxygen may breach the furnace environment. This leads to combustion, which effectively turns your valuable hydrochar into ash rather than activated carbon.
Ensuring a "Strictly Inert" Environment
The reference specifically highlights the need for a strictly inert atmosphere. Precise flow control ensures a continuous positive pressure that physically blocks ambient air from entering the reaction zone.
Managing Reaction Dynamics
Removal of Gaseous Byproducts
During activation, the hydrochar releases volatile gases and tars. A stable flow rate acts as a sweeping mechanism, effectively removing these gaseous byproducts from the immediate reaction zone.
Stabilizing Chemical Potential
If byproducts are allowed to linger, they alter the chemical equilibrium near the hydrochar surface. By flushing these byproducts away at a constant rate, the carrier gas maintains a stable chemical potential, ensuring the activation reaction proceeds uniformly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Flow Instability
The requirement for "precise" control implies that deviations in either direction are detrimental.
Inconsistent Reaction Kinetics
If the flow is not stable, the removal of byproducts becomes inconsistent. This leads to variable chemical potential, resulting in uneven activation and unpredictable surface area or porosity in the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your hydrochar activation process, adjust your flow control strategy based on your specific quality targets:
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Yield: Prioritize a flow rate high enough to guarantee a strictly inert seal, preventing any loss of carbon mass to oxidation or combustion.
- If your primary focus is Material Consistency: Focus on the stability of the flow over time to ensure constant chemical potential and uniform pore development across the sample.
Mastering the flow rate is the first step in transforming raw hydrochar into a high-performance material.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Role in Hydrochar Activation | Consequence of Poor Control |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere | Prevents oxygen ingress and material oxidation | Material turns to ash through combustion |
| Byproduct Removal | Sweeps away volatile gases and tars | Altered chemical potential and uneven activation |
| Pressure Stability | Maintains continuous positive pressure | Inconsistent reaction kinetics and low porosity |
| Flow Rate (e.g., 150 mL/min) | Stabilizes the chemical environment | Variable surface area and unpredictable quality |
Elevate Your Carbon Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let unstable gas flows compromise your material yields. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, and CVD furnace systems specifically designed for precise atmospheric control. Whether you are activating hydrochar or synthesizing advanced materials, our customizable lab solutions ensure the strictly inert environment you need for consistent, high-quality results.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique needs with our technical specialists!
Visual Guide
References
- Reuse of Polymeric Resin for Production of Activated Hydrochar Applied in Removal of Bisphenol A and Diclofenac Synthetic Aqueous Solution. DOI: 10.3390/coatings15010027
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 304 316 Stainless Steel High Vacuum Ball Stop Valve for Vacuum Systems
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of employing Ozone (O3) treatment following the AS-ALD of Al2O3? Boost Film Purity and Density
- Why is precise temperature control critical for drying carbon nanotube films? Achieve Perfect 80°C Thermal Stability
- How does a crucible furnace work? A Guide to Efficient Metal Melting
- What advantages does a vacuum drying oven offer? Superior Chemical Stability & Efficient Dehydration
- How do industrial furnaces and quenching tanks affect TiCp/Fe composites? Optimize Heat Treatment Performance
- What is the function of magnetron sputtering equipment in Diamond/Cu composites? Enhance Bonding with Precision Coating
- How does the analysis of optimized process paths assist in lab equipment selection? Expert Guide for Research Success
- What is the purpose of a microwave digestion furnace? Unlock Precise ICP-MS Results through Matrix Destruction



















